How To Install Drupal on AlmaLinux 10

Drupal stands as one of the most powerful and flexible content management systems available today, powering millions of websites worldwide from small blogs to enterprise-level applications. When combined with AlmaLinux 10, a robust and secure enterprise-grade Linux distribution, you create an ideal hosting environment that delivers exceptional performance, stability, and security.
AlmaLinux 10 offers several compelling advantages for Drupal hosting, including long-term support, excellent security features, and seamless compatibility with enterprise applications. This comprehensive guide will walk you through every step of installing Drupal on AlmaLinux 10, from initial system preparation to post-installation optimization.
By following this tutorial, you’ll establish a production-ready Drupal installation that leverages the full potential of both platforms. Whether you’re a system administrator, web developer, or website owner, this guide provides the technical depth and practical insights needed to successfully deploy Drupal on AlmaLinux 10. The entire process typically takes 45-60 minutes, depending on your server specifications and internet connection speed.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Before beginning the Drupal installation process, ensure your system meets the necessary requirements for optimal performance. A successful installation requires specific hardware specifications and system access levels.
Your AlmaLinux 10 server should have a minimum of 2GB RAM, though 4GB or more is recommended for production environments. Storage requirements include at least 10GB of available disk space, with additional space allocated based on your expected content volume. A dual-core processor provides adequate performance for most installations, while multi-core processors enhance handling of concurrent users.
System access requirements include root privileges or sudo access to install packages and modify system configurations. A stable internet connection is essential for downloading packages, Drupal core files, and future updates. Additionally, having a registered domain name pointed to your server’s IP address streamlines the setup process, though you can initially configure Drupal using the server’s IP address.
Basic familiarity with Linux command-line operations significantly improves the installation experience. Understanding file permissions, text editors like nano or vim, and basic navigation commands helps troubleshoot potential issues during installation.
Preparing AlmaLinux 10 System
System Updates and Package Management
Begin by updating your AlmaLinux 10 system to ensure all packages reflect the latest security patches and feature updates. Connect to your server via SSH and execute the following commands:
sudo dnf update -y
sudo dnf install -y wget curl unzip epel-releaseThe system update process downloads and installs available package updates, while the additional packages provide essential utilities for the Drupal installation process. The EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) repository expands available software options beyond the standard AlmaLinux repositories.
Configure your system’s timezone to match your geographic location or preferred timezone for accurate logging and scheduling:
sudo timedatectl set-timezone America/New_York
sudo timedatectl statusReplace “America/New_York” with your preferred timezone. Use timedatectl list-timezones to view available options.
Security Configuration
Initial security hardening protects your server from common attack vectors. Configure the firewall to allow necessary services while blocking unauthorized access:
sudo systemctl start firewalld
sudo systemctl enable firewalld
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=ssh
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadVerify SELinux status to ensure proper security context enforcement:
sudo getenforceSELinux should return “Enforcing” for optimal security. If disabled, enable it by editing /etc/selinux/config and setting SELINUX=enforcing, then reboot the system.
Installing and Configuring LAMP Stack
Apache Web Server Installation
Apache HTTP Server provides the web server foundation for your Drupal installation. Install and configure Apache with the following commands:
sudo dnf install -y httpd httpd-tools
sudo systemctl start httpd
sudo systemctl enable httpd
sudo systemctl status httpdThe Apache installation includes essential modules and tools for web server functionality. Starting and enabling the service ensures Apache automatically starts during system boot, maintaining consistent availability.
Test your Apache installation by opening a web browser and navigating to your server’s IP address. You should see the AlmaLinux Apache test page, confirming successful installation.
Configure Apache’s main configuration file to optimize performance:
sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confLocate and modify the following directives for improved Drupal compatibility:
ServerTokens Prod
ServerSignature Off
KeepAlive On
MaxKeepAliveRequests 100
KeepAliveTimeout 5These settings enhance security by reducing information disclosure and improve performance through connection reuse.
