How To Install BalenaEtcher on Debian 13

BalenaEtcher stands as one of the most reliable and user-friendly tools for creating bootable USB drives and SD cards from disk images. This comprehensive guide walks you through multiple installation methods for BalenaEtcher on Debian 13, ensuring you can flash operating system images safely and efficiently on the latest Debian testing distribution.
Whether you’re a system administrator preparing installation media, a developer working with embedded systems, or a Linux enthusiast exploring different operating systems, this tutorial provides step-by-step instructions for successful BalenaEtcher installation and configuration.
What is BalenaEtcher?
BalenaEtcher is an open-source, cross-platform application designed specifically for flashing OS images to removable media devices. Developed by Balena, this powerful tool simplifies the process of creating bootable drives through an intuitive three-step interface that eliminates common pitfalls associated with disk imaging.
The application excels in several key areas that make it the preferred choice for disk imaging on Linux. BalenaEtcher automatically validates drives before and after flashing, preventing corrupted installations and data loss. Its elegant user interface presents a streamlined workflow: select your image file, choose your target device, and initiate the flash process.
BalenaEtcher supports multiple image formats including ISO, IMG, ZIP, and various compressed archives. The software runs natively on Windows, macOS, and Linux distributions, making it an excellent choice for cross-platform environments. Additionally, BalenaEtcher includes built-in safety features that prevent accidentally overwriting your system drive by hiding mounted partitions from the target selection menu.
Common use cases include creating bootable installation media for Linux distributions, preparing recovery drives for system maintenance, flashing firmware to embedded devices, and duplicating disk images across multiple devices. The tool’s reliability and ease of use have made it a standard choice in educational institutions, development environments, and professional IT settings.
System Requirements and Prerequisites
Before proceeding with BalenaEtcher installation on Debian 13, ensure your system meets the necessary requirements. Your system should feature a 64-bit processor architecture as BalenaEtcher primarily supports x86_64 systems. While the application can run on systems with 4GB RAM, 8GB or more is recommended for optimal performance, especially when working with large image files.
Sufficient storage space is essential for both the application installation and temporary files during the flashing process. Plan for at least 500MB of free disk space, though more may be required depending on your chosen installation method. Your Debian 13 system should have administrator privileges (sudo access) for installation procedures and system modifications.
An active internet connection is necessary for downloading BalenaEtcher packages and any required dependencies. The installation process may need to fetch additional libraries or updates from Debian repositories.
BalenaEtcher compatibility extends to various image formats, making it versatile for different use cases. The application handles ISO files from Linux distributions, IMG files from Raspberry Pi and other embedded systems, and compressed archives containing disk images. Ensure your target USB drives or SD cards are compatible with your system’s USB ports and have sufficient capacity for your intended disk images.
Pre-Installation Preparation
Proper preparation ensures a smooth BalenaEtcher installation process on your Debian 13 system. Begin by updating your package repositories and installed software to the latest versions available in the testing branch.
Execute the following commands to refresh your system:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -yThis command combination updates the package list and upgrades all installed packages to their newest versions. The process may take several minutes depending on the number of available updates and your internet connection speed.
Verify your system architecture to ensure compatibility with BalenaEtcher packages:
uname -mThe output should display x86_64 for 64-bit systems. If you see different output, you may need to seek alternative installation methods or verify your system’s compatibility.
Install essential development tools and dependencies that may be required during the installation process:
sudo apt install curl wget gnupg2 software-properties-common apt-transport-httpsThese packages provide secure download capabilities, GPG verification tools, and advanced package management features that ensure safe and reliable software installation.
Create a system backup or at least document your current system state before proceeding. While BalenaEtcher installation is generally safe, maintaining good backup practices protects against unexpected issues. Consider creating a system snapshot if you’re using virtual machines or backup your important configuration files.
Method 1: Installing BalenaEtcher via AppImage
The AppImage installation method offers the most straightforward approach for running BalenaEtcher on Debian 13. This portable application format requires no system modifications and provides access to the latest software versions directly from the developers.
Downloading the AppImage
Navigate to the official BalenaEtcher website or GitHub releases page to obtain the latest AppImage package. The AppImage download process can be completed through your web browser or command line tools for automated installations.
