How To Install Apache Solr on Linux Mint 22

Installing a powerful search platform on your Linux Mint 22 system doesn’t have to be complicated. Apache Solr stands as one of the most robust open-source search engines available today, offering enterprise-grade functionality for applications requiring sophisticated search capabilities.
This comprehensive guide walks you through every step of installing Apache Solr on Linux Mint 22 “Wilma,” ensuring you have a fully functional search server ready for production use. Whether you’re building a content management system, e-commerce platform, or data analytics application, this tutorial provides the foundation you need.
By the end of this installation process, you’ll have Apache Solr running securely on your Linux Mint 22 system with proper configuration, security measures, and optimization settings in place.
Understanding Apache Solr and Its Benefits
Apache Solr represents a mature, feature-rich search platform built on Apache Lucene technology. This enterprise search server provides full-text search capabilities, faceted search functionality, and real-time indexing features that scale from small applications to massive enterprise deployments.
The platform excels in handling complex search queries across large datasets while maintaining exceptional performance. Solr’s distributed architecture supports clustering and replication, making it ideal for high-availability environments where search functionality must remain consistently accessible.
Linux Mint 22 provides an excellent foundation for Solr deployment due to its Ubuntu 24.04 LTS base, ensuring long-term stability and security updates through 2029. The operating system’s package management system and security features complement Solr’s architecture perfectly.
Key advantages include cost-effectiveness compared to proprietary search solutions, extensive documentation and community support, and seamless integration with popular programming languages and frameworks. The platform’s RESTful API design simplifies integration with existing applications while providing powerful administrative tools through its web-based interface.
System Requirements and Prerequisites
Linux Mint 22 Compatibility Assessment
Linux Mint 22 “Wilma” builds upon Ubuntu 24.04 LTS, providing excellent compatibility for Apache Solr installation. This foundation ensures access to up-to-date package repositories and security patches essential for maintaining a secure search server environment.
The Cinnamon desktop environment doesn’t interfere with server applications, making Linux Mint 22 suitable for both development and production Solr deployments. Long-term support extending until 2029 guarantees stability for enterprise applications requiring consistent platform availability.
Hardware Requirements for Optimal Performance
Minimum hardware specifications require a dual-core processor running at 2.5 GHz or higher, though quad-core processors deliver significantly better performance for production workloads. Memory requirements start at 4GB RAM, but 8GB or more is strongly recommended for handling substantial document collections and concurrent search requests.
Storage considerations demand at least 100GB available disk space for production environments, accounting for index growth, log files, and system operations. SSD storage dramatically improves index performance and query response times compared to traditional hard drives.
Network configuration should support the bandwidth requirements of your expected search traffic. Gigabit Ethernet connections provide adequate performance for most installations, while high-traffic environments may benefit from bonded network interfaces or higher-speed connections.
Java Environment Requirements
Apache Solr 9.x requires Java 11 as the minimum supported version, though Java 17 is recommended for optimal performance and security features. The Java Development Kit (JDK) provides additional tools useful for troubleshooting and development, making it preferable over the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) alone.
To verify your current Java installation, execute the following command:
java -versionIf Java isn’t installed or requires updating, proceed with the installation steps outlined in the next section. Oracle JDK and OpenJDK both work effectively with Solr, though OpenJDK offers better integration with Linux package management systems.
Essential Software Dependencies
Several utility packages enhance the Solr installation and management experience. The curl package enables command-line testing of Solr’s REST API, while lsof helps diagnose port conflicts and network connectivity issues.
Additional tools include wget for downloading software packages and tar for extracting compressed archives. Most Linux Mint 22 installations include these utilities by default, but verification ensures compatibility throughout the installation process.
Pre-Installation System Setup
Updating System Packages and Security
Begin by updating your Linux Mint 22 system to ensure all packages reflect the latest security patches and feature updates. This foundation step prevents compatibility issues and security vulnerabilities that could affect Solr operation.
Execute the following commands to update your system:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade -yThe update process may require several minutes depending on the number of available updates. Review any package hold notifications or dependency conflicts that might require manual resolution before proceeding.
Security considerations for production environments include configuring automatic security updates, implementing proper firewall rules, and establishing user access controls. Consider disabling unnecessary services and removing unused packages to minimize the attack surface.
Java Installation and Configuration Process
Install OpenJDK 17 using the apt package manager to ensure optimal Solr compatibility:
sudo apt install openjdk-17-jdk -yAfter installation, configure the JAVA_HOME environment variable to ensure Solr can locate the Java installation correctly. Add the following line to your /etc/environment file:
echo 'JAVA_HOME="/usr/lib/jvm/java-17-openjdk-amd64"' | sudo tee -a /etc/environmentReload the environment variables:
source /etc/environmentVerify the Java installation and environment configuration:
java -version
echo $JAVA_HOMECommon Java installation issues include multiple Java versions creating conflicts or incorrect JAVA_HOME paths. Use update-alternatives to manage multiple Java installations if necessary.