MariaDB Database Server Setup
MariaDB serves as the database backend for Drupal, storing content, user information, and configuration data. Install MariaDB server and client packages:
sudo dnf install -y mariadb-server mariadb
sudo systemctl start mariadb
sudo systemctl enable mariadbSecure your MariaDB installation using the built-in security script:
sudo mysql_secure_installationThe security script prompts for several configuration options. Respond as follows:
- Set root password: Yes (choose a strong password)
- Remove anonymous users: Yes
- Disallow root login remotely: Yes
- Remove test database: Yes
- Reload privilege tables: Yes
Test database connectivity to ensure proper installation:
sudo mysql -u root -pEnter your root password when prompted. Successfully connecting to the MariaDB prompt confirms proper installation.
PHP Installation and Configuration
PHP processes dynamic content and connects Drupal to the database. Install PHP along with essential extensions required for Drupal functionality:
sudo dnf install -y php php-mysqlnd php-gd php-xml php-mbstring php-curl php-zip php-json php-opcache php-intl php-ldap php-soapThese PHP extensions provide:
php-mysqlnd: Database connectivityphp-gd: Image processing capabilitiesphp-xml: XML parsing functionalityphp-mbstring: Multibyte string handlingphp-curl: HTTP client functionalityphp-zip: Archive handlingphp-opcache: Performance optimizationphp-intl: Internationalization support
Configure PHP settings for optimal Drupal performance by editing the main configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/php.iniModify the following settings:
memory_limit = 256M
upload_max_filesize = 64M
post_max_size = 64M
max_execution_time = 300
max_input_vars = 3000
date.timezone = America/New_YorkThese configurations ensure adequate resources for Drupal operations, including file uploads, form processing, and memory-intensive operations.
Restart Apache to load the new PHP configuration:
sudo systemctl restart httpdDatabase Setup for Drupal
Create a dedicated database and user account for your Drupal installation. This approach follows security best practices by limiting database access to specific credentials.
Access the MariaDB command line interface:
sudo mysql -u root -pExecute the following SQL commands to create the database structure:
CREATE DATABASE drupal_db CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
CREATE USER 'drupal_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'strong_password_here';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON drupal_db.* TO 'drupal_user'@'localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;Replace ‘strong_password_here’ with a secure password combining uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. The UTF8MB4 character set ensures full Unicode support, including emojis and special characters from various languages.
Test the database connection using the new credentials:
mysql -u drupal_user -p drupal_dbSuccessful connection confirms proper database setup. Exit the MariaDB prompt to continue with Drupal installation.
Downloading and Installing Drupal
Obtaining Drupal Source Code
Download the latest stable Drupal release from the official website. Navigate to a temporary directory and download the archive:
cd /tmp
wget https://www.drupal.org/download-latest/tar.gz -O drupal-latest.tar.gzVerify the download completed successfully by checking the file size and type:
ls -lh drupal-latest.tar.gz
file drupal-latest.tar.gzExtracting and Positioning Files
Extract the Drupal archive and move files to the web server directory:
tar -xzf drupal-latest.tar.gz
sudo cp -R drupal-*/* /var/www/html/
sudo cp -R drupal-*/.[^.]* /var/www/html/The second copy command ensures hidden files (those beginning with a dot) are also transferred to the web directory.
Create the Drupal sites directory structure:
sudo mkdir -p /var/www/html/sites/default/files
sudo cp /var/www/html/sites/default/default.settings.php /var/www/html/sites/default/settings.phpSetting File Permissions
Proper file permissions ensure security while allowing Drupal to function correctly. Configure ownership and permissions:
sudo chown -R apache:apache /var/www/html/
sudo find /var/www/html/ -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
sudo find /var/www/html/ -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;
sudo chmod 666 /var/www/html/sites/default/settings.php
sudo chmod 777 /var/www/html/sites/default/files/These commands establish secure default permissions while allowing Drupal’s installer to modify necessary files during setup.
