How To Install Btop on openSUSE

System monitoring has evolved dramatically from the basic command-line tools of the past. While traditional utilities like top served their purpose, modern Linux administrators need more sophisticated monitoring solutions that provide better visualization and interactive capabilities. Enter btop—a revolutionary terminal-based resource monitor that transforms how we observe system performance.
Btop represents a significant advancement in system monitoring technology. Unlike its predecessors, this modern tool offers an aesthetically pleasing interface with real-time graphs, mouse support, and comprehensive system metrics all displayed in a single, unified view. For openSUSE users seeking an enhanced monitoring experience, btop delivers unparalleled functionality while maintaining the efficiency that command-line tools are known for.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through every aspect of installing btop on openSUSE systems. Whether you’re running openSUSE Tumbleweed, Leap, or any other variant, you’ll discover multiple installation methods, configuration options, and troubleshooting techniques to ensure a successful setup.
Understanding Btop: Features and Capabilities
Modern Interface Design
Btop revolutionizes system monitoring with its thoughtful approach to information presentation. The tool features elegant graphs, charts, and visual meters with smooth animations that make system monitoring genuinely enjoyable. Unlike traditional monitoring tools that prioritize raw data over user experience, btop creates a “modern, aesthetically pleasing design with thoughtful information hierarchy”.
The interface supports beautiful themes and customization options, allowing users to personalize their monitoring environment. This visual appeal doesn’t come at the expense of functionality—btop maintains comprehensive system information while making it more accessible through superior design.
Comprehensive Monitoring Capabilities
Btop excels at real-time system monitoring across multiple subsystems. The tool provides detailed information about CPU usage, memory consumption, disk activity, and network statistics, all displayed in an integrated view with graphical representations. This comprehensive approach ensures administrators can quickly identify performance bottlenecks and system issues.
The tool offers “good all-around monitoring with visual context” that displays “CPU, memory, network, and disk information in an integrated view with graphical representations that make patterns immediately apparent”. This visual context proves invaluable during troubleshooting sessions where quick pattern recognition can save significant time.
Interactive Process Management
Beyond passive monitoring, btop provides robust process management capabilities. Users can interact with running processes through both keyboard shortcuts and mouse controls, making it easy to send signals, adjust priorities, and filter process lists. This interactive approach bridges the gap between monitoring and system administration tasks.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Supported openSUSE Versions
Btop supports various openSUSE distributions with different installation methods available depending on your specific version. The tool is “available in the main repository of openSUSE Tumbleweed but not the other variants of openSUSE”. However, community repositories provide access for all openSUSE variants.
System Requirements
Before installing btop, ensure your openSUSE system meets the basic hardware requirements. For openSUSE installations, “a minimum of 1024 MB of memory is required for a minimal installation”. While btop itself has minimal resource requirements, having adequate system resources ensures smooth operation during intensive monitoring sessions.
Your system should have network connectivity for accessing package repositories. Additionally, you’ll need either root access or sudo privileges to install packages through zypper or add new repositories to your system.
Checking System Version
Verify your openSUSE version before proceeding with installation. Run the following command in your terminal:
cat /etc/os-releaseThis command displays your distribution information, helping you choose the appropriate installation method for your specific openSUSE variant.
Installation Methods for openSUSE
Method 1: Standard Repository Installation (Tumbleweed)
For openSUSE Tumbleweed users, btop installation is straightforward since the package exists in the main repository. This method provides the most seamless installation experience with automatic dependency resolution and system integration.
Open your terminal and execute the following command:
sudo zypper install btopThis command automatically downloads and installs btop along with any required dependencies. The package manager handles all aspects of the installation process, ensuring proper integration with your system.
Method 2: Using OPI for Other openSUSE Variants
For openSUSE Leap and other variants, the Open Package Index (OPI) provides access to btop through community repositories. This method simplifies the process of finding and installing packages from various openSUSE repositories.
First, ensure OPI is installed on your system. If not, install it using:
sudo zypper install opiThen install btop through OPI:
sudo opi btopOPI automatically searches available repositories and presents installation options for btop, making the process user-friendly even for less experienced users.
Method 3: Backports Repository Installation
OpenSUSE Backports repositories provide access to newer software versions for stable releases. This method is particularly useful for openSUSE Leap users who want access to recent btop versions.
