How To Install BalenaEtcher on Fedora 42

Creating bootable USB drives is an essential skill for Linux enthusiasts and system administrators. Whether you’re installing a fresh copy of Fedora, testing a new distribution, or creating recovery media, having a reliable tool makes all the difference. BalenaEtcher stands out as one of the most user-friendly and efficient solutions for this task, especially on Fedora 42. This comprehensive guide walks you through various methods to install and use BalenaEtcher on Fedora 42, ensuring you can create perfect bootable USB drives every time.
What is BalenaEtcher?
BalenaEtcher (formerly known as just Etcher) is an open-source utility designed to flash OS images to SD cards and USB drives safely and efficiently. Unlike many alternatives, BalenaEtcher provides a clean, intuitive interface that simplifies the process down to three steps: select image, select drive, and flash. The application supports a wide variety of image formats including .iso, .img, .dmg, and compressed files like .zip, .gz, and .xz.
What sets BalenaEtcher apart from other tools is its validation process. After writing the image to your USB drive, it automatically verifies that the data was written correctly, reducing the chances of corrupt installation media. This feature alone saves countless hours of troubleshooting failed installations. Additionally, BalenaEtcher is cross-platform, running on Linux, macOS, and Windows, making it a versatile choice for mixed-environment workflows.
Developed by Balena (formerly resin.io), this tool has gained popularity due to its focus on simplicity while maintaining powerful functionality. For Fedora users specifically, BalenaEtcher offers native compatibility and excellent performance on the platform.
Prerequisites for Installation
Before diving into the installation process, ensure your system meets the necessary requirements. BalenaEtcher isn’t particularly resource-intensive, but checking these prerequisites will help avoid common issues:
- Fedora 42 with up-to-date packages
- Administrator (sudo) privileges on your system
- At least 200MB of free disk space
- Active internet connection for downloading packages
- Basic familiarity with terminal commands
- A USB drive (4GB or larger) for later usage
It’s always a good practice to back up any important data on your system before installing new software, especially when adding third-party repositories. While BalenaEtcher installation is generally safe, following this precaution provides peace of mind.
If you’re planning to use BalenaEtcher to create bootable media, ensure you have your target ISO file downloaded and verified before proceeding with the installation.
Preparing Your Fedora 42 System
Before installing BalenaEtcher, update your Fedora 42 system to ensure all dependencies are current. Open your terminal and run:
sudo dnf update -yThis command refreshes your package lists and installs available updates. The `-y` flag automatically confirms the update process without requiring additional input.
Next, check if you have the necessary dependencies installed. BalenaEtcher requires packages like libXScrnSaver. Most Fedora installations have these dependencies preinstalled, but it’s worth verifying:
sudo dnf install libXScrnSaver -yEnsure your internet connection is stable, as you’ll need to download packages during installation. You can test your connection with:
ping -c 4 google.comIf you receive responses, your connection is working correctly. With these preparations complete, you’re ready to begin installing BalenaEtcher using one of the following methods.
Method 1: Installing via Official Repository
Using the official repository is the recommended approach for installing BalenaEtcher on Fedora 42. This method ensures you receive automatic updates and proper integration with your system. Follow these detailed steps:
First, ensure you have curl installed, which is needed to download the repository setup script:
sudo dnf install curl -yNext, download and run the official Balena repository setup script:
curl -1sLf 'https://dl.cloudsmith.io/public/balena/etcher/setup.rpm.sh' | sudo -E bashThis script adds the Balena repository to your system’s package sources. The command uses curl to download the script and pipes it directly to bash for execution with administrator privileges.
After adding the repository, update your package lists:
sudo dnf updateNow, install BalenaEtcher using DNF:
sudo dnf install balena-etcherDuring installation, DNF will resolve and install all necessary dependencies automatically. When prompted, type ‘y’ and press Enter to confirm the installation.
To verify that BalenaEtcher was installed correctly, run:
balena-etcher --versionThis should display the version number of the installed application. The repository method offers several advantages, including streamlined updates through your system’s package manager and proper integration with Fedora’s desktop environment.
