How To Install Consul Server on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Consul Server on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS. Consul, a powerful service mesh and distributed networking tool, has become increasingly popular among developers and system administrators. It provides features such as service discovery, health checking, configuration management, and secure service communication.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Consul Server on Ubuntu 22.04. You can follow the same instructions for Ubuntu 22.04 and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint, Elementary OS, Pop!_OS, and more as well.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Ubuntu 22.04, 20.04, and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- Access the terminal on your Ubuntu system, where we’ll execute the commands for a seamless Roundcube installation.
- An active internet connection. You’ll need an internet connection to download the necessary packages and dependencies.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to the root user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Consul Server on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Jammy Jellyfish
Step 1. To begin, update your Ubuntu system to ensure you have the latest packages and security patches. Open a terminal and run the following commands:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
These commands will refresh the package index and upgrade any outdated packages to their latest versions.
Step 2. Installing Dependencies.
Consul requires a few dependencies to function properly. Install them by executing the following command:
sudo apt install unzip curl gnupg
Step 3. Installing Consul Server on Ubuntu.
To ensure the authenticity of the Consul package, add HashiCorp’s GPG key to your system’s trusted keys. Run the following command to download and add the key:
curl -fsSL https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
Next, add the official HashiCorp Linux repository for Ubuntu to your system’s package sources. This will allow you to install and update Consul using the apt package manager. Execute the following command:
sudo apt-add-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com $(lsb_release -cs) main"
After adding the repository, update the package index to include the newly added source:
sudo apt update
With the HashiCorp repository added and the package index updated, you can now install Consul. Run the following command:
sudo apt install consul
To verify the installation, run:
consul version
If the installation was successful, you should see the version number of Consul printed in the terminal.
Step 4. Configure Consul Server.
To set up Consul as a server, you need to create a configuration file. Start by creating a directory to store the configuration:
sudo mkdir /etc/consul.d
Open a new configuration file using your preferred text editor:
sudo nano /etc/consul.d/server.hcl
Add the following configuration to the file:
datacenter = "dc1"
data_dir = "/opt/consul"
server = true
bootstrap_expect = 1
ui_config {
enabled = true
}
bind_addr = "0.0.0.0"
client_addr = "0.0.0.0"
advertise_addr = "{{ GetInterfaceIP \"eth0\" }}"
This configuration sets up Consul as a server in the “dc1” datacenter, enables the web UI, and configures the network addresses.
Step 5. Configure Systemd.
To manage the Consul service using systemd, create a unit file. Open a new file using your text editor:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/consul.service
Add the following content to the file:
[Unit] Description=Consul Service Discovery Agent After=network-online.target Wants=network-online.target [Service] Type=simple User=consul Group=consul ExecStart=/usr/bin/consul agent -config-dir=/etc/consul.d ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID KillMode=process KillSignal=SIGTERM Restart=on-failure LimitNOFILE=65536 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save the file and exit the text editor, then reload the systemd daemon to apply the changes:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Start the Consul service and enable it to start automatically on system boot:
sudo systemctl start consul sudo systemctl enable consul
Step 6. Open Required Ports.
To allow incoming connections to Consul, open the required ports using the UFW firewall. Run the following commands:
sudo ufw allow 8300/tcp sudo ufw allow 8301/tcp sudo ufw allow 8301/udp sudo ufw allow 8302/tcp sudo ufw allow 8302/udp sudo ufw allow 8500/tcp sudo ufw allow 8600/tcp sudo ufw allow 8600/udp
These commands open the necessary ports for Consul’s communication and web UI access.
Step 7. Verify Consul Installation.
To verify that Consul is running correctly, check the member status by executing:
consul members
You should see the Consul server listed as a member of the cluster.
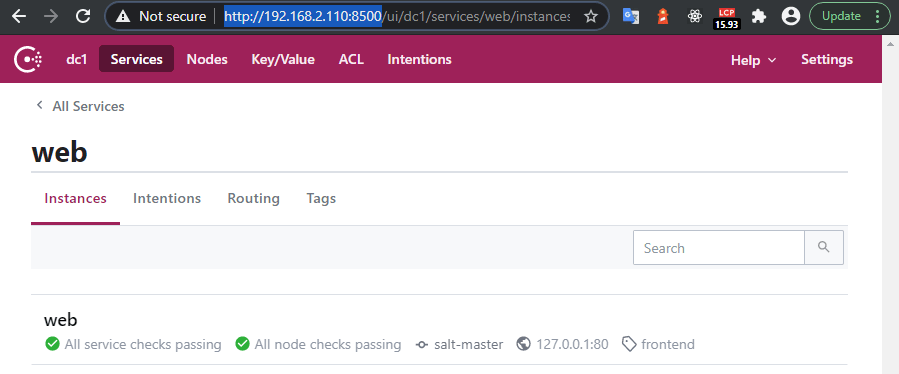
Access the Consul web UI by opening a web browser and navigating to http://your-server-ip:8500. You should see the Consul web interface displaying the cluster’s status and services.
You can also query the Consul HTTP API to retrieve information about the cluster. For example, to retrieve the list of registered services, run:
curl http://localhost:8500/v1/catalog/services
Step 8. Troubleshooting Common Issues.
If you encounter any issues during the installation or operation of Consul, consider the following troubleshooting tips:
- Consul service fails to start: Check the Consul log file (
/var/log/consul/consul.log) for any error messages. Ensure that the configuration file is properly formatted and contains valid options. - Firewall blocking Consul ports: Verify that the required ports (8300, 8301, 8302, 8500, 8600) are open in your firewall configuration. Use the
ufw statuscommand to check the firewall rules. - Errors in Consul configuration files: Double-check the syntax and options in your Consul configuration files. Make sure there are no typos or missing values.
- Consul nodes not joining the cluster: Ensure that the network connectivity between the nodes is functioning correctly. Verify that the
bind_addr,client_addr, andadvertise_addroptions are set correctly in the configuration file.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed the Consul Server. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Consul Server on the Ubuntu system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Consul HashiCorp website.