
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install ArangoDB on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS. For those of you who didn’t know, ArangoDB is an open-source NoSQL database with an open-source year and a flexible data model for documents, key values, and graphs. This database is easily managed using the integrated web interface or command-line interface.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of ArangoDB on Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal Fossa). You can follow the same instructions for Ubuntu 18.04, 16.04, and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Ubuntu 20.04, 18.04, 16.04, and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install ArangoDB on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Focal Fossa
Step 1. First, make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date by running the following apt commands in the terminal.
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade sudo apt install curl apt-transport-https
Step 2. Installing ArangoDB on Ubuntu 20.04.
Now run the following command to add an apt repository to your system:
echo 'deb https://download.arangodb.com/arangodb34/DEBIAN/ /' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/arangodb.list
Next, import the GPG key used for signing the packages:
wget -q https://download.arangodb.com/arangodb34/DEBIAN/Release.key -O- | sudo apt-key add -
After that, we can install the ArangoDB software using the following command:
sudo apt update sudo apt install arangodb3
If you had missed to set the root password during installation, you can secure ArangoDB after installation by running:
sudo arango-secure-installation
Once the installation has been completed, start the ArangoDB service and enable it to start at system reboot with the following command:
sudo systemctl start arangodb3 sudo systemctl enable arangodb3
Step 3. Accessing the ArangoDB Shell.
ArangoDB comes with a command-line utility to manage the databases. You can connect the ArangoDB shell with the following command:
arangosh
Output:
$ arangosh
Please specify a password: _
__ _ _ __ __ _ _ __ __ _ ___ ___| |__
/ _` | '__/ _` | '_ \ / _` |/ _ \/ __| '_ \
| (_| | | | (_| | | | | (_| | (_) \__ \ | | |
\__,_|_| \__,_|_| |_|\__, |\___/|___/_| |_|
|___/
arangosh (ArangoDB 3.4.9 [linux] 64bit, using jemalloc, build tags/v3.4.9-0-g1001202f8, VPack 0.1.33, RocksDB 5.16.0, ICU 58.1, V8 5.7.492.77, OpenSSL 1.1.0l 20 May 2021)
Copyright (c) ArangoDB GmbH
Command-line history will be persisted when the shell is exited.
Connected to ArangoDB 'http+tcp://127.0.0.1:8529' version: 3.4.9 [SINGLE, server], database: '_system', username: 'root'
Type 'tutorial' for a tutorial or 'help' to see common examples
127.0.0.1:8529@_system>
Now, create a database named mydb with the following command:
127.0.0.1:8529@_system> db._createDatabase("mydb");
Next, create a database user with the following command:
127.0.0.1:8529@_system> var users = require("@arangodb/users");
127.0.0.1:8529@_system> users.save("myuser@localhost", "your-strong-password");
Output:
{
"user" : "myuser@localhost",
"active" : true,
"extra" : {
},
"code" : 201
}
Next, grant all the privileges to the mydb database with the following command:
127.0.0.1:8529@_system> users.grantDatabase("myuser@localhost", "mydb");
Now, exit from the ArangoDB shell with the following command:
127.0.0.1:8529@_system> exit
Step 4. Accessing ArangoDB Web Interface.
ArangoDB server comes with a built-in web interface for administration. It lets you manage databases, collections, documents, users, graphs, run and explain queries, see server stats, and much more. You can configure it by editing the file /etc/arangodb3/arangod.conf:
nano /etc/arangodb3/arangod.conf
Find the following line:
endpoint = tcp://127.0.0.1:8529
And replace it with the following line:
endpoint = tcp://your-server-ip-address:8529
Restart ArangoDB service after making this change:
sudo systemctl restart arangodb3
Now open your web browser and go to http://your-server-ip-address:8529 and you will see the following:
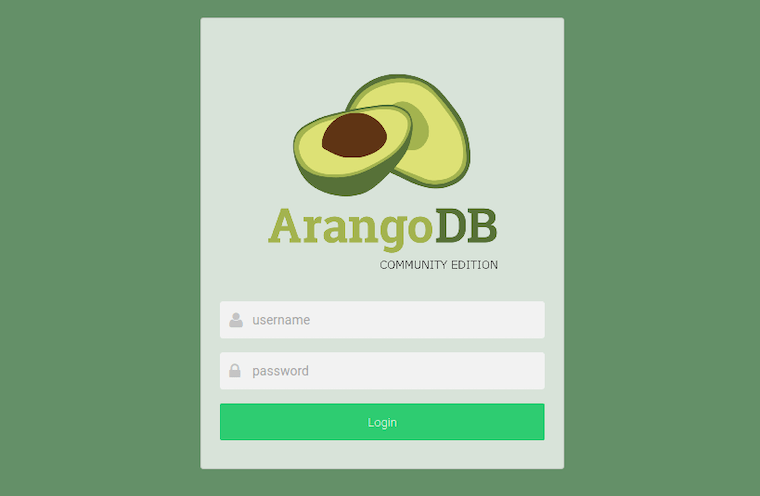
Congratulations! You have successfully installed ArangoDB. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing ArangoDB on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Focal Fossa system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official ArangoDB website.