Method 2: Manual RPM Installation
If you prefer not to add an external repository to your system or encounter issues with the repository method, manually installing the RPM package is a viable alternative:
First, visit the official BalenaEtcher GitHub releases page (https://github.com/balena-io/etcher/releases) to download the latest version for Fedora/RedHat. Look for files ending with `.x86_64.rpm` for 64-bit systems.
Next, open your terminal and navigate to the directory where you downloaded the RPM file:
cd ~/DownloadsVerify the integrity of the downloaded file (replace filename with your actual downloaded file):
sha256sum balena-etcher-1.x.x.x86_64.rpmCompare the output with the checksum provided on the download page to ensure the file wasn’t corrupted during download.
Install the package using DNF, which handles dependencies better than the rpm command:
sudo dnf install ./balena-etcher-1.x.x.x86_64.rpmDNF will automatically attempt to resolve and install any required dependencies. If dependency issues occur, you can try:
sudo dnf install libXScrnSaver libappindicator libnotifyThe manual installation method gives you control over exactly which version you install and doesn’t require adding external repositories to your system. However, you’ll need to manually download and install new versions when updates are released.
Method 3: Flatpak Installation
Fedora has excellent support for Flatpak, which offers another way to install BalenaEtcher with good isolation from your system. This method works particularly well if you prefer containerized applications:
First, ensure Flatpak is installed and configured on your system:
sudo dnf install flatpak -y
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoNext, install BalenaEtcher via Flatpak:
flatpak install flathub io.balena.EtcherConfirm the installation when prompted. Flatpak will download and install BalenaEtcher and all its dependencies in an isolated environment.
To run BalenaEtcher installed through Flatpak:
flatpak run io.balena.EtcherThe Flatpak method offers advantages like isolation from your system, which can prevent conflicts with other software. However, Flatpak applications may sometimes have limited access to system resources unless properly configured, and the initial download might be larger due to the contained dependencies.
Launching and First-time Setup
After installing BalenaEtcher, you can launch it in several ways depending on how you installed it:
- From the application menu: Look for “balenaEtcher” or simply “Etcher” in your application launcher
- From the terminal:
- Repository or RPM installation:
balena-etcher - Flatpak installation:
flatpak run io.balena.Etcher
- Repository or RPM installation:
When you first launch BalenaEtcher, you might be prompted to allow administrative access since writing to USB drives requires elevated permissions. This is normal and necessary for the application to function correctly.
The interface is intentionally minimal, displaying a three-step process:
- Select Image
- Select Target
- Flash!
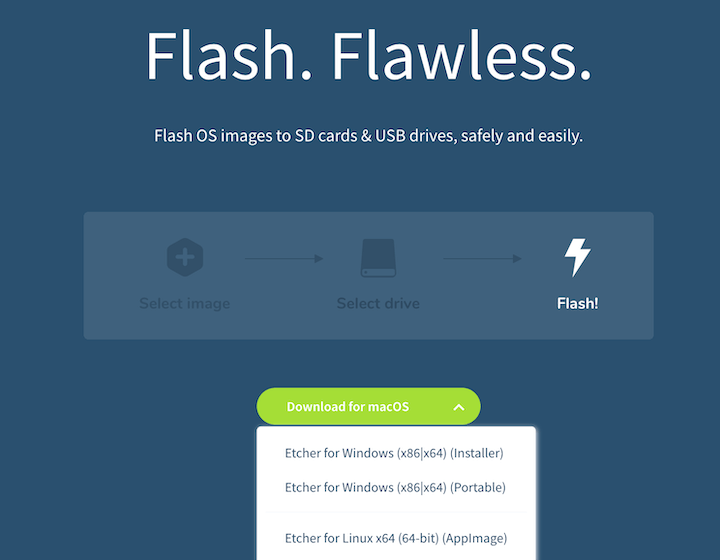
No additional setup is typically required, as BalenaEtcher is designed to work out of the box. The application will remember your preferences and settings between sessions, such as whether you want to automatically unmount drives.
If you want to customize the application behavior, click the gear icon in the top-right corner to access settings like automatic updates, drive validation, and interface options.
Creating Your First Bootable USB Drive
Now that BalenaEtcher is installed, let’s create a bootable USB drive. This section walks through the entire process with detailed explanations:
- Prepare Your USB Drive: Insert your USB drive into your computer. Note that BalenaEtcher will erase all data on the selected drive, so back up any important files beforehand.
