How To Install Amarok Music Player on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS

Amarok Music Player has long been revered by Linux enthusiasts for its powerful music collection management, versatile playlists, and seamless integration with web services such as Last.fm. Whether you are a longtime Amarok user or discovering it for the first time, this guide will help you install and configure Amarok on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS in several ways. In addition, you will learn how to tweak its settings for peak performance, address common errors, and explore advanced features like dynamic playlists and audio bookmarking.
In this tutorial, you will find a thorough explanation of the system prerequisites, detailed step-by-step instructions on both command-line and Flatpak methods, best practices for audio configuration, and helpful troubleshooting techniques. With the help of Amarok’s core functionalities, you can rediscover your music and enjoy a more personalized and interactive listening experience. Use the power of Ubuntu 24.04 LTS and the reliability of this KDE-backed music player to organize, bookmark, and explore your favorite tracks with minimal fuss.
Introduction
Ubuntu 24.04 LTS is known for its stability and updated core components, making it an excellent foundation for running modern software applications. Amarok, a KDE-based audio player, has reemerged with improved features, Qt6/KDE Frameworks 6 support (while still backward compatible with Qt5/KDE Frameworks 5), comprehensive playlist management, and integration with widely used music services. Amarok’s development was once paused, but recent releases have breathed new life into this legendary application, allowing it to compete with other music players on the Linux scene.
If you crave flexibility in playlist creation, advanced tagging options, and integrated streaming services, Amarok is a top contender. Whether you are a casual listener wanting an intuitive interface or a power user looking for advanced tools, Amarok strikes a solid balance between clean design and feature-rich software.
Below, we will explore how to install and configure Amarok Music Player on your Ubuntu 24.04 LTS system. By following these in-depth steps, you can avoid potential pitfalls, solve typical audio-driver hurdles, and enjoy seamless music playback across multiple devices. Let’s get started!
What Is Amarok?
Amarok is a music player initially created for KDE (the K Desktop Environment), but it now runs on various desktop environments with minimal extra dependencies. As a KDE flagship audio player, it boasts a dynamic approach to organizing and enjoying music libraries. Its motto “Rediscover Your Music” reflects its goal of promoting music exploration through powerful built-in tools.
Here are some core features and benefits:
- Dynamic Playlists: Create smart lists that automatically update according to criteria you specify, for instance “recently played” or “most played.”
- Last.fm Integration: Scrobble songs, keep track of playback stats, and learn about new music you might enjoy
- Audio Bookmarking: Mark and label specific passages in a track, which is especially useful if you listen to podcasts, audio lessons, or lengthy mixes.
- Context View: Displays extensive track metadata, album art, Wikipedia articles about the currently playing artist, and more.
- Scripting & Plugins: Extend Amarok’s functionality with community-developed scripts. This can include new streaming services or specialized tools.
- Collection Management: Organize your entire music library with powerful tagging, rating, and sorting options for a highly curated listening experience.
Because Amarok pairs well with Ubuntu’s stability and performance, it remains a great choice for anyone who wants a robust, tried-and-true music player that easily handles large libraries.
System Requirements
Before proceeding with the installation, confirm that your system meets the minimum requirements for successful Amarok performance on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS.
- Operating System: Ubuntu 24.04 LTS or a derivative (e.g., Kubuntu, Xubuntu).
- Hardware: Modern CPU (64-bit), 1 GB RAM (2 GB+ recommended for handling big collections smoothly).
- Available Storage: At least 300 MB free space for installation, although more is advised for music libraries.
- KDE Frameworks and Libraries: Amarok runs best with KDE Frameworks 5 or 6. Some extra KDE components might be installed if you are on GNOME or a non-KDE environment.
- Sound Card & Drivers: Confirm that your audio drivers are working correctly. If you experience no sound, you may need to reload ALSA or PulseAudio.
4. Installation Methods
Amarok can be installed in multiple ways on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS. In this article, we’ll explore two common methods to ensure you pick the one that best fits your usage:
- Using a Personal Package Archive (PPA) and the command-line.
- Using Flatpak, an easy method to keep the application isolated and updated independently from the main system packages.
You can choose whichever fits your preference. The PPA approach integrates deeper with your system, while Flatpak offers a sandboxed environment.
Method 1: Installing via PPA (Command-Line)
This route is ideal for those who want easy integration with system libraries. Several PPAs exist for Amarok. For Ubuntu 24.04 LTS, you can make use of either Pedro Gomes’ PPA or Joseph Yasi’s. Below, we’ll explore a generic approach.
- Update Your Package Index
Before adding any repository, it is wise to synchronize the current APT index. Open your terminal (CTRL + ALT + T) and run:sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgradeThis ensures your system is fully up to date.