Using the command line provides better control and verification options:
cd ~/Downloads
wget https://github.com/balena-io/etcher/releases/download/v2.0.0/balenaEtcher-2.0.0-x64.AppImageThis command downloads the latest BalenaEtcher AppImage to your Downloads directory. The version number in the filename may vary depending on the current release. Verify the download integrity by checking the file size and comparing it with the information provided on the GitHub releases page.
For users preferring graphical downloads, visit the BalenaEtcher website and click the download link for Linux. The site automatically detects your operating system and provides the appropriate AppImage file.
Check the downloaded file to ensure it completed successfully:
ls -lh ~/Downloads/balenaEtcher*.AppImageThe output should display the file with its size, typically around 100-150MB for recent versions.
Making the AppImage Executable
AppImage files require executable permissions before they can be launched. Debian systems typically download files with read-only permissions for security purposes, necessitating manual permission modification.
Set the executable permission using the chmod command:
chmod +x ~/Downloads/balenaEtcher*.AppImageThis command grants execute permissions to the AppImage file, allowing it to run as a standalone application. The asterisk wildcard ensures the command works regardless of the specific version number in the filename.
Alternative GUI method for setting permissions involves right-clicking the AppImage file in your file manager, selecting “Properties” or “Permissions,” and checking the “Execute” or “Allow executing file as program” option. Different desktop environments may present slightly different interface options.
Verify the executable status by examining the file permissions:
ls -l ~/Downloads/balenaEtcher*.AppImageThe output should begin with -rwxr-xr-x or similar, indicating executable permissions are set correctly.
Running BalenaEtcher AppImage
Launch BalenaEtcher directly from the command line or file manager. The AppImage execution process is straightforward and doesn’t require installation to system directories.
Command line execution:
cd ~/Downloads
./balenaEtcher*.AppImageThe application should start immediately, presenting the familiar three-step BalenaEtcher interface. If you encounter permission errors, verify that you’ve set the executable bit correctly and that your system supports FUSE (Filesystem in Userspace), which AppImages require.
Creating desktop shortcuts enhances accessibility for frequent use. Most desktop environments allow you to create launchers by right-clicking on the desktop and selecting “Create Launcher” or similar options. Point the launcher to the full path of your AppImage file.
For system-wide accessibility, consider moving the AppImage to a standard location:
sudo mv ~/Downloads/balenaEtcher*.AppImage /opt/balenaetcher.AppImage
sudo ln -s /opt/balenaetcher.AppImage /usr/local/bin/balenaetcherThis approach places the AppImage in the /opt directory and creates a symbolic link in /usr/local/bin, allowing all users to run BalenaEtcher by typing balenaetcher in any terminal.
Advantages and Considerations
The AppImage installation method offers several significant benefits for Debian 13 users. Primary advantages include access to the latest software versions without waiting for package maintainers, no system modifications that could affect stability, and easy removal by simply deleting the AppImage file.
AppImages are completely self-contained, including all necessary dependencies within the package. This characteristic eliminates compatibility issues with system libraries and ensures consistent behavior across different Linux distributions and versions.
Portability represents another key advantage – you can copy the AppImage to external storage and run BalenaEtcher on any compatible Linux system without installation. This feature proves valuable for system administrators working across multiple machines or users who frequently switch between different systems.
However, AppImage limitations include manual update management and larger file sizes compared to traditional packages. AppImages don’t integrate automatically with system update mechanisms, requiring users to monitor for new releases and download updates manually. The self-contained nature also means multiple AppImage applications may duplicate common libraries, consuming additional disk space.
Method 2: Installing via Repository (Deprecated Warning)
Historical Repository Method
Previously, BalenaEtcher provided an official APT repository for Debian-based systems, offering convenient installation and automatic updates through the standard package management system. This method involved adding the Balena repository to your system’s source list and installing the package using familiar apt commands.
The historical installation process followed these steps:
# WARNING: This method is no longer supported
curl -1sLf 'https://dl.cloudsmith.io/public/balena/etcher/setup.deb.sh' | sudo -E bash
sudo apt update
sudo apt install balena-etcher-electronThis approach provided seamless integration with Debian’s package management system, allowing BalenaEtcher to receive updates alongside other system packages. Users appreciated the automatic dependency resolution and the ability to remove the software cleanly using standard package management commands.
The repository installation offered several benefits including automatic security updates, integration with system package managers, and standardized installation locations that followed Debian packaging guidelines. System administrators particularly valued this method for its consistency with other enterprise software deployment practices.