- Launch BalenaEtcher: Open the application using your preferred method as described in the previous section.
- Select Image: Click on the “Flash from file” button to choose your OS image. Navigate to where you’ve stored your ISO file (e.g., Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-42.iso) and select it. BalenaEtcher supports various formats including .iso, .img, .dmg, and compressed archives.
- Select Target: Click “Select target” and choose your USB drive from the list. BalenaEtcher tries to identify and show only removable storage devices to prevent accidental overwrites of your system drives. Double-check that you’ve selected the correct drive, as this process will erase all data on it.
- Flash: Click the “Flash!” button to begin the process. You’ll be prompted to enter your administrator password since writing to drives requires elevated privileges.
- Wait for Completion: The flashing process typically takes 5-15 minutes depending on the image size and your USB drive speed. BalenaEtcher displays a progress bar with estimated time remaining.
- Verification: After writing the image, BalenaEtcher automatically verifies the data to ensure it was written correctly. This step helps prevent boot failures caused by corrupted data and can take almost as long as the flashing process itself.
- Completion: Once verification is complete, BalenaEtcher will notify you that the process has finished successfully. Your USB drive will be automatically unmounted and is ready to use.
If you encounter any errors during this process, the application provides specific error messages to help troubleshoot the issue. Common problems include insufficient permissions, write-protected USB drives, or connectivity issues with the drive.
Advanced Features of BalenaEtcher
Beyond basic USB flashing, BalenaEtcher offers several advanced features that power users will appreciate:
Multi-Drive Flashing: One of BalenaEtcher’s standout features is the ability to write the same image to multiple USB drives simultaneously. This is invaluable when preparing installation media for multiple systems or creating backup drives. Simply select multiple targets in the drive selection screen to enable this feature.
Command-Line Interface: For automation and scripting, BalenaEtcher provides a command-line interface. This is particularly useful for system administrators who need to create multiple drives regularly. The basic syntax is:
balena-etcher-cli [options] <image>Flash from URL: Instead of downloading an image separately, you can directly flash from a URL. Click on “Flash from URL” instead of “Flash from file” and enter the direct download link to the image. BalenaEtcher will download and flash in one operation.
Validation Settings: By default, BalenaEtcher validates all written data, but you can disable this feature to speed up the process if you’re confident in your hardware’s reliability. This option is available in the settings menu.
Portable Mode: Although not officially supported on Linux, you can run BalenaEtcher from a directory without installing it system-wide by extracting the AppImage version (available from the official website) to a location of your choice.
These advanced features make BalenaEtcher a versatile tool for both casual users and professionals working with Linux systems.
Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
Even with straightforward installation procedures, issues can sometimes arise. Here are solutions to common problems you might encounter when installing BalenaEtcher on Fedora 42:
Repository Connection Problems: If you receive errors about connecting to the Balena repository, check your internet connection and try again. If problems persist, temporarily switch to a different DNS server:
echo "nameserver 8.8.8.8" | sudo tee /etc/resolv.conf > /dev/nullDependency Conflicts: Sometimes dependency conflicts occur, especially if you have other applications that use different versions of shared libraries. Try installing with the --allowerasing flag:
sudo dnf install balena-etcher --allowerasingPermission Errors: If you see “EACCES: permission denied” errors during installation, ensure you’re using sudo for commands that require administrative privileges. If the error occurs even with sudo, check file permissions in your home directory:
ls -la ~ | grep .configApplication Not Launching: If BalenaEtcher doesn’t start after installation, try launching it from the terminal to see any error messages:
balena-etcherLook for specific error messages that might indicate missing dependencies or configuration issues.
Desktop Integration Issues: If BalenaEtcher doesn’t appear in your application menu or shows with a generic icon, refresh the desktop database:
sudo update-desktop-databaseResource Usage Concerns: BalenaEtcher uses Electron, which can be memory-intensive. If your system has limited resources, close other applications before running BalenaEtcher to ensure it has sufficient memory available.
