
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install and configuration the VNC Server on Ubuntu 14.04. For those of you who didn’t know, VNC (Virtual Network Computing) server is free and open-source software that is designed for allowing remote access to the Desktop Environment of the server to the VNC Client whereas the VNC viewer is used on the remote computer to connect to the server.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation VNC Server on an Ubuntu 14.04 server.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Ubuntu 14.04, and any other Debian-based distribution.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install VNC Server on Ubuntu 14.04
Step 1. First, make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date by running the following apt-get commands in the terminal.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
Step 2. Installing a VNC Server on the Ubuntu system.
By default, most Linux server installations will not come with a graphical desktop environment. In this case, you need to install one that you can work with. In this example, we will install xfce4:
apt-get install gnome-core xfce4 firefox apt-get install vnc4server
Step 3. Configure VNC Server.
First, add a new user called vncuser you can use any user as you want:
adduser idroot passwd idroot
Now switch to the user you want to log in to the VNC server with. We are going to modify xstartup file to start the xfce4 session whenever VNC server is started:
su - idroot vncserver
VNC server will ask you for a password you want to use to log in to the VNC server. This is the sample output:
root@server:~$ vncserver You will require a password to access your desktops. Password: Verify: xauth: file /home/vncuser/.Xauthority does not exist New 'idroot:1 (vncuser)' desktop is idroot:1 Creating default startup script /home/vncuser/.vnc/xstartup Starting applications specified in /home/vncuser/.vnc/xstartup Log file is /home/vncuser/.vnc/idroot:1.log
After VNC Server started and created some of its files. We are now can turn it off to modify the xstartup file (startup script) to make it start with xfce4:
vncserver -kill :1
Before we begin configuring our new xstartup file, let’s back up the original in case we need it later:
cp ~/.vnc/xstartup ~/.vnc/xstartup.bak > ~/.vnc/xstartup nano ~/.vnc/xstartup
Add the following lines:
#!/bin/sh unset SESSION_MANAGER unset DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS startxfce4 & [ -x /etc/vnc/xstartup ] && exec /etc/vnc/xstartup [ -r $HOME/.Xresources ] && xrdb $HOME/.Xresources xsetroot -solid grey vncconfig -iconic &
The next step is to create a VNC Server startup script. You must do this with the root user:
su - nano /etc/init.d/vncserver
Copy this configuration and save it into the file:
#!/bin/bash
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: tightvncserver
# Required-Start: $syslog
# Required-Stop: $syslog
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: vnc server
#
### END INIT INFO
unset VNCSERVERARGS
VNCSERVERS=""
[ -f /etc/vncserver/vncservers.conf ] && . /etc/vncserver/vncservers.conf
prog=$"VNC server"
start() {
. /lib/lsb/init-functions
REQ_USER=$2
echo -n $"Starting $prog: "
ulimit -S -c 0 >/dev/null 2>&1
RETVAL=0
for display in ${VNCSERVERS}
do
export USER="${display##*:}"
if test -z "${REQ_USER}" -o "${REQ_USER}" == ${USER} ; then
echo -n "${display} "
unset BASH_ENV ENV
DISP="${display%%:*}"
export VNCUSERARGS="${VNCSERVERARGS[${DISP}]}"
su ${USER} -c "cd ~${USER} && [ -f .vnc/passwd ] && vncserver :${DISP} ${VNCUSERARGS}"
fi
done
}
stop() {
. /lib/lsb/init-functions
REQ_USER=$2
echo -n $"Shutting down VNCServer: "
for display in ${VNCSERVERS}
do
export USER="${display##*:}"
if test -z "${REQ_USER}" -o "${REQ_USER}" == ${USER} ; then
echo -n "${display} "
unset BASH_ENV ENV
export USER="${display##*:}"
su ${USER} -c "vncserver -kill :${display%%:*}" >/dev/null 2>&1
fi
done
echo -e "\n"
echo "VNCServer Stopped"
}
case "$1" in
start)
start $@
;;
stop)
stop $@
;;
restart|reload)
stop $@
sleep 3
start $@
;;
condrestart)
if [ -f /var/lock/subsys/vncserver ]; then
stop $@
sleep 3
start $@
fi
;;
status)
status Xvnc
;;
*)
echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart|condrestart|status}"
exit 1
esac
Make vnc server startup script executable:
chmod +x /etc/init.d/vncserver
Now we are going to create a VNC Server configuration file in /etc/ directory:
mkdir -p /etc/vncserver nano /etc/vncserver/vncservers.conf
Next, Copy the content to vncservers.conf file. The first line is for VNC ports and VNC users. number “1” is the VNC port, it’s port “1” or “5901”, you can add or change the port to “2” or “5902” and so on. If you want more users to connect to your VNC server, you must include those users here. The second line VNCSERVERARGS is to set VNC screen size.
VNCSERVERS="1:idroot" VNCSERVERARGS[1]="-geometry 1024x768"
The final step is to make VNC Server starts on boot:
update-rc.d vncserver defaults 99
Reboot your Ubuntu 14.04 system and test out your new VNC Server on Ubuntu 14.04:
reboot
Step 4. Accessing VNC.
To access the remote desktop on the VNC server from the windows system, you must have a VNC viewer installed on your system. There is various VNC viewer available to use. Download anyone and install it on your system, for example:
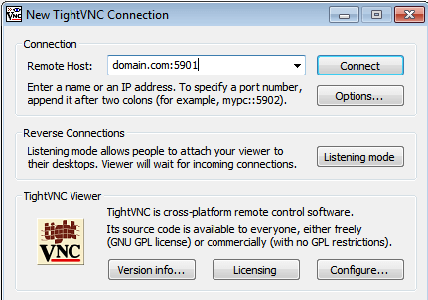
Congratulations! You have successfully installed VNC Server. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing VNC Server on your Ubuntu 14.04 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official VNC website.