How To Install Cockpit on Fedora 41

In the realm of Linux server management, having the right tools can make a significant difference in efficiency and ease of use. One such powerful tool is Cockpit, a web-based interface that simplifies the administration of your systems. This article will guide you through the process of installing Cockpit on Fedora 41, ensuring you have a robust platform for managing your server effectively.
Understanding Cockpit
What is Cockpit?
Cockpit is an open-source server management tool designed to provide an intuitive web interface for system administrators. It allows users to monitor system performance, manage services, and perform administrative tasks without needing to rely solely on the command line. With its user-friendly design, Cockpit can help both novice and experienced users navigate their Linux systems more effectively.
Benefits of Using Cockpit
- User-Friendly Interface: Cockpit features a clean and modern interface that makes it easy to manage multiple servers from a single dashboard.
- Remote Management Capabilities: Access your servers from anywhere via a web browser, making it perfect for remote administration.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Monitor CPU usage, memory consumption, disk activity, and network traffic in real-time.
Prerequisites for Installation
System Requirements
Before installing Cockpit, ensure your system meets the following requirements:
- Operating System: Fedora 41 or later versions.
- Hardware: Minimum of 1 GB RAM and 1 GHz processor; however, more resources are recommended for better performance.
User Permissions
You must have sudo privileges to install Cockpit. This ensures that you can execute commands that require administrative access without any issues.
Installing Cockpit on Fedora 41
Step-by-Step Installation Process
The installation process for Cockpit on Fedora 41 is straightforward. Follow these steps to get started:
- Open Terminal: Access your terminal application. You can usually find it in your applications menu or by searching for “Terminal.”
- Update Your System: Before installing any new software, it’s good practice to ensure your system is up to date. Run the following command:
sudo dnf update - Install Cockpit: Now that your system is updated, install Cockpit with this command:
sudo dnf install cockpit - Verify Installation Success: After installation, check if Cockpit was installed correctly by running:
rpm -q cockpitThis command should return the version number of Cockpit installed on your system.
Starting the Cockpit Service
Once installed, you need to start the Cockpit service to begin using it:
- Enable and Start the Service: Execute the following command to enable and start the Cockpit socket:
sudo systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket - Check the Status of the Service: Ensure that the service is running smoothly by checking its status:
sudo systemctl status cockpitLook for “active (running)” in the output to confirm that everything is working as expected.
Common Installation Issues
If you encounter issues during installation, consider these troubleshooting tips:
- If you receive errors during installation, ensure that your system is fully updated and try reinstalling with `sudo dnf install cockpit` again.
- If the service does not start, check for any conflicting services or firewall rules that may be preventing it from running.
Configuring the Firewall
Why Firewall Configuration is Necessary
A properly configured firewall helps protect your server from unauthorized access. Since Cockpit operates over a specific port (9090), it’s essential to allow traffic through this port in your firewall settings.
Steps to Allow Cockpit Through Firewall
You can easily configure your firewall to allow access to Cockpit by executing these commands:
- Add the service to your firewall rules:
sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=cockpit --permanent - Reload Firewall Settings: Apply the changes by reloading the firewall:
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Verifying Firewall Settings
You can verify whether Cockpit is allowed through the firewall by running:
sudo firewall-cmd --list-allLook for “cockpit” in the list of allowed services.
Accessing Cockpit
How to Access the Web Interface
Cockpit can be accessed via any web browser. To do so, enter the following URL format in your browser’s address bar:
http://<server_ip>:9090
Replace `<server_ip>` with the actual IP address of your Fedora server.
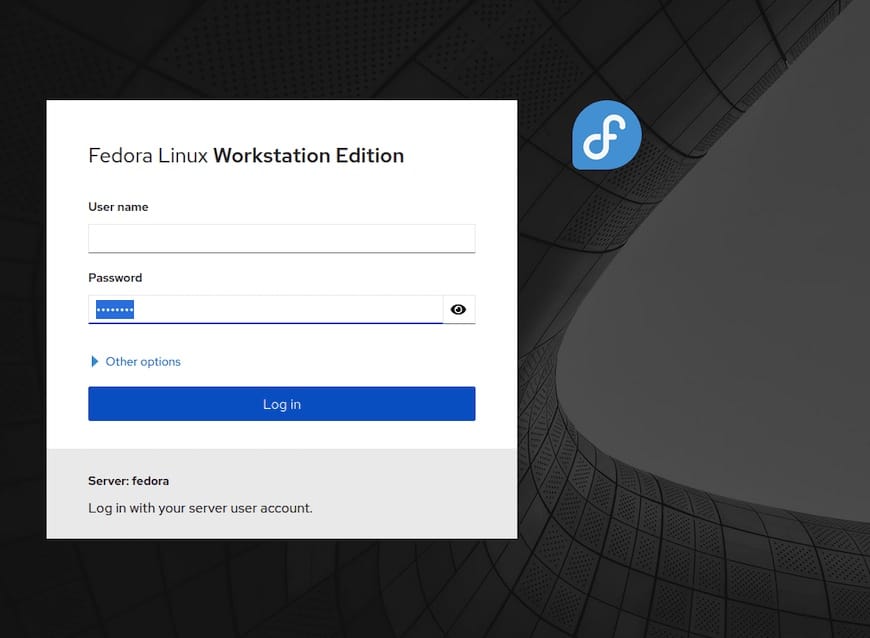
Login Process
You will be prompted to log in. Use your root or administrative user credentials. Once logged in, you’ll be greeted with the Cockpit dashboard.
Overview of the Cockpit Dashboard
The dashboard provides an overview of system health and performance metrics. Key features include:
- Status indicators for CPU usage, memory consumption, disk space, and network activity.
- A navigation menu allowing access to various management tools like services, storage management, and logs.
Basic Usage of Cockpit
Navigating the Dashboard
The dashboard is designed for ease of use. Each section provides intuitive controls and information about different aspects of your server’s operation. Familiarize yourself with these sections as they will be essential for effective management.
Common Tasks You Can Perform with Cockpit
Cockpit allows you to perform several essential tasks:
- Starting/Stopping Services: Easily manage services by navigating to the “Services” section where you can start or stop services as needed.
- Managing Storage Devices: View storage usage and configure disks under “Storage.” You can create partitions or manage file systems directly from this interface.
- Monitoring System Performance and Logs: Access real-time logs and performance metrics under “Logs” and “Performance” sections respectively. This helps in troubleshooting issues quickly.
Advanced Features and Extensions
Overview of Additional Features
Cockpit offers a range of advanced features that enhance its functionality:
- User Management: Create and manage user accounts directly through Cockpit.
- Scripting Support: Cockpit allows you to run scripts directly from its interface, enabling automation of routine tasks.
- Kubernetes Integration: If you’re using Kubernetes, you can manage clusters directly from Cockpit with appropriate extensions.
Cockpit supports various extensions that can enhance its capabilities significantly. To find and install additional packages, follow these steps:
- Browse Available Extensions: You can find available extensions by searching online or checking within Cockpit’s interface under “Applications.”
- Add Extensions Using DNF: If you find an extension you’d like to install, use:
sudo dnf install cockpit- - Selectively Enable Extensions: You may need to enable certain extensions after installation through their respective settings in the Cockpit dashboard.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Cockpit. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Cockpit web-based graphical interface for managing Linux servers on Fedora 41 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Cockpit website.