Configuring SELinux for Drupal
SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux) provides mandatory access control, requiring specific context labels for web applications to function properly.
Install SELinux management utilities:
sudo dnf install -y policycoreutils-python-utilsApply appropriate SELinux contexts to Drupal files:
sudo setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect on
sudo setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect_db on
sudo semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_exec_t "/var/www/html(/.*)?"
sudo semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t "/var/www/html/sites/default/files(/.*)?"
sudo restorecon -Rv /var/www/html/These commands enable Apache to establish network connections and properly handle Drupal’s file operations within SELinux constraints.
Verify SELinux contexts are correctly applied:
ls -Z /var/www/html/sites/default/files/The output should display httpd_sys_rw_content_t context for the files directory.
Apache Virtual Host Configuration
Create a dedicated virtual host configuration for your Drupal site to enable advanced features like clean URLs and SSL support.
Create a new virtual host file:
sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/drupal.confAdd the following configuration:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName yourdomain.com
ServerAlias www.yourdomain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
<Directory "/var/www/html">
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ index.php?q=$1 [L,QSA]
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/drupal_error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/drupal_access.log combined
</VirtualHost>Replace “yourdomain.com” with your actual domain name. The AllowOverride directive enables Drupal’s .htaccess file functionality, while the RewriteRule enables clean URLs.
Test the Apache configuration syntax:
sudo httpd -tIf the syntax test returns “Syntax OK,” restart Apache to apply the changes:
sudo systemctl restart httpdWeb-Based Drupal Installation
Accessing the Installation Wizard
Open your web browser and navigate to your domain name or server IP address. The Drupal installation wizard should appear automatically.
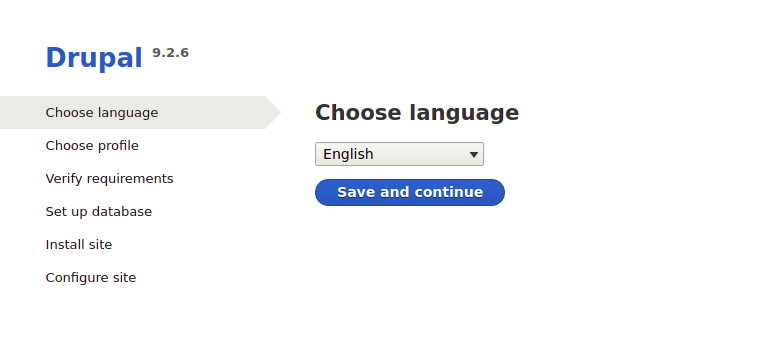
Select your preferred language from the available options. Drupal supports multiple languages out of the box, with additional language packs available for download.
Choose an installation profile based on your site requirements:
- Standard: Includes common features and modules for typical websites
- Minimal: Basic installation with minimal modules enabled
- Demo: Pre-configured with sample content for testing
For most installations, the Standard profile provides an optimal balance of features and performance.
Database Configuration
The installation wizard prompts for database connection details. Enter the following information:
- Database type: MySQL, MariaDB, or equivalent
- Database name: drupal_db (or your chosen database name)
- Database username: drupal_user
- Database password: Your database user password
- Advanced options: Leave default unless specific configuration is required
Click “Save and continue” to test the database connection. Successful connection proceeds to the next installation step, while connection failures require reviewing database credentials and server configuration.
Site Configuration
Configure essential site settings during the final installation step:
Site Information:
- Site name: Your website’s display name
- Site email address: Administrative email for system notifications
Site Maintenance Account:
- Username: Administrative user account name
- Email address: Administrator’s email address
- Password: Strong administrative password
Server Settings:
- Default country: Geographic location for timezone and regional settings
- Default timezone: System timezone for content timestamps
Update Notifications:
- Check for updates automatically: Recommended for security updates
- Receive email notifications: Optional administrative preference
Complete the installation by clicking “Save and continue.” The system finalizes configuration and redirects to your new Drupal website.