Creating Dedicated Service Account
Security best practices recommend running Solr under a dedicated user account rather than root or personal accounts. The Solr installation script automatically creates a solr user account with appropriate permissions and security restrictions.
This dedicated account limits potential security exposure by restricting file system access and preventing privilege escalation attacks. The account configuration includes disabled login capabilities while maintaining the ability to run the Solr service effectively.
Directory ownership and permission management ensure the Solr user can access necessary files while preventing unauthorized modifications to system configuration files. This approach balances operational requirements with security principles essential for production deployments.
Downloading and Installing Apache Solr
Obtaining the Latest Solr Release
Navigate to the official Apache Solr download page to access the most current stable release. Version 9.7.0 represents the latest stable release at the time of writing, offering improved performance and security features over previous versions.
Download the Solr distribution using wget:
cd /tmp
wget https://www.apache.org/dyn/closer.lua/solr/solr/9.9.0/solr-9.9.0.tgzVerify the download integrity by checking the file size and comparing checksums when available. This verification step prevents issues caused by corrupted downloads or network transmission errors.
Extracting and Preparing Installation Files
Extract the installation script from the downloaded archive:
tar xzf solr-9.9.0.tgz solr-9.9.0.tgz/bin/install_solr_service.sh --strip-components=2The installation script automates the complex process of extracting files, creating user accounts, configuring services, and establishing proper file permissions. Understanding the script’s functionality helps troubleshoot potential installation issues.
Verify the script permissions and ensure it’s executable:
chmod +x install_solr_service.sh
ls -la install_solr_service.shThe installation script creates the directory structure under /opt/solr by default, establishing separate directories for configuration files, data storage, and log files. This organization follows Linux filesystem hierarchy standards and simplifies administration tasks.
Executing the Installation Process
Run the installation script with administrator privileges to complete the Solr setup:
sudo ./install_solr_service.sh solr-9.9.0.tgzThe installation process displays progress information including user creation, file extraction, service configuration, and initial startup attempts. Monitor this output for error messages or warnings that might require attention.
Installation typically completes within several minutes, depending on system performance and storage speed. The script automatically starts the Solr service upon successful installation, though additional configuration may be required for production environments.
Default installation parameters place Solr under /opt/solr with configuration files in /var/solr/data and logs in /var/solr/logs. Understanding this directory structure facilitates future administration and troubleshooting tasks.
Verifying Installation Success
Confirm the Solr service status using systemctl:
sudo systemctl status solrA successful installation displays “active (exited)” status, which is normal for Solr’s service configuration. This status indicates the service started successfully and is ready to handle requests.
Test network accessibility by checking if Solr responds on the default port:
curl http://localhost:8983/solr/The response should include Solr version information and basic system status. If the command fails, review firewall settings and service logs for potential issues.
Access the web interface by opening a browser and navigating to http://your_server_ip:8983/solr/. The admin interface should display the Solr dashboard with system information and available collections.
Configuration and Optimization
Basic Solr Configuration Settings
Edit the main configuration file to customize Solr for your environment:
sudo nano /etc/default/solr.in.shKey configuration parameters include memory allocation, network binding, and security settings. The SOLR_HEAP setting controls memory allocation and should be adjusted based on your system’s available RAM and expected workload.
For systems with 8GB RAM, allocate 4GB to Solr:
SOLR_HEAP="4g"Configure network access by modifying the SOLR_JETTY_HOST setting. The default localhost configuration restricts access to the local machine, which is appropriate for development but requires modification for production deployments.
Set the timezone and locale settings to ensure proper log timestamps and data handling:
SOLR_TIMEZONE="UTC"Network and Security Configuration
Enable external access by configuring the Jetty host setting:
SOLR_JETTY_HOST="0.0.0.0"This configuration allows connections from any network interface, making Solr accessible from remote systems. However, implement proper firewall rules and access controls to prevent unauthorized access.
Configure firewall rules using ufw to control network access:
sudo ufw allow 8983/tcp
sudo ufw enableFor production environments, restrict access to specific IP addresses or network ranges:
sudo ufw allow from 192.168.1.0/24 to any port 8983Consider implementing reverse proxy configurations using Apache or Nginx to provide additional security layers, SSL termination, and load balancing capabilities for high-availability deployments.
Service Management and Auto-Start Configuration
Enable automatic startup on system boot:
sudo systemctl enable solrTest service management commands to ensure proper operation:
sudo systemctl start solr
sudo systemctl stop solr
sudo systemctl restart solrMonitor service logs to identify potential issues or performance bottlenecks:
sudo tail -f /var/solr/logs/solr.logConfigure log rotation to prevent disk space issues from accumulating log files. The default configuration should handle most environments, but high-traffic installations may require customized log management.