For openSUSE systems requiring backports, you can add the appropriate repository and install btop. The process varies depending on your specific system configuration:
For step installations, run the following as root:
zypper addrepo https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/openSUSE:Backports:SLE-15-SP4/step/openSUSE:Backports:SLE-15-SP4.repo
zypper refresh
zypper install btopFor standard installations, execute:
zypper addrepo https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/openSUSE:Backports:SLE-15-SP4/standard/openSUSE:Backports:SLE-15-SP4.repo
zypper refresh
zypper install btopMethod 4: Factory Repository Installation
The Factory repository contains the latest development versions of packages. While this provides access to cutting-edge features, use this method only if you need specific functionality not available in stable releases.
Add the Factory repository and install btop:
zypper addrepo https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/openSUSE:Factory/standard/openSUSE:Factory.repo
zypper refresh
zypper install btopMethod 5: Building from Source
For users requiring the absolute latest version or custom compilation options, building from source provides maximum flexibility. This method requires development tools and takes more time but offers complete control over the installation.
First, install development dependencies:
sudo zypper install git gcc-c++ makeThen clone and build btop:
git clone https://github.com/aristocratos/btop.git
cd btop
make
sudo make installStep-by-Step Installation Walkthrough
Preparation Phase
Begin by updating your system packages to ensure compatibility and access to the latest repository information:
sudo zypper refresh
sudo zypper updateThis preparation step prevents potential conflicts and ensures your package manager has current repository metadata.
Choosing Your Installation Method
Select the installation method based on your openSUSE variant and requirements:
- Tumbleweed users: Use the standard repository method for simplicity and automatic updates
- Leap users: Choose between OPI or backports repositories depending on your preference for community support versus official repositories
- Enterprise users: Consider backports repositories for tested packages in enterprise environments
- Developers: Source compilation provides access to latest features and customization options
Execution and Verification
After choosing your method, execute the installation commands and verify success. Regardless of your chosen method, test the installation by running:
btop --versionThis command confirms btop is properly installed and accessible from your system PATH.
First Launch and Basic Usage
Starting Btop
Launch btop by simply typing the command in your terminal:
btopUpon starting, you’ll encounter “a clean, tabbed interface divided into sections for CPU, memory, disks, networks, and processes”. The interface immediately displays real-time system information with visual graphs and metrics.
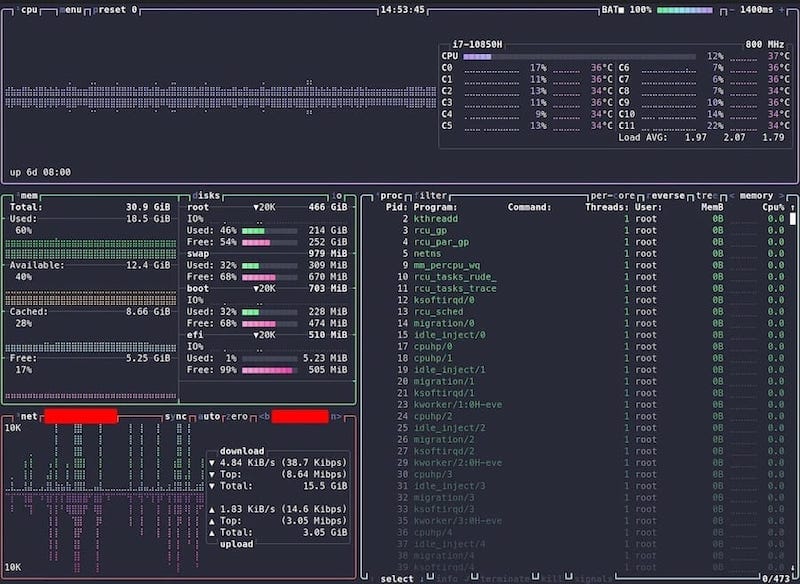
Understanding the Interface
The btop interface consists of four main sections arranged in a logical layout. The CPU section shows processor usage with individual core monitoring. Memory statistics display both RAM and swap usage with visual indicators. Network and disk sections provide I/O statistics with historical graphs.
Basic Navigation
Navigation in btop uses intuitive controls. Arrow keys move between different sections and processes. Mouse support allows clicking on various interface elements for interaction. The interface responds smoothly to both keyboard and mouse input, providing flexibility in how you interact with the tool.