Current Status and Alternatives
The official BalenaEtcher repository has been deprecated and is no longer maintained by the development team. This change reflects broader industry trends toward universal package formats like AppImage, Snap, and Flatpak that provide better cross-distribution compatibility and simplified maintenance.
Attempting to use the legacy repository installation will result in package not found errors or outdated versions that may contain security vulnerabilities. The Balena team has discontinued repository maintenance to focus resources on developing universal installation methods that serve a broader user base.
For users with existing repository installations, migration to alternative installation methods is strongly recommended:
# Remove deprecated repository installation
sudo apt remove balena-etcher-electron
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/balena-etcher.list
sudo apt updateThese commands remove the old package installation and clean up repository configuration files that are no longer needed. After removal, proceed with either the AppImage or DEB package installation methods described in this guide.
Alternative installation approaches focus on the AppImage method for most users due to its simplicity and reliability. The DEB package method provides system integration benefits while maintaining compatibility with Debian 13’s package management principles.
Method 3: Installing via DEB Package
The DEB package installation method provides excellent system integration while maintaining compatibility with Debian’s package management infrastructure. This approach offers automatic dependency resolution and proper integration with desktop environments and system services.
Downloading the DEB Package
BalenaEtcher DEB packages are available directly from the GitHub releases page, ensuring you receive authentic software packages from the official development team. Navigate to the releases section to find the latest stable version compatible with Debian 13.
Download the appropriate DEB package using wget or your preferred download method:
cd ~/Downloads
wget https://github.com/balena-io/etcher/releases/download/v2.1.4/balena-etcher_2.1.4_amd64.debThe version number in the URL will change with each release, so verify you’re downloading the most recent stable version. The amd64 designation indicates compatibility with 64-bit Intel and AMD processors, which covers most modern desktop and laptop systems.
Verify the package integrity by checking the file size and comparing it with the information provided on the GitHub releases page. Legitimate DEB packages typically range from 80-120MB depending on the version and included dependencies.
Alternative download methods include using curl or downloading through your web browser. Browser downloads may be preferable for users less comfortable with command-line tools:
curl -L -o balena-etcher.deb https://github.com/balena-io/etcher/releases/download/v2.1.4/balena-etcher_2.1.4_amd64.debInstalling the DEB Package
DEB package installation can be accomplished through multiple methods, each offering different advantages for dependency management and error handling. The dpkg method provides direct package installation, while apt offers superior dependency resolution.
Install using dpkg:
sudo dpkg -i ~/Downloads/balena-etcher_*.debIf dependency issues arise during installation, resolve them using apt:
sudo apt-get install -fThe -f flag instructs apt to fix broken dependencies by installing missing packages from the Debian repositories. This command automatically resolves any library requirements that weren’t satisfied during the initial dpkg installation.
Alternative installation using apt handles dependencies automatically:
sudo apt install ~/Downloads/balena-etcher_*.debThis method leverages apt’s dependency resolution engine to automatically download and install any required libraries before installing BalenaEtcher. Most users will find this approach more reliable and less prone to dependency conflicts.
Verify successful installation by checking the package status:
dpkg -l | grep balena-etcherThe output should display package information confirming BalenaEtcher is properly installed and registered with the package management system.
Integration and System Registration
DEB package installation provides comprehensive system integration that AppImages cannot match. The package automatically registers BalenaEtcher with your desktop environment’s application menu, creates appropriate file associations, and establishes proper system service integration.
Application menu integration occurs automatically during installation, placing BalenaEtcher in the Graphics or System Tools category depending on your desktop environment. Users can launch the application through the graphical menu system without needing to remember command-line syntax or file locations.
Command-line access is also configured during installation:
balena-etcherThis command launches BalenaEtcher from any terminal session, providing flexibility for both graphical and command-line workflows. The system PATH is automatically updated to include BalenaEtcher’s executable location.
Desktop file registration enables proper integration with file managers and desktop environments. Right-clicking on compatible image files may present BalenaEtcher as an option for opening or flashing the file, streamlining the workflow for frequent users.
Advantages of DEB Installation
DEB package installation offers superior system integration compared to AppImage alternatives. The package management system tracks all installed files, making removal clean and complete when necessary. System administrators appreciate the consistent behavior with other enterprise software deployments.
Automatic dependency management ensures all required libraries are properly installed and maintained. The package system handles library updates automatically, reducing security risks and compatibility issues that might affect standalone AppImage installations.