Creating Your First Collection
Initialize a test collection to verify Solr functionality:
sudo -u solr /opt/solr/bin/solr create -c test_collectionThis command creates a collection using the default data_driven_schema_configs configuration set, which automatically detects field types and configures indexing accordingly. While convenient for testing, production environments typically require custom schema configurations.
Verify collection creation through the web interface or API:
curl http://localhost:8983/solr/admin/collections?action=LISTThe response should include your newly created collection in the list of available collections, confirming successful creation and proper API functionality.
Security Implementation
Access Control and Authentication Setup
Implement basic authentication to secure Solr access in production environments. Create a security configuration file:
sudo mkdir -p /var/solr/data/security
sudo nano /var/solr/data/security/security.jsonConfigure basic authentication with the following content:
{
"authentication":{
"blockUnknown": true,
"class":"solr.BasicAuthPlugin",
"credentials":{"admin":"IV0EHq1OnNrj6gvRCwvFwTrZ1+z1oBbnQdiVC3otuq0= Ndd7LKvVBAaZIF0QAVi1ekCfAJXr1GGfLtRUXhgrF8c="}
},
"authorization":{
"class":"solr.RuleBasedAuthorizationPlugin",
"permissions":[{"name":"security-edit","role":"admin"}],
"user-role":{"admin":"admin"}
}
}Restart Solr to activate authentication:
sudo systemctl restart solrTLS/SSL Configuration for Secure Communications
Generate SSL certificates for encrypted communications. For development environments, self-signed certificates provide adequate security:
sudo mkdir -p /opt/solr/server/etc
sudo keytool -genkeypair -alias solr-ssl -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -validity 3650 -keystore /opt/solr/server/etc/solr-ssl.keystore.jksConfigure SSL in the Solr configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/default/solr.in.shAdd SSL configuration parameters:
SOLR_SSL_KEY_STORE=/opt/solr/server/etc/solr-ssl.keystore.jks
SOLR_SSL_KEY_STORE_PASSWORD=your_keystore_password
SOLR_SSL_TRUST_STORE=/opt/solr/server/etc/solr-ssl.keystore.jks
SOLR_SSL_TRUST_STORE_PASSWORD=your_keystore_password
SOLR_SSL_NEED_CLIENT_AUTH=false
SOLR_SSL_WANT_CLIENT_AUTH=falseProduction environments should use certificates issued by trusted certificate authorities rather than self-signed certificates to ensure proper client validation and security.
System-Level Security Hardening
Configure file permissions to restrict access to sensitive configuration files:
sudo chmod 600 /var/solr/data/security/security.json
sudo chown solr:solr /var/solr/data/security/security.jsonImplement regular security updates through automated processes:
sudo apt install unattended-upgrades
sudo dpkg-reconfigure unattended-upgradesMonitor system logs for unauthorized access attempts and configure intrusion detection systems for production environments. Log monitoring tools can identify suspicious patterns and trigger automated responses to potential security threats.
Testing and Verification Procedures
Web Interface Functionality Testing
Access the Solr admin interface at http://your_server_ip:8983/solr/ to verify proper installation and configuration. The dashboard should display system information, available collections, and administrative tools.
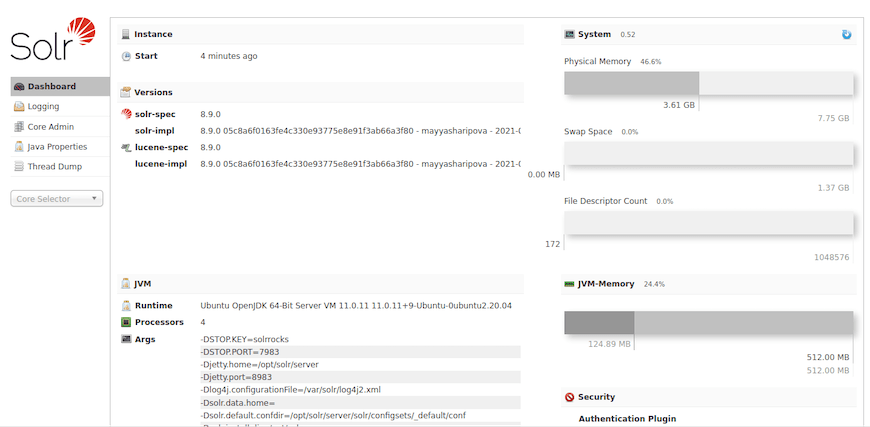
Navigate through different sections of the interface to confirm functionality:
- Core/Collection management
- Schema browser
- Query interface
- Logging configuration
- Cloud management (if applicable)
Test basic search functionality by adding sample documents to your test collection and performing queries through the web interface. This verification ensures the indexing and search pipeline operates correctly.