Post-Installation Configuration and Security
Essential Security Hardening
Immediately after installation, implement critical security measures to protect your Drupal site from common vulnerabilities.
Remove write permissions from the settings file:
sudo chmod 644 /var/www/html/sites/default/settings.phpUpdate Drupal core and all installed modules through the administrative interface or using Drush (Drupal Shell):
cd /var/www/html
wget https://github.com/drush-ops/drush/releases/download/8.4.12/drush.phar
chmod +x drush.phar
sudo mv drush.phar /usr/local/bin/drush
drush status
drush upConfigure automated security updates by enabling the Update Manager module and configuring notification preferences in the administrative interface.
Performance Optimization
Enable Drupal’s built-in caching mechanisms to improve site performance:
- Navigate to Configuration > Performance in the administrative interface
- Enable “Cache pages for anonymous users”
- Enable “Cache blocks”
- Set appropriate cache lifetime based on content update frequency
- Enable CSS and JavaScript aggregation and compression
Configure database optimization settings in MariaDB:
sudo nano /etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnfAdd the following optimization settings under the [mysqld] section:
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 1G
query_cache_size = 64M
query_cache_limit = 2M
thread_cache_size = 50Adjust values based on your server’s available memory and expected traffic patterns.
Backup Strategy Implementation
Establish regular backup procedures to protect against data loss and enable rapid recovery:
Database Backup Script:
#!/bin/bash
DATE=$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S)
mysqldump -u drupal_user -p drupal_db > /backup/drupal_db_$DATE.sqlFile System Backup:
tar -czf /backup/drupal_files_$DATE.tar.gz /var/www/html/sites/default/files/Schedule automated backups using cron:
sudo crontab -eAdd the following entries for daily backups:
0 2 * * * /path/to/database_backup.sh
0 3 * * * /path/to/files_backup.shTroubleshooting Common Issues
Permission Errors: Verify file ownership and permissions match Apache requirements. Use sudo chown -R apache:apache /var/www/html/ to correct ownership issues.
Database Connection Problems: Check database credentials, service status, and firewall configuration. Verify MariaDB is running with sudo systemctl status mariadb.
SELinux Access Denied: Review SELinux logs using sudo ausearch -m avc -ts recent to identify blocked operations. Apply appropriate boolean settings or file contexts as needed.
Clean URL Configuration: Ensure Apache’s mod_rewrite module is enabled and the virtual host allows .htaccess overrides. Test rewrite functionality through Drupal’s configuration interface.
Memory Limit Exceeded: Increase PHP memory limits in /etc/php.ini and restart Apache. Monitor resource usage during peak traffic periods.
SSL Certificate Issues: Verify certificate installation, intermediate certificate chain, and cipher suite compatibility. Use online SSL testing tools to validate configuration.
Next Steps and Best Practices
With Drupal successfully installed on AlmaLinux 10, consider implementing additional enhancements:
- Essential Modules: Install popular contrib modules like Views, Pathauto, Token, and Admin Toolbar to extend functionality and improve administrative experience.
- Theme Customization: Select responsive themes optimized for your content type and audience. Consider accessibility standards and mobile compatibility.
- User Management: Configure user roles and permissions based on organizational requirements. Implement two-factor authentication for administrative accounts.
- Performance Monitoring: Install monitoring tools like New Relic or implement log analysis to track performance metrics and identify optimization opportunities.
- Content Strategy: Develop content types, taxonomy vocabularies, and editorial workflows that align with your organizational goals and user experience requirements.
Regular maintenance tasks include applying security updates, monitoring log files, optimizing database performance, and reviewing user access patterns. Join the Drupal community through forums, local meetups, and online resources to stay current with best practices and emerging trends.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Drupal. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Drupal CMS (content management system) on your AlmaLinux OS 10 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Drupal website.