
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Cherokee Web Server on CentOS 6. For those of you who didn’t know, Cherokee is a free and open-source high-performance web server. It is very fast, flexible, and easy to configure. It offers support for the widespread technologies nowadays: FastCGI, SCGI, PHP, CGI, SSI, TLS and SSL encrypted connections, Virtual hosts, Authentication, on the fly encoding, Load Balancing, Apache compatible log files, Data Base Balancer, downtime-free updates, and upgrades, Reverse HTTP Proxy, and much more. The best thing about Cherokee is that, unlike Apache or Nginx, Cherokee can be administered completely through its admin web interface
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of Cherokee on CentOS 6.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: CentOS 6.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Cherokee Web Server on CentOS 6
Step 1. First, you need to enable the EPEL repository on your system.
## RHEL/CentOS 6 64-Bit ## # wget http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm # rpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm ## RHEL/CentOS 6 32-Bit ## # wget http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm # rpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
Step 2. Installing Cherokee Web Server using Yum.
yum update yum install cherokee rrdtool
Start the webserver and make it start automatically on every reboot:
service cherokee start chkconfig cherokee on
Step 3. Configuring Cherokee web server.
The best part about using Cherokee Web Server is being able to manage all of its configurations through a simple-to-use web interface. It can be started through the cherokee-admin command:
cherokee-admin
By default, cherokee-admin can only access from localhost. If you need to access the admin for other network addresses using the parameter ‘-b’. If you don’t mention any IP address, it will automatically listen to all network interfaces. Then you can connect to cherokee-admin another network address.
cherokee-admin -b
Access Cherokee admin from a specific network address:
cherokee-admin -b 192.169.1.2
#sudo cherokee-admin -b Cherokee Web Server 1.2.103 (Dec 16 2014): Listening on port 127.0.0.1:9090, TLS disabled, IPv6 enabled, using epoll, 4096 fds system limit, max. 2041 connections, caching I/O, 2 threads, 1020 connections per thread, standard scheduling policy Login: User: admin One-time Password: idrootEMfQRantyWWa6h Web Interface: URL: http://127.0.0.1:9090/
Important: The password is for one-time use only. If you need to log in again, you should use the same command for generating it.
Step 4. Now access Cherokee-Admin by navigating your browser to http://127.0.0.1:9090. Type user name and password for accessing it.
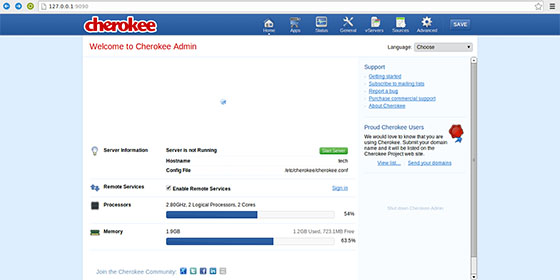
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Cherokee. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Cherokee web server on CentOS 6 systems. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Cherokee website.