Command Line API Testing
Verify API functionality using curl commands to test core Solr operations. Add a sample document to your collection:
curl -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' 'http://localhost:8983/solr/test_collection/update?commit=true' --data-binary '[
{
"id": "1",
"title": "Test Document",
"content": "This is a test document for Apache Solr installation verification."
}
]'Perform a search query to verify document indexing and retrieval:
curl 'http://localhost:8983/solr/test_collection/select?q=test&wt=json&indent=true'The response should include the document you added, confirming successful indexing and search functionality. Test various query parameters and response formats to ensure comprehensive API operation.
Performance Optimization and Best Practices
Memory and JVM Tuning
Optimize garbage collection settings for better performance in production environments. Add JVM tuning parameters to the Solr configuration:
sudo nano /etc/default/solr.in.shConfigure garbage collection options:
GC_TUNE="-XX:+UseG1GC -XX:+UseStringDeduplication -XX:+PerfDisableSharedMem"Monitor garbage collection performance using JVM logging:
GC_LOG_OPTS="-Xlog:gc*:$SOLR_LOGS_DIR/solr_gc.log:time,tags"Adjust heap size based on your data volume and query patterns. Larger heaps reduce garbage collection frequency but may increase pause times. Monitor application performance and adjust accordingly.
Index Optimization Strategies
Configure automatic index optimization to maintain search performance:
curl 'http://localhost:8983/solr/test_collection/update?optimize=true'Schedule regular optimization tasks during low-traffic periods to minimize impact on search performance. Large indexes may require several hours to optimize completely.
Implement index warming queries to preload frequently accessed data into memory:
<listener event="firstSearcher" class="solr.QuerySenderListener">
<arr name="queries">
<lst><str name="q">*:*</str><str name="rows">10</str></lst>
</arr>
</listener>Production Readiness Considerations
Implement comprehensive backup strategies including automated snapshots and off-site storage. Configure backup retention policies based on business requirements and available storage capacity.
Set up monitoring systems to track key performance metrics:
- Query response times
- Index size and growth rates
- Memory utilization
- Error rates and exceptions
Establish capacity planning procedures to anticipate hardware upgrades and scaling requirements. Monitor growth trends and plan infrastructure improvements before performance degradation occurs.
Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
Resolving Java Version Conflicts
Multiple Java installations can cause conflicts and prevent Solr from starting correctly. Identify all Java installations:
sudo update-alternatives --config javaSelect the appropriate Java version and verify the JAVA_HOME environment variable points to the correct installation directory. Remove or disable conflicting Java versions if necessary.
Test Java functionality after making changes:
java -version
$JAVA_HOME/bin/java -versionAddressing Permission and Ownership Problems
File permission issues often prevent Solr from accessing configuration files or writing log data. Verify ownership of Solr directories:
sudo chown -R solr:solr /opt/solr
sudo chown -R solr:solr /var/solrCheck and correct file permissions:
sudo chmod -R 755 /opt/solr
sudo chmod -R 775 /var/solr/dataResolving Port Conflicts and Network Issues
Identify processes using port 8983:
sudo lsof -i :8983
sudo netstat -tulpn | grep :8983Configure alternative ports if conflicts exist:
sudo nano /etc/default/solr.in.shAdd port configuration:
SOLR_PORT=8984Update firewall rules to accommodate port changes and restart the Solr service to apply new configurations.
Service Startup Failure Diagnosis
Examine service logs for startup errors:
sudo journalctl -u solr -f
sudo tail -f /var/solr/logs/solr.logCommon startup issues include insufficient memory allocation, configuration file syntax errors, or dependency conflicts. Address identified issues and restart the service.
Verify service dependencies and ensure required packages are installed and functioning correctly before attempting to restart Solr.
Advanced Configuration and Management
Clustering and High Availability Setup
For production environments requiring high availability, configure SolrCloud with Apache ZooKeeper. Install ZooKeeper ensemble for coordination:
sudo apt install zookeeper -y
sudo systemctl enable zookeeper
sudo systemctl start zookeeperConfigure Solr for cloud mode by modifying startup parameters:
SOLR_MODE="solrcloud"
ZK_HOST="localhost:2181"Create distributed collections with replication factors appropriate for your availability requirements. Multiple replicas provide fault tolerance and improved query performance through load distribution.
Monitoring and Maintenance Procedures
Implement comprehensive monitoring using tools like Prometheus and Grafana to track Solr performance metrics. Configure alerting for critical issues such as high memory usage, slow query response times, or service unavailability.
Establish regular maintenance schedules including:
- Log file rotation and cleanup
- Index optimization during low-traffic periods
- Security patch application
- Backup verification procedures
Document standard operating procedures for common administrative tasks to ensure consistent management practices across team members.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Apache Solr. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Apache Solr on the Linux Mint 22 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Apache website.