Essential Keyboard Shortcuts
Key shortcuts enhance productivity when using btop:
Escorq: Opens the exit menu instead of immediately quitting- Arrow keys: Navigate between sections and processes
Tab: Cycle through different interface panelsSpace: Pause/resume real-time updates+and-: Adjust update intervals
Process Interaction
Btop provides comprehensive process management capabilities. Select processes using arrow keys or mouse clicks. Send signals to processes through keyboard shortcuts or menu options. The tool supports all standard process signals including TERM, KILL, and custom signals.
Configuration and Customization
Accessing Options Menu
When you press Esc or q, btop displays an exit menu with three options: Options, Help, and Quit. The Options menu provides access to extensive customization settings where you can “customize the interface, adjust colors, and configure other preferences”.
Theme Customization
Btop supports extensive theme customization, allowing users to personalize their monitoring experience. The tool includes several built-in themes and supports custom theme creation. Popular themes like Everforest transform btop into “not just a functional monitoring tool but a genuinely beautiful interface that’s a pleasure to use during long troubleshooting sessions”.
Performance Settings
Configure update intervals to balance information freshness with system resource usage. Adjust the refresh rate based on your monitoring needs—higher frequencies provide more responsive updates but consume more CPU resources. Lower frequencies reduce system impact while still providing adequate monitoring capabilities.
Display Preferences
Customize which information panels appear in your btop interface. Enable or disable specific graphs and meters based on your monitoring requirements. Adjust graph scales and time ranges to focus on relevant metrics for your use case.
Saving Configuration
Btop automatically saves configuration changes, ensuring your preferences persist across sessions. This automatic saving eliminates the need to reconfigure the tool each time you launch it, providing a consistent monitoring experience.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Repository Access Problems
If you encounter repository access errors, verify your network connectivity and repository URLs. Outdated repository metadata can cause installation failures. Refresh your repositories using:
sudo zypper refreshFor persistent repository issues, manually verify repository URLs and consider using alternative repositories or installation methods.
Permission Errors
Installation failures due to permission errors typically indicate insufficient privileges. Ensure you’re using sudo with zypper commands. If you’re not in the sudoers file, contact your system administrator or use the root account directly.
Package Dependency Conflicts
Dependency conflicts can occur when mixing repositories or using outdated package information. Resolve conflicts by updating your system packages first, then attempting the btop installation. If conflicts persist, consider using a different installation method or consulting openSUSE community forums.
Performance Issues
If btop consumes excessive system resources, adjust the update interval to reduce CPU usage. Lower refresh rates decrease system impact while maintaining monitoring functionality. Additionally, disable unnecessary graphs or features that you don’t actively use.
Terminal Display Problems
Graphics display issues in terminal environments can affect btop’s visual elements. Ensure your terminal supports Unicode and color display. Modern terminal emulators like GNOME Terminal, Konsole, or Alacritty provide the best compatibility with btop’s advanced features.
Updating and Uninstalling
Keep btop updated through your package manager using:
sudo zypper update btopTo uninstall btop, use:
sudo zypper remove btopIf you installed from source, remove manually-installed files from /usr/local/bin/ and related directories.
Advanced Usage Tips and Best Practices
System Troubleshooting Workflows
Integrate btop into your troubleshooting methodology by using its visual cues to identify performance anomalies quickly. The graphical representation of system metrics makes pattern recognition more intuitive than traditional text-based tools. Focus on correlation between different metrics—high CPU usage combined with low disk activity might indicate different issues than high CPU with high disk I/O.
Monitoring Specific Resources
Customize btop’s display to emphasize metrics relevant to your current investigation. If troubleshooting network issues, expand the network panel and monitor connection statistics. For storage problems, focus on disk I/O metrics and process-specific disk usage patterns.
Integration with System Administration
Use btop as part of a comprehensive monitoring strategy alongside system logs and other diagnostic tools. The real-time visual feedback complements static log analysis, providing immediate context for logged events. Combine btop monitoring with log analysis tools for complete system visibility.
Security Considerations
When using btop in multi-user environments, be aware that the tool displays information about all system processes, potentially revealing sensitive information about running applications. Consider user permissions and whether process visibility aligns with your security policies.
Performance Impact Management
Monitor btop’s own resource consumption, especially on resource-constrained systems. Adjust update frequencies and disable unnecessary features to minimize impact on system performance. Remember that monitoring tools should enhance system observability without significantly affecting system performance.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Btop. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Btop real-time system monitor tool on openSUSE Linux system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Btop website.