
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Nagios on Ubuntu 15.04. For those of you who didn’t know, Nagios is open-source software that can be used for network and infrastructure monitoring. Nagios will monitor servers, switches, applications, and services. It alerts the System Administrator when something went wrong and also alerts back when the issues have been rectified. Resources that can be monitored include CPU, memory, and disk space loads, log files, temperature, or hardware errors. It can monitor various parameters and problems for services like HTTP, SMTP, and DNS, and with the help of plugins, it can be highly extended. Nagios Core was originally designed to run under Linux, although it should work under most other units as well.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple. I will show you the step-by-step installation of Nagios in the ubuntu 15.04 server.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Ubuntu 15.04, and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Nagios on Ubuntu 15.04
Step 1. First, make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date by running the following apt-get commands in the terminal.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
Step 2. Install LAMP server.
A Ubuntu 15.04 LAMP server is required. If you do not have LAMP installed, you can follow our guide here. Also, install the dependencies for Nagios:
apt-get install build-essential php5-gd wget libgd2-xpm-dev libapache2-mod-php5 apache2-utils daemon unzip
Step 3. Create users and groups for Nagios.
useradd nagios groupadd nagcmd usermod -a -G nagcmd nagios usermod -a -G nagcmd www-data
Step 4. Install Nagios service and Nagios plugins.
Download the latest stable version of Nagios, At the moment of writing this article it is version 4.4.6:
cd /tmp/ wget https://assets.nagios.com/downloads/nagioscore/releases/nagios-4.4.6.tar.gz cd nagios-4.4.6/ sudo ./configure --with-command-group=nagcmd sudo make all sudo make install sudo make install-init sudo make install-config sudo make install-commandmode sudo make install-webconf
Download the latest Nagios-plugins source and install using the following commands:
cd /tmp wget http://nagios-plugins.org/download/nagios-plugins-2.0.3.tar.gz tar xzf nagios-plugins-2.0.3.tar.gz cd nagios-plugins-2.0.3 ./configure --with-nagios-user=nagios --with-nagios-group=nagios make make install
Configuration Nagios
Step 5. Configure Nagios.
Edit the /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/contacts.cfg config file with your favorite editor and change the email address associated with the nagiosadmin contact definition to the address you’d like to use for receiving alerts.
nano /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/contacts.cfg
Change the email address field to receive the notification:
[...]
define contact{
contact_name nagiosadmin ; Short name of userus
generic-contact ; Inherit default values from generic-contact template (defined above)
alias Nagios Admin ; Full name of useremail
admin@idroot.us ; <<***** CHANGE THIS TO YOUR EMAIL ADDRESS ******
[...]
Step 6. Configure Apache webserver.
nano /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/nagios.conf
Edit the following lines if you want to access Nagios administrative console from a particular IP series, Here, I want to allow Nagios administrative access from 192.168.1.0/24 series only:
[...] ## Comment the following lines ## # Order allow,deny # Allow from all ## Uncomment and Change lines as shown below ## Order deny,allow Deny from all Allow from 127.0.0.1 192.168.1.0/24 [...]
Enable Apache’s rewrite and cgi modules:
sudo a2enmod rewrite sudo a2enmod cgi
Configure Apache authentication:
We need to set up the password for the user nagiosadmin. This username will be used to access the web interface so it is important to remember the password that you will input here. Set the password running the following command and enter the password twice:
# sudo htpasswd -s -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users nagiosadmin New password: Re-type new password: Adding password for user nagiosadmin
Restart Apache for the changes to take effect:
systemctl restart apache2
Step 7. Verify and Start Nagios service.
Next, we have to make Nagios start at boot time, so first verify that the configuration file has no errors running the following command:
sudo /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
And you should get the output:
[...] Checking objects... Checked 8 services. Checked 1 hosts. Checked 1 host groups. Checked 0 service groups. Checked 1 contacts. Checked 1 contact groups. Checked 24 commands. Checked 5 time periods. Checked 0 host escalations. Checked 0 service escalations. Checking for circular paths... Checked 1 hosts Checked 0 service dependencies Checked 0 host dependencies Checked 5 timeperiods Checking global event handlers... Checking obsessive compulsive processor commands... Checking misc settings... Total Warnings: 0 Total Errors: 0 Things look okay - No serious problems were detected during the pre-flight check [...]
If there are no errors, start Nagios service and make it start automatically on every boot:
sudo service nagios start
When you try to start the Nagios and got the following error with Nagios to init script. To fix this error, copy /etc/init.d/skeleton to /etc/init.d/nagios using the following command:
cp /etc/init.d/skeleton /etc/init.d/nagios
Edit file /etc/init.d/nagios:
nano /etc/init.d/nagios
Add the following lines:
DESC="Nagios" NAME=nagios DAEMON=/usr/local/nagios/bin/$NAME DAEMON_ARGS="-d /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg" PIDFILE=/usr/local/nagios/var/$NAME.lock
Finally, you need to change the permissions:
chmod +x /etc/init.d/nagios
You can start the Nagios using the following command:
/etc/init.d/nagios start
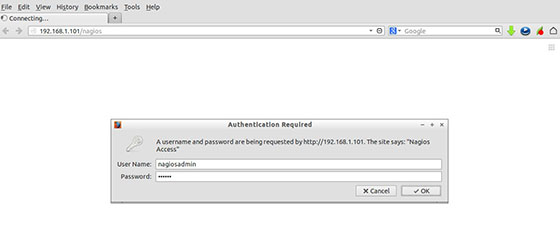
Step 8. Access Nagios from the web browser.
Nagios creates its own apache configuration file /etc/httpd/conf.d/nagios.conf. There is no need to make any changes to it. Simply open the URL in a browser http://nagios-server-ip/nagios.
When prompted for a username and password you will introduce the username “nagiosadmin” and the password that you entered in step 6. In case you forget this password you can modify it by rerunning the htpasswd command in step 5.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Nagios. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Nagios in ubuntu 15.04 systems. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official Nagios website.