
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Django on AlmaLinux 8. For those of you who didn’t know, Django is a free and open-source full-featured Python web framework used to develop dynamic frameworks and applications. Django’s primary goals are simplicity, re-usability, rapid development, and scalability.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you through the step-by-step installation of the Django web framework on an AlmaLinux 8. You can follow the same instructions for CentOS and Rocky Linux.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: AlmaLinux 8, CentOS, or Rocky Linux 8.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Django on AlmaLinux 8
Step 1. First, let’s start by ensuring your system is up-to-date.
sudo dnf update sudo dnf install epel-release
Step 2. Installing Python.
Django is a Python-based framework, now we run the following command to install Python:
sudo dnf install python36 python3-pip
Check the installed version of Python:
python3 -V
Also, check the installed version of Pip:
pip3 -V
Step 3. Installing Django on AlmaLinux 8.
Now we install Django using the pip command below:
sudo pip3 install Django
After a successful installation, check the version of Django installed:
django-admin --version
Step 4. Create a Django Project.
Now, it’s time to build a Django app. You can create Django applications using the django-admin command in the new directory for our project:
sudo mkdir –p /home/project/django django-admin startproject djangoproject
Next, change the directory to djangoprojectand migrate changes with the following command below:
cd djangoproject python3 manage.py migrate
Then, create an admin user account to manage your Django project:
python3 manage.py createsuperuser
Output:
Username (leave blank to use 'root'): admin Email address: admin@idroot.us Password: Password (again): Superuser created successfully.
After that, we need to modify the settings.py the file inside our project folder to allow Django to be accessed by external users:
sudo nano djangoproject/settings.py
Change the following line:
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['your-server-ip-address']
Save and close the file. Then, run the Django application with the following command below:
sudo python3 manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000
Step 5. Configure Firewall.
In order to allow access to port 8000, you need to modify firewall rules in a new SSH connection:
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=8000/tcp --zone=public --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=80/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Step 6. Accessing Django Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, you can access the Django application by visiting the URL http://your-server-ip-address:8000. You will see the following page:
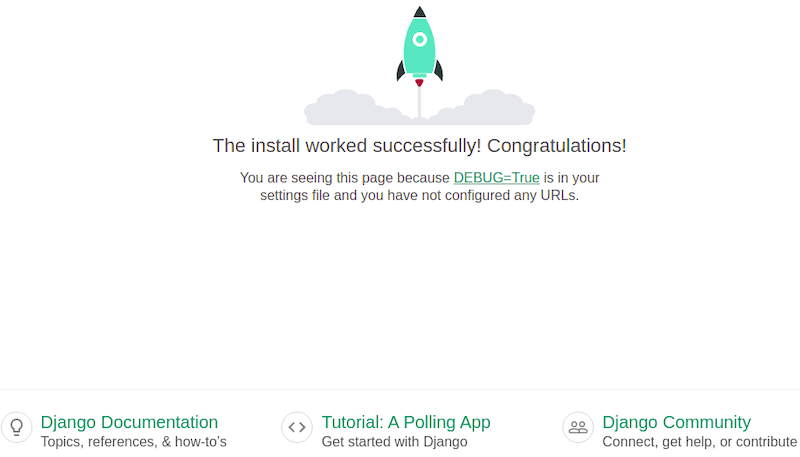
You can also access Django’s admin interface using the URL http://your-server-ip-address:8000/admin. You will see the following page:
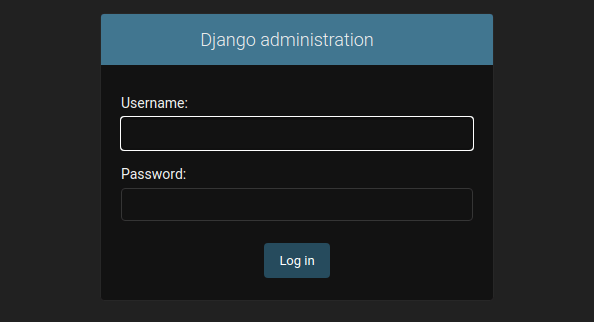
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Django. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Django Python web framework on your AlmaLinux 8 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Django website.