
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Apache Spark on Debian 10. For those of you who didn’t know, Apache Spark is a fast and general-purpose cluster computing system. It provides high-level APIs in Java, Scala, and Python, and also an optimized engine that supports overall execution charts. It also supports a rich set of higher-level tools including Spark SQL for SQL and structured information processing, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX for graph processing, and Spark Streaming.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of Apache Spark on a Debian 10 (Buster).
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Debian 10 (Buster).
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Apache Spark on Debian 10 Buster
Step 1. Before running the tutorial below, it’s important to make sure your system is up to date by running the following apt commands in the terminal:
sudo apt update
Step 2. Installing Java.
Apache Spark requires Java to run, let’s make sure we have Java installed on our Debian system:
sudo apt install default-jdk
Verify Java version using the command:
java -version
Step 3. Installing Scala.
Now we install the Scala package on Debian systems:
sudo apt install scala
Check the version of Scala:
scala -version
Step 4. Installing Apache Spark on Debian.
Now we can download the Apache Spark binary:
wget https://www.apache.org/dyn/closer.lua/spark/spark-3.1.1/spark-3.1.1-bin-hadoop2.7.tgz
Next, extract the Spark tarball:
tar xvf spark-3.1.1-bin-hadoop2.7.tgz sudo mv spark-3.1.1-bin-hadoop2.7/ /opt/spark
Once done, set Spark environment:
nano ~/.bashrc
At the end of the file, add the following lines:
export SPARK_HOME=/opt/spark export PATH=$PATH:$SPARK_HOME/bin:$SPARK_HOME/sbin
Save the changes and close the editor. To apply the changes run:
source ~/.bashrc
Now start Apache Spark with these commands, one of which is the master of the cluster:
start-master.sh
To view the Spark Web user interface looks below, open a web browser and enter the localhost IP address on port 8080:
http://127.0.0.1:8080/
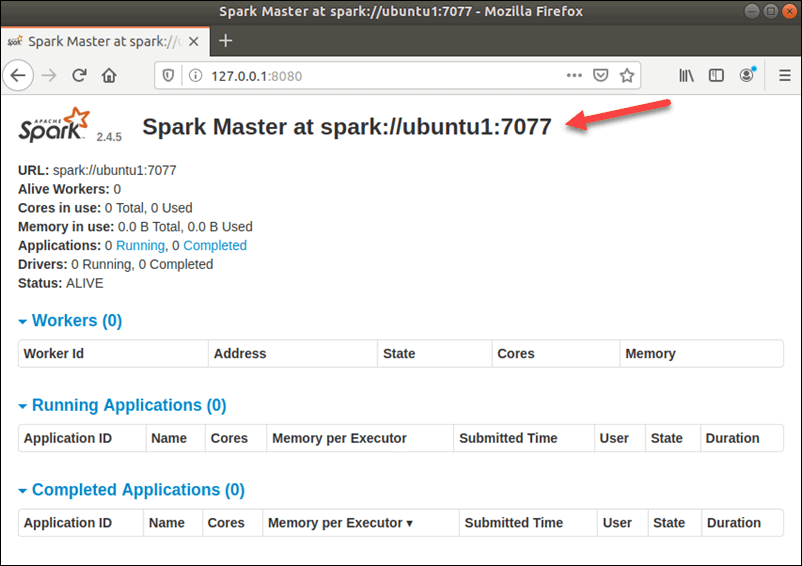
In this single-server, standalone setup, we will start one slave server along with the master server. The start-slave.sh a command is used to start the Spark Worker Process:
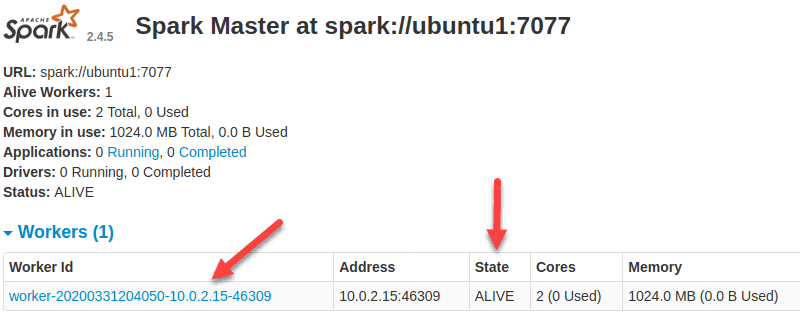
start-slave.sh spark://ubuntu1:7077
Now that a worker is up and running, if you reload Spark Master’s Web UI, you should see it on the list:
Once finish the configuration, start the master and slave server, and test if the Spark shell works:
spark-shell
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Spark. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the latest version of Apache Spark on the Debian system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Apache Spark website.