- Add the Amarok PPA
For demonstration, let’s say we choose a PPA. Note that the actual repository might differ. Assuming a suitable PPA isppa:joe-yasi/amarok-kde5:sudo add-apt-repository ppa:joe-yasi/amarok-kde5 sudo apt-get updateThis makes the Amarok packages accessible to your local package manager.
- Install Amarok
After updating your package lists:sudo apt install amarokThe package manager will download and install Amarok along with any dependencies. If asked for confirmation, press Y and continue.
- Launch Amarok
Once installed, launch it by searching “Amarok” in your application menu or by typing:amarokAmarok’s interface should open. If you’re using GNOME, it might pull in some KDE dependencies; this is normal.
Installing via PPA is a straightforward way to utilize the latest Amarok releases, as well as help you quickly get patches in case of bugs.
Method 2: Installing via Flatpak
Flatpak provides a sandboxed environment for Linux apps, ensuring minimal conflicts with system libraries. This approach is especially convenient if you use multiple distros or prefer a more isolated setup.
- Set Up Flatpak
Ubuntu 24.04 might already include Flatpak, but if not, install it:sudo apt install flatpakFor GNOME Software integration, you can also install:
sudo apt install gnome-software-plugin-flatpakIf you are using KDE, a plugin is commonly available or it might already be integrated.
- Add the Flathub Repository
Amarok is often packaged and distributed via Flathub. Integrate Flathub by running:sudo flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoThis step gives you access to the broad library of Flatpak applications.
- Install Amarok from Flathub
Once added, look for Amarok:flatpak search amarokIf you find org.kde.amarok, proceed to install:
sudo flatpak install flathub org.kde.amarokThis downloads the required runtime and the Amarok Flatpak package.
- Launch Amarok via Flatpak
After installation, run:flatpak run org.kde.amarokOptionally, create a desktop launcher to start Amarok from your application menu.
The sandbox nature of Flatpak helps protect your overall system from any conflicts. Also, updates are easy to manage:
sudo flatpak update
Using this method, you always have an up-to-date version. The only downside is it takes more disk space due to including all the necessary runtimes.
5. Configuration Guide
After installing Amarok on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS, you can fine-tune it to streamline your music playback and exploration.
First-Time Setup
- Specify Your Music Library Folder
On first launch, Amarok will prompt you to select or scan your music folder. Choose the directory where your audio files are stored. Amarok will index the files and create a searchable library. - Collection Management
If you missed the initial prompt, open:Settings > Configure Amarok > CollectionSet or add your music paths. Amarok will keep things synchronized in real time.
- Initial Database Setup
Amarok typically relies on MySQL or SQLite to handle music metadata. The default configuration is Embedded MySQL. If, for any reason, you experience database issues (like an error message stating unavailable service), ensure that the Amarok package was built with the required dependencies.
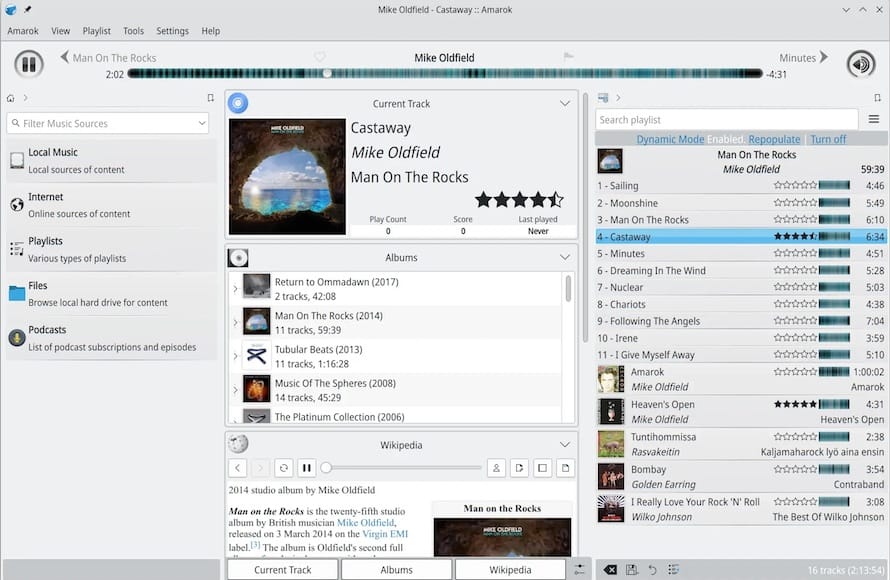
Interface Customization
- Layout and Panels: Click the View menu to enable or disable different panels, such as the Context or Playlist pane. You can rearrange them to suit your workflow.
- Context View Applets: Amarok uses small widgets for lyrics, Wikipedia articles, or track statistics. You can enable or disable these under:
Settings > Configure Amarok > Context View - Skin and Appearance: Although Amarok is a KDE application, you can customize the color scheme to blend into Ubuntu’s default GNOME look. This might require installing additional KDE theme components.
Audio Settings Optimization
- Phonon Backend: Amarok uses Phonon as an abstraction layer to talk to your audio drivers. Depending on your system, set your preferred backend to GStreamer or VLC. Access these by navigating to:
Settings > Configure Amarok > Playback - Volume Normalization and ReplayGain: If you want uniform loudness across tracks, enable ReplayGain in the settings. This is especially useful for large, varied collections.
- Equalizer: Although Amarok does not come with a built-in advanced equalizer by default, advanced users might leverage PulseAudio or PipeWire equalizer modules at the system level.
At this point, Amarok’s interface and music library should be set up efficiently, helping you quickly find the media you need and enjoy high-quality playback.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Below are some frequently encountered problems that you might face while installing or using Amarok on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS, along with tips to resolve them.
No Sound or Audio Driver Issues
If you experience silence or broken audio output, you can try:
- Reloading ALSA:
sudo alsa force-reloadThen reboot your system.
- PulseAudio Reinstallation:
sudo apt-get install --reinstall pulseaudioFollow by shutting down and restarting your machine.
- Testing Other Backends: Switch from a GStreamer-based backend to VLC or vice versa in Amarok’s playback settings.
Database Connection Error
Occasionally, you may see a prompt about Amarok’s embedded MySQL not running:
- Cause: Your distribution’s build might be missing MySQL or was compiled without embedded SQL support.
- Solution: Install a separate MySQL server or switch to SQLite if Amarok supports it in your build. Check package logs for build configuration flags.
Playlist or Collection Scanning Problems
- Check File Permissions: If Amarok cannot read from your music folder, ensure you have the correct ownership and read permissions.
chmod -R a+rx /path/to/your/music - Corrupted Cache: Clear or rename Amarok’s configuration folder, typically found at:
~/.kde/share/apps/amarok ~/.config/amarokThen relaunch Amarok to let it rebuild the database.
Crashes or Freezes
- Check for Missing Dependencies: KDE-based packages or libraries may be missing. Rerun:
sudo apt-get install --fix-broken - Update Amarok: If you used the PPA or Flatpak, ensure you have the latest release with bug fixes:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgradeor
sudo flatpak update - Run Amarok from Terminal: Observe any error messages that appear in your terminal window for potential leads.
Advanced Features
Amarok stands out among music players thanks to distinctive features that enable more in-depth management and interaction with your audio library. Here are a few advanced functionalities you might explore once the basics are up and running:
Playlist Management & Dynamic Mode
One of Amarok’s flagship abilities is building Dynamic Playlists. These playlists update automatically based on your listening habits and rules you define. To configure:
- Open Amarok and click the Playlist tab.
- Select Dynamic or Automatic Playlist Generator (APG).
- Specify parameters: favorite artists, minimum star ratings, or recently played filters.
- Enable randomization or weighted picks for variety.
This can significantly boost engagement with your library, helping you rediscover songs you had forgotten about.
Audio Bookmarking
Audio bookmarks let you anchor certain points in songs or tracks. This feature is particularly beneficial if you listen to audiobooks, podcasts, speaker sessions, or language lessons. For example, you can mark a timestamp of an instructive segment and label it for easy searching:
- Right-click the track you want to bookmark in your Playlist pane.
- Select Bookmark > Add Bookmark.
- Label the bookmark with a descriptive name.
- To revisit a bookmark later, open Bookmarks from the main menu or from the track’s right-click context menu.
This approach is rarely found in other popular music players, setting Amarok apart for those who often reference certain parts of long audio files.
Last.fm Integration
Amarok integrates seamlessly with Last.fm so that you can scrobble your tracks, get personalized music recommendations, and keep a record of your listening history:
- Go to Settings > Configure Amarok > Plugins or Services.
- Enable the Last.fm option and insert your Last.fm credentials if required.
- Whenever you play music in Amarok, the data is automatically sent to your Last.fm profile so that you can see charts and stats.
This feature is extremely beneficial to discover new music from artists you have not explored yet.
Cover Art Management
Neat album covers enhance your listening experience visually. Amarok can automatically fetch art from the internet, or you can assign images from your local folders:
- Automatic Cover Fetch: Right-click on the album > Fetch Cover. Amarok tries to match album and artist metadata with online databases.
- Manual Cover Assigning: If the metadata is incomplete, you can upload any .jpg or .png file as the album cover by browsing your filesystem.
Scripting Capabilities
For the advanced user who wants total control:
- KDE Script Management: Access Settings > Configure Amarok > Script Manager to browse or install scripts from the online store. Some scripts automate tasks or integrate with external services.
- Custom Scripts: If you have development skills, you can create your own Python or Ruby scripts to automate library tasks, generate new interactive panels, or add new streaming services.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Amarok. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Amarok Music Player on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Amarok website.