Update mechanisms work through the standard apt upgrade process, though users should note that BalenaEtcher updates require manual download and installation of new DEB packages. The package doesn’t automatically receive updates through Debian repositories since it’s not part of the official distribution.
Integration with system security policies allows BalenaEtcher to work properly with AppArmor, SELinux, and other security frameworks that may restrict AppImage execution. Enterprise environments often prefer DEB installations for their predictable behavior and comprehensive audit trails.
Post-Installation Verification
Confirming successful BalenaEtcher installation requires testing both the application launch process and core functionality. Proper verification ensures your installation is complete and ready for production use.
Testing Installation Success
Launch BalenaEtcher through your desktop environment by accessing the application menu and locating BalenaEtcher in the Graphics or System Tools category. The application should start without error messages and display the familiar three-step interface.
Command-line verification provides additional confirmation:
balena-etcher --versionThis command should return version information confirming the installed release. If you receive “command not found” errors, verify your installation method and check that the executable is properly located in your system PATH.
GUI launch testing involves opening BalenaEtcher and confirming all interface elements load correctly. The application window should display three main sections: “Flash from file,” “Select target,” and the flash button. Any missing elements or error messages indicate installation problems requiring troubleshooting.
Interface responsiveness testing includes clicking various buttons and menu options to ensure the application responds properly to user input. Sluggish performance or unresponsive elements may indicate resource constraints or compatibility issues with your desktop environment.
Functional Testing
USB device recognition testing verifies BalenaEtcher can properly detect and interact with removable storage devices. Insert a USB flash drive or SD card and confirm it appears in the target selection interface. The device should be listed with appropriate size and identifier information.
Image file selection testing confirms BalenaEtcher supports your intended file formats. Navigate to the “Flash from file” section and browse for ISO, IMG, or compressed archive files. Supported formats should be selectable, while unsupported files should be filtered from the selection dialog.
Safety feature verification ensures BalenaEtcher properly protects your system drives from accidental overwriting. Connected hard drives and system partitions should be hidden from the target selection menu, displaying only removable media devices appropriate for flashing operations.
Process simulation using a small test image and expendable USB device confirms the complete flashing workflow functions correctly. Create or download a small ISO file (such as a Linux live distribution) and perform a complete flash operation to verify all stages complete successfully.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Permission-related problems often manifest as “access denied” errors when attempting to access USB devices. Add your user account to the appropriate system groups:
sudo usermod -a -G disk,dialout $USERLog out and back in for group membership changes to take effect. This grants necessary permissions for accessing removable storage devices without requiring root privileges for every operation.
Missing dependency issues may cause application crashes or feature limitations. Install common multimedia and system libraries:
sudo apt install libnss3 libatk-bridge2.0-0 libdrm2 libxss1 libgtk-3-0 libxrandr2 libasound2 libpangocairo-1.0-0 libatk1.0-0 libcairo-gobject2 libgtk-3-0 libgdk-pixbuf2.0-0These libraries support various BalenaEtcher features and ensure compatibility with different desktop environments and hardware configurations.
Display and graphics issues may require updating graphics drivers or adjusting application launch parameters. For systems with integrated graphics or older hardware, try launching BalenaEtcher with software rendering:
balena-etcher --disable-gpuThis parameter bypasses hardware acceleration that may cause compatibility problems on certain systems.
Using BalenaEtcher on Debian 13
BalenaEtcher operation follows a streamlined three-step process designed for simplicity and safety. Understanding each stage ensures successful disk imaging operations while minimizing risks to your data and hardware.
Basic Operation Workflow
Step 1: Flash from file begins your disk imaging operation by selecting the source image file. Click the “Flash from file” button to open a file browser dialog showing supported image formats including ISO, IMG, ZIP, and various compressed archives. Navigate to your desired image file and select it for flashing.
The application displays image file information including filename, size, and detected format after selection. Verify this information matches your expectations before proceeding to target selection. Large image files may take several seconds to analyze, particularly when working with compressed archives that require decompression calculations.
Step 2: Select target requires choosing your destination USB drive or SD card from the available removable media devices. BalenaEtcher automatically detects and displays compatible target devices while hiding system drives and mounted partitions to prevent accidental data loss.
Device information display includes storage capacity, device identifier, and manufacturer details when available. Double-check the selected device matches your intended target, as the flashing process will completely overwrite all existing data on the selected device.
