
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Django on Fedora 35. For those of you who didn’t know, Django is a free and open-source high-level Python Web framework built by experienced developers to encourage rapid development and pragmatic design of web applications for programmers and developers. Its main goal is to ease the creation of complex applications and take care of the internal structure.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Django Python Framework on a Fedora 35.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Fedora 35.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Django on Fedora 35
Step 1. Before proceeding, update your Fedora operating system to make sure all existing packages are up to date. Use this command to update the server packages:
sudo dnf upgrade sudo dnf update
Step 2. Installing Python3 and Pip3.
Now we install Python 3 on your Fedora system using the following command below:
sudo dnf install python3 python3-pip
Verify Python and pip version:
python3 -V pip3 -V
Step 3. Installing Django on Fedora 35.
By default, Django is not available on Fedora 35 base repository. Now install Django using the following command:
pip3 install Django
After installing Django, you can check the version of Django with the following command:
django-admin --version
Step 4. Create Test Django Application.
We create a Django test application by following the instructions below:
mkdir idroot-projects cd idroot-projects django-admin startproject test_app cd test_app
Then, necessary to execute the pending migrations by executing the following command:
python3 manage.py migrate python3 manage.py createsuperuser python3 manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000
By default, Django doesn’t allow external hosts to access the web interface. To allow external hosts, edit the settings.py file and add IP under ALLOWED_HOSTS:
nano django_app/settings.py
Add the following file:
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['192.168.77.21']
Save and close, then start Django application server:
python3 manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8090
Step 5. Configure Firewall.
In order to allow access to port 8000, you need to modify firewall rules in a new SSH connection:
firewall-cmd --add-port=8000/tcp --zone=public --permanent firewall-cmd --reload
Step 6. Accessing Django Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, now open your favorite browser and navigate tohttp://192.168.77.21:8000. You should see the following page:
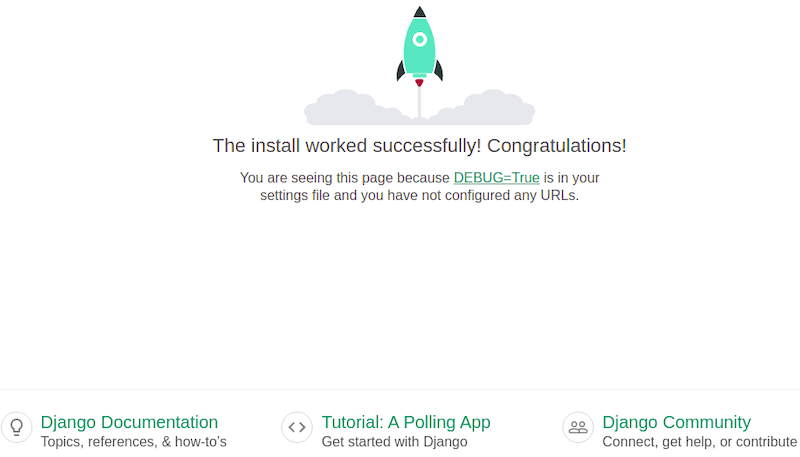
You can also access the Django admin interface using the URL http://192.168.77.21:8000/admin. You should see the following page:
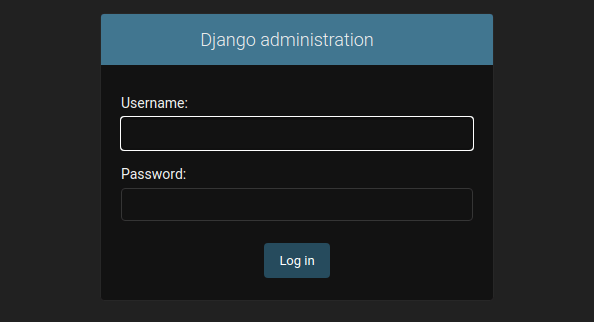
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Django. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Django Python Framework on your Fedora 35 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Django website.