
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Htop on your CentOS 7. For those of you who didn’t know, Htop is an interactive and real-time system-monitor process-viewer written for Linux. It is designed to replace the Unix program top. It shows a frequently updated list of the processes running on a computer, normally ordered by the amount of CPU usage. Unlike top, htop provides a full list of processes running, instead of the top resource-consuming processes. Htop uses color and gives visual information about the processor, swap, and memory status. It is a must-have when you want to monitor the resources of your Linux server over an ssh connection for example.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation htop on a CentOS 7 server.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: CentOS 7.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Htop on CentOS 7
Step 1. Update Your CentOS 7 system.
First, add the EPEL repository and make sure that all packages are up to date.
yum -y install epel-release yum -y update
Step 2. Install Htop.
- Install htop using the official CentOS repository.
Install htop process monitoring tool using yum command:
yum -y install htop
After installation, launch htop by entering:
htop
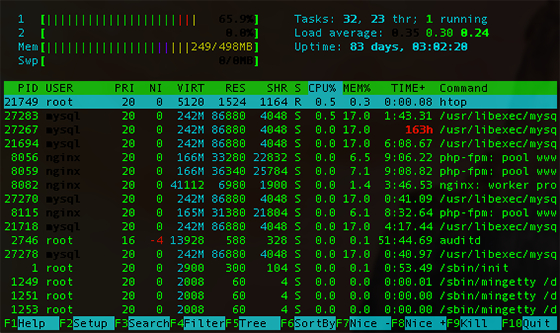
- Install htop from the source code.
Another option is to compile and install htop from the source. This option is useful when you want to install the latest version of htop:
yum groupinstall "Development Tools" yum install ncurses-devel wget http://hisham.hm/htop/releases/1.0.3/htop-1.0.3.tar.gz tar -xvf htop-1.0.3.tar.gz cd htop-1.0.3 ./configure make make install
Step 3. Essential keys and actions
- Navigation and selection:
- Up/Down, PageUp/PageDown, Home/End: move through processes.
- Left/Right: move across columns.
- Space: tag/untag a process; U: untag all.
- Views and filtering:
- F5 (t): toggle Tree view (see parent/child hierarchy).
- F4: Filter—type a substring to show only matching processes.
- F3: Search—find a process by name/command.
- F6: Sort—choose the column to sort on.
- Managing processes:
- F9: Kill—choose signal (e.g., 15 SIGTERM, 9 SIGKILL).
- F7/F8: Increase/decrease priority (renice) of the selected process; requires root for higher priority (negative nice).
- e: Show environment variables for the selected process.
- Configuration:
- F2 (Setup):
- Meters: choose what to show in Left/Right columns (e.g., CPU average vs per‑core, MIPS, IO rate on newer builds).
- Display options: highlight program groups, hide kernel threads, show tree, enable detailed CPU time, etc.
- Colors: pick color schemes suitable for terminals or accessibility.
- F2 (Setup):
Useful command‑line options
- htop -d 30: set update delay to 3.0 seconds (value is tenths of a second).
- htop -u <user>: show only processes of a specific user.
- htop -p <pid1>,<pid2>: focus on specific PIDs.
- htop -s <column>: sort by a specific column at start (e.g., CPU%, MEM%, TIME+, USER).
- htop -t: start in tree view.
- htop –no-color: disable colors for monochrome terminals.
Step 4. Troubleshooting install issues on CentOS 7
- If yum install htop fails with “No package htop available,” ensure epel-release is installed and the repo metadata is updated (yum clean all && yum makecache fast).
- If behind a proxy or with restricted repos, download the matching .rpm for your architecture and EL7 version and install via rpm -ivh or yum localinstall to resolve dependencies.
- For the latest upstream on CentOS 7, ensure build dependencies (gcc, ncurses-devel, autotools or cmake per version) before building from source.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed htop. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing htop process monitoring tool on CentOS 7 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official htop website.