How To Install FreeFileSync on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install FreeFileSync on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS. FreeFileSync stands as one of the most powerful open-source file synchronization and backup tools available for Linux users. If you’re running Ubuntu 24.04 LTS (Noble Numbat) and need a reliable way to keep your files synchronized across different locations, FreeFileSync offers a robust solution. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about installing and using FreeFileSync on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS, from basic setup to advanced configuration options.
Understanding FreeFileSync
FreeFileSync is a free, open-source file synchronization utility designed to create and manage backup copies of your important files efficiently. Unlike traditional backup methods that copy every file regardless of changes, FreeFileSync intelligently identifies differences between source and target folders, transferring only the minimum amount of data necessary.
Key Features and Capabilities
FreeFileSync offers an impressive array of features that make it stand out from other synchronization tools:
- Folder comparison with visual difference highlighting
- Multiple synchronization modes (Mirror, Two-Way, and Update)
- Custom filtering options to include or exclude specific files
- Detection of moved files to avoid unnecessary copying
- Support for handling locked files using Volume Shadow Copy Service
- Capability to work with long file paths (over 260 characters)
- Full Unicode compatibility
- FTP/FTPS synchronization support
- Batch job creation and scheduling
- Real-time synchronization monitoring
The latest version (14.3 as of the time of writing) includes improvements such as support for internationalized domain names for FTP connections, performance statistics for file content comparison, and better terminal integration on Linux systems.
Why Use FreeFileSync on Ubuntu 24.04
Ubuntu 24.04 LTS (Noble Numbat) benefits significantly from FreeFileSync’s capabilities due to several Linux-specific advantages:
- Seamless integration with the Ubuntu file system
- Resource efficiency optimized for Linux environments
- High performance with support for multi-core processing
- Free and open-source nature aligns with Ubuntu’s philosophy
- Cross-platform compatibility allows synchronization between Ubuntu and other operating systems
- Support for Linux-specific file attributes and permissions
The software takes full advantage of 64-bit architecture and multiple CPU cores when available, ensuring optimal performance on modern Ubuntu systems.
Prerequisites for Installation
Before proceeding with the installation, ensure your system meets the following requirements:
- Ubuntu 24.04 LTS operating system
- Administrative (sudo) privileges
- At least 100MB of free disk space
- Stable internet connection for downloading the installer
- Basic familiarity with the Terminal
A properly configured Ubuntu 24.04 system should meet all hardware requirements for running FreeFileSync without issues.
Pre-Installation Steps
Proper preparation ensures a smooth installation process. Follow these steps before installing FreeFileSync:
1. Update Your System
Always start with a system update to ensure all packages are current:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgradeThis ensures any dependencies are updated and your system is in optimal condition for the installation.
2. Install Required Dependencies
FreeFileSync requires certain libraries to function properly. Install them with:
sudo apt install libgtk-3-0 libwebkit2gtk-4.0-373. Create a Backup (Optional)
While not strictly necessary, it’s good practice to back up any critical data before installing new software.
Method 1: Installing via Official Installer
The recommended way to install FreeFileSync on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS is through the official installer provided on the FreeFileSync website.
1. Download the Official Installer
Visit the FreeFileSync website and download the Linux package. As of writing, the latest version is 14.3.
Alternatively, you can use wget to download directly from the terminal:
wget https://freefilesync.org/download/FreeFileSync_14.3_Linux.tar.gz2. Extract the Downloaded Package
Navigate to your Downloads folder and extract the downloaded tarball:
cd ~/Downloads
tar -xvf FreeFileSync_14.3_Linux.tar.gzThis will create a new directory containing the FreeFileSync files.
3. Run the Installer
Navigate to the extracted directory and run the installer:
cd FreeFileSync
sudo ./FreeFileSync_14.3_Install.run4. Follow the Installation Prompts
The installer will start in a terminal window. You’ll need to:
- Type ‘y’ and press Enter to accept the license terms (or ‘s’ to show details)
- Choose the installation type:
- Type ‘1’ for current user only
- Default (just press Enter) for system-wide installation to /opt/ directory
- Optionally type ‘2’ to change the installation directory
- Type ‘3’ to choose whether to add desktop icons
- Press Enter to start the installation process
If everything goes well, you’ll see a confirmation message indicating the installation is complete.
Method 2: Manual Installation
For users who prefer more control over the installation process, a manual installation is possible.
1. Create an Installation Directory
First, create a directory to hold the FreeFileSync files:
mkdir -p ~/Software2. Extract the FreeFileSync Files
Extract the downloaded tarball to your chosen directory:
tar -xf FreeFileSync_14.3_Linux.tar.gz -C ~/Software/3. Extract Icons
Extract the program icons for desktop integration:
cd ~/Software/FreeFileSync
unzip Resources.zip FreeFileSync.png RealTimeSync.png
mkdir -p ~/.local/share/icons/hicolor/256x256/apps/
mv {FreeFileSync,RealTimeSync}.png ~/.local/share/icons/hicolor/256x256/apps/4. Create Desktop Entries
Create desktop entries to make FreeFileSync accessible from your application menu:
mkdir -p ~/.local/share/applications/Create a desktop file for FreeFileSync:
cat > ~/.local/share/applications/freefilesync.desktop << EOF
[Desktop Entry]
Name=FreeFileSync
Comment=Keep files and folders synchronized
Exec=~/Software/FreeFileSync/FreeFileSync %f
Terminal=false
Type=Application
Icon=FreeFileSync
MimeType=application/x-freefilesync-ffs;application/x-freefilesync-batch
Categories=Utility;FileTools;GTK;
StartupWMClass=FreeFileSync
StartupNotify=true
EOFAnd for RealTimeSync:
cat > ~/.local/share/applications/realtimesync.desktop << EOF
[Desktop Entry]
Name=RealtimeSync
Comment=Start synchronization in real time
Exec=~/Software/FreeFileSync/RealