
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Apache Hadoop on CentOS 8. For those of you who didn’t know, Apache Hadoop is an open-source framework used for distributed storage as well as distributed processing of big data on clusters of computers that run on commodity hardware. Rather than rely on hardware to deliver high availability, the library itself is designed to detect and handle failures at the application layer, so delivering a highly-available service on top of a cluster of computers, each of which may be prone to failures.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of Apache Hadoop on a CentOS 8 server.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: CentOS 8.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Apache Hadoop on CentOS 8
Step 1. First, let’s start by ensuring your system is up-to-date.
sudo dnf update
Step 2. Installing Java.
Apache Hadoop is written in Java and supports only Java version 8. You can install OpenJDK 8 using the following command:
sudo dnf install java-1.8.0-openjdk ant
Check the Java version:
java -version
Step 3. Installing Apache Hadoop CentOS 8.
It is recommended to create a normal user to configure Apache Hadoop, create a user using the following command:
useradd hadoop passwd hadoop
Next, we will need to configure passwordless SSH authentication for the local system:
su - hadoop ssh-keygen -t rsa cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys chmod 640 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Verify the password-less ssh configuration with the command:
ssh localhost
Next steps, download the latest stable version of Apache Hadoop, At the moment of writing this article it is version 3.2.1:
wget http://apachemirror.wuchna.com/hadoop/common/hadoop-3.2.1/hadoop-3.2.1.tar.gz tar -xvzf hadoop-3.2.1.tar.gz mv hadoop-3.2.1 hadoop
Then, you will need to configure Hadoop and Java Environment Variables on your system:
nano ~/.bashrc
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/jre-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.232.b09-2.el8_1.x86_64/ export HADOOP_HOME=/home/hadoop/hadoop export HADOOP_INSTALL=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_COMMON_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_HDFS_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_YARN_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_COMMON_LIB_NATIVE_DIR=$HADOOP_HOME/lib/native export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_HOME/sbin:$HADOOP_HOME/bin export HADOOP_OPTS="-Djava.library.path=$HADOOP_HOME/lib/native"
Now we activate the environment variables with the following command:
source ~/.bashrc
Next, open the Hadoop environment variable file:
nano $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/jre-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.232.b09-2.el8_1.x86_64/
Hadoop has many configuration files, which need to configure as per the requirements of your Hadoop infrastructure. Let’s start with the configuration with a basic Hadoop single node cluster setup:
cd $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop
Edit core-site.xml:
<configuration> <property> <name>fs.default.name</name> <value>hdfs://localhost:9000</value> </property> </configuration>
Create the namenode and datanode directories under hadoop user home /home/hadoop directory:
mkdir -p ~/hadoopdata/hdfs/{namenode,datanode}
Edit hdfs-site.xml:
<configuration> <property> <name>dfs.replication</name> <value>1</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.name.dir</name> <value>file:///home/hadoop/hadoopdata/hdfs/namenode</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.data.dir</name> <value>file:///home/hadoop/hadoopdata/hdfs/datanode</value> </property> </configuration>
Edit mapred-site.xml:
<configuration> <property> <name>mapreduce.framework.name</name> <value>yarn</value> </property> </configuration>
Edit yarn-site.xml:
<configuration> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services</name> <value>mapreduce_shuffle</value> </property> </configuration>
Now format namenode using the following command, do not forget to check the storage directory:
hdfs namenode -format
Start both NameNode and DataNode daemons by using the scripts provided by Hadoop:
start-dfs.sh
Step 4. Configure Firewall.
Run the following command to allow Apache Hadoop connections through the firewall:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=9870/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=8088/tcp firewall-cmd --reload
Step 5. Accessing Apache Hadoop.
Apache Hadoop will be available on HTTP port 9870 and port 50070 by default. Open your favorite browser and navigate to http://your-domain.com:9870 or http://your-server-ip:9870.
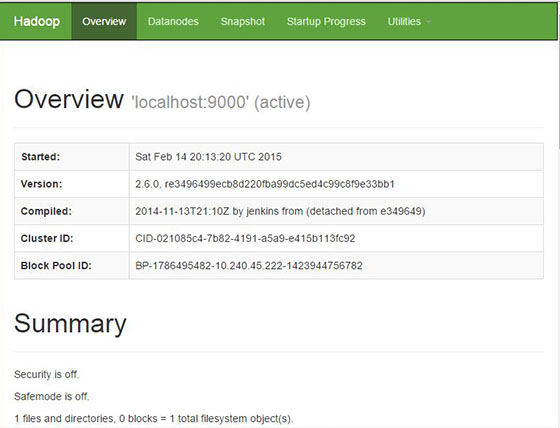
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Apache Hadoop. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Hadoop on CentOS 8 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official Apache Hadoop website.