Troubleshooting Common Usage Issues
After successfully installing BalenaEtcher, you might encounter issues during actual usage. Here are solutions to common problems:
Drive Not Detected: If BalenaEtcher doesn’t show your USB drive, try:
- Unplugging and reconnecting the drive
- Checking if the drive appears in Fedora’s Disks utility
- Using a different USB port (preferably a direct connection rather than through a hub)
- Formatting the drive with GParted before attempting to use it with BalenaEtcher
Image Validation Failures: If your downloaded image fails validation:
- Verify the checksum of your downloaded file matches the one provided by the source
- Re-download the image file, preferably using a download manager that can verify integrity
- Check your storage device for errors
Flash Verification Errors: If flashing completes but verification fails:
- Try a different USB drive, as the current one might have bad sectors
- Use a slower writing speed (available in settings)
- Disable verification temporarily to see if the drive still works (though this isn’t recommended for critical applications)
Performance Issues: If flashing is extremely slow:
- Check if your USB drive supports the expected speed class
- Use a USB 3.0+ port with a compatible drive for faster transfers
- Close resource-intensive applications while running BalenaEtcher
- Try updating your USB drivers and controller firmware
Interrupted Flashing Recovery: If the flashing process is interrupted:
- The USB drive will likely be corrupted and need reformatting
- Use GParted to create a new partition table on the drive
- Format the drive with a filesystem like FAT32
- Restart the flashing process from the beginning
Updating BalenaEtcher on Fedora 42
Keeping BalenaEtcher updated ensures you have the latest features and security patches. The update process depends on how you installed the application:
Repository Method Updates: If you installed BalenaEtcher through the official repository, updating is straightforward:
sudo dnf update balena-etcherRunning this command will check for updates and install them if available. You can also update all your system packages including BalenaEtcher with:
sudo dnf updateManual RPM Updates: If you installed via the manual RPM method, you’ll need to:
- Download the latest RPM from the official GitHub releases page
- Install it using the same process as your initial installation:
sudo dnf install ./balena-etcher-new-version.x86_64.rpmThe new version will replace the old one, preserving your settings.
Flatpak Updates: For Flatpak installations, update with:
flatpak update io.balena.EtcherOr update all Flatpak applications including BalenaEtcher:
flatpak updateIt’s generally recommended to update BalenaEtcher whenever a new version is released, particularly for security updates. The application itself may notify you of available updates in its interface.
Removing BalenaEtcher
If you need to uninstall BalenaEtcher from your Fedora 42 system, the process varies depending on your installation method:
Repository Installation Removal:
sudo dnf remove balena-etcherTo also remove the repository configuration:
sudo rm /etc/yum.repos.d/balena-etcher.repoManual RPM Installation Removal:
sudo dnf remove balena-etcherFlatpak Installation Removal:
flatpak uninstall io.balena.EtcherTo remove unused Flatpak dependencies after uninstallation:
flatpak uninstall --unusedAfter uninstallation, you might want to check for and remove any configuration files left in your home directory:
rm -rf ~/.config/balena-etcherIf you plan to reinstall the application later, consider keeping the configuration files to preserve your settings.
Security Considerations
When using BalenaEtcher, especially on a system like Fedora 42 that emphasizes security, keep these important considerations in mind:
- Application Permissions: BalenaEtcher requires administrator privileges to write directly to block devices. This is necessary for its functionality but means the application has significant system access. Always download BalenaEtcher from official sources to mitigate risks.
- Image File Safety: Only download OS images from trusted sources like official project websites. Verify checksums before flashing to ensure the integrity of downloaded files. Malicious images can compromise your system when booted.
- USB Drive Security: After creating bootable media, be careful about inserting it into untrusted systems. USB drives can be vectors for malware transmission between computers. Consider using dedicated drives for system installation purposes.
- Repository Trust: When adding third-party repositories like Balena’s, you’re trusting that source to provide secure software. The official Balena repository is generally trustworthy, but always be cautious with external package sources.
- Data Protection: Remember that BalenaEtcher completely erases target drives. Always verify you’ve selected the correct device before flashing to avoid data loss. The application tries to identify and hide system drives, but double-checking is essential.
Following these practices will help maintain your system’s security while using BalenaEtcher on Fedora 42.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed BalenaEtcher. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the BalenaEtcher on Fedora 42 Linux system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official BalenaEtcher website.