Step 3: Flash process begins after clicking the prominent “Flash!” button in the interface. The operation proceeds through several phases including image preparation, data writing, and verification stages. Progress indicators show completion percentages and estimated time remaining for each phase.
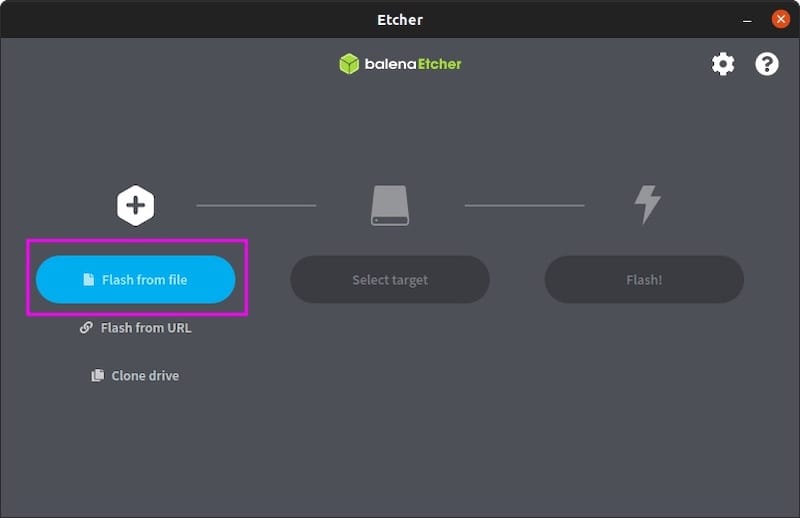
Monitor the flashing process carefully for any error messages or warnings. Modern BalenaEtcher versions include built-in verification that compares written data against the source image to ensure integrity. This verification stage may double the total operation time but provides crucial data integrity confirmation.
Advanced Features and Options
Flash from URL capability allows direct imaging from internet-hosted files without requiring local downloads. This feature proves valuable for frequently updated images or when working with limited local storage space. Enter the complete URL to an image file in the “Flash from URL” option to begin direct network flashing.
Clone drive functionality enables disk-to-disk copying operations for duplicating existing installations or creating backup images. Select an existing disk as the source and another device as the target to perform complete drive cloning including partition tables and boot sectors.
Validation settings control the verification process that ensures flashing accuracy. Users can enable or disable post-flash validation depending on time constraints and confidence levels. Disabling validation speeds up operations but sacrifices data integrity confirmation.
Multi-target flashing supports simultaneous operations across multiple devices when sufficient system resources are available. This advanced feature requires careful attention to device selection and adequate USB port power distribution to ensure successful concurrent operations.
Best Practices and Safety
Data backup importance cannot be overstated when working with disk imaging operations. Always backup important data from target devices before beginning flash operations, as the process completely erases existing content without possibility of recovery through BalenaEtcher.
Device identification verification prevents costly mistakes that could result in data loss or system corruption. Take time to carefully verify target device selection, particularly when working with multiple connected storage devices. Consider disconnecting unnecessary devices to reduce selection confusion.
Image file verification ensures source file integrity before beginning flash operations. Download images from official sources and verify checksums when provided by the distributor. Corrupted source images will result in non-functional target devices and wasted time.
Safe removal procedures protect both the target device and your system from data corruption or hardware damage. Always use proper eject or unmount procedures before physically disconnecting devices. BalenaEtcher typically provides clear completion notifications indicating when safe removal is permitted.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
BalenaEtcher troubleshooting requires systematic approaches to identify and resolve various installation and operational problems. Understanding common issues and their solutions enables quick problem resolution and successful disk imaging operations.
Installation Problems
Permission denied errors during installation typically indicate insufficient user privileges or incorrect sudo usage. Ensure your user account has sudo privileges and use the complete sudo command syntax:
sudo apt install ./balena-etcher_*.debIf permission errors persist, verify your user is a member of the sudo group:
groups $USERThe output should include “sudo” among the listed groups. If not, add your user to the sudo group:
sudo usermod -a -G sudo $USERDependency conflicts on Debian 13 may arise from testing branch package versions or conflicting software installations. Resolve dependency issues by updating package lists and attempting automatic fixes:
sudo apt update
sudo apt --fix-broken installThese commands refresh package databases and attempt automatic resolution of dependency conflicts that may prevent BalenaEtcher installation.
AppImage execution problems often relate to FUSE filesystem support or missing library dependencies. Install FUSE support if not already available:
sudo apt install fuseFor systems where FUSE installation isn’t possible or desired, extract and run AppImages using alternative methods:
./balenaEtcher*.AppImage --appimage-extract
./squashfs-root/AppRunDownload failures may result from network connectivity issues, repository problems, or DNS resolution failures. Test network connectivity and try alternative download methods or mirror servers when experiencing persistent download problems.
Runtime Issues
Application crashes during operation may indicate memory constraints, hardware compatibility problems, or corrupted installation files. Monitor system resource usage during BalenaEtcher operation and ensure adequate RAM is available for both the application and image processing operations.
Memory optimization for large image files involves closing unnecessary applications and enabling swap space if not already configured:
sudo fallocate -l 2G /swapfile
sudo chmod 600 /swapfile
sudo mkswap /swapfile
sudo swapon /swapfileThis creates a 2GB swap file providing additional virtual memory for demanding operations.
Device recognition problems prevent BalenaEtcher from detecting connected USB drives or SD cards. Verify devices are properly connected and functional:
lsblk
sudo fdisk -lThese commands display connected storage devices and their current status. Devices should appear in the output even if not mounted or accessible through file managers.
Flashing failures may result from write protection, hardware failures, or insufficient power delivery. Check target device write protection switches and try different USB ports or powered USB hubs for devices requiring additional power.
Debian 13 Specific Considerations
Testing branch stability affects BalenaEtcher compatibility as Debian 13 represents an active development version. Package versions and library dependencies may change frequently, potentially causing compatibility issues not present in stable releases.
Library version requirements may conflict with rapidly changing packages in the testing branch. Monitor BalenaEtcher GitHub issues for Debian 13 specific problems and potential workarounds:
sudo apt list --installed | grep -E "(gtk|electron|nss)"This command displays versions of common libraries that may affect BalenaEtcher operation.
Alternative solutions for persistent compatibility problems include using different disk imaging tools or running BalenaEtcher in containers:
# Alternative: dd command for experienced users
sudo dd if=image.iso of=/dev/sdX bs=4M status=progress
# Alternative: GNOME Disks (Disk Utility)
sudo apt install gnome-disk-utilityCommunity support resources provide valuable assistance for Debian 13 specific issues. Monitor the BalenaEtcher GitHub repository, Debian testing forums, and Linux community resources for updates and workarounds related to testing branch compatibility.
Security and Best Practices
BalenaEtcher security considerations encompass both software authenticity verification and safe operational practices. Implementing proper security measures protects your system from malicious software and prevents data loss during disk imaging operations.
Security Considerations
Source verification ensures you download authentic BalenaEtcher packages from official sources only. Always obtain software directly from the BalenaEtcher website, GitHub releases page, or verified Debian repositories. Avoid third-party download sites that may distribute modified or malicious versions.
GPG signature verification provides cryptographic confirmation of package authenticity when available. Check for GPG signatures on downloaded packages and verify them using official public keys:
# Example verification process (when signatures are available)
gpg --verify balena-etcher_*.deb.sig balena-etcher_*.debAppImage security advantages include sandboxing benefits that limit application access to system resources. AppImages run in isolated environments with restricted file system access, reducing potential security risks compared to traditional package installations.
System impact assessment involves understanding what changes each installation method makes to your system. DEB packages modify system directories and may add services or background processes, while AppImages remain completely self-contained with minimal system interaction.
Maintenance and Updates
Keeping BalenaEtcher updated requires different approaches depending on your chosen installation method. AppImage users must manually monitor for new releases and download updated versions, while DEB package users need to download new packages when available.
Update monitoring strategies include subscribing to BalenaEtcher GitHub releases notifications or checking the project website periodically for version announcements. Security-conscious users should prioritize prompt updates that address vulnerabilities or compatibility issues.
Security patch awareness involves staying informed about discovered vulnerabilities and their remediation status. Monitor security advisories from both the BalenaEtcher project and Debian security team for relevant security information.
Backup and recovery preparation protects against installation problems or system changes. Document your current BalenaEtcher configuration and create recovery points before major updates or system modifications that might affect application functionality.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed BalenaEtcher. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the latest version of BalenaEtcher on Debian 13 “Trixie”. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official BalenaEtcher website.