
This tutorial will show you how to install Logtop on CentOS 7. For those of you who didn’t know, Logtop is a handy log analyzer that can show real-time statistics from any given text file. A common usage example is redirecting the output of your log files to it, in order to get the top visitors of your web pages or the top hosts requesting pages through your proxy server, all of this in a real-time top list.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of Logtop on a CentOS 7 server.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: CentOS 7 or RHEL-based.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Logtop on CentOS 7
Step 1. First, you need to enable the EPEL repository on your system.
## RHEL/CentOS 7 64-Bit ## # wget http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/e/epel-release-7-5.noarch.rpm # rpm -ivh epel-release-7-5.noarch.rpm
Step 2. Install Logtop and all dependencies.
By default, Logtop is not available on Rocky Linux 9 AppStream repository. Now run the following command below to install the latest version of Logtop on your CentOS Linux system:
yum install git ncurses-devel uthash-devel git clone https://github.com/JulienPalard/logtop.git
Dive into its directory and compile it:
cd logtop make make install
Step 3. Accessing Logtop on CentOS Linux.
After successfully installed, here are some common examples of logtop:
tail -f /var/log/httpd/access_log | awk {'print $1; fflush();'} | logtop
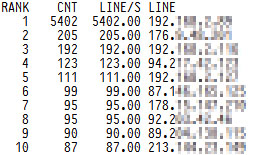
tail -f /var/log/squid/access.log | awk {'print $1; fflush();'} | logtop
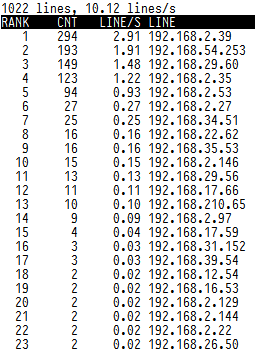
Congratulations! You have successfully installed the logtop. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing log top real-time log in CentOS 7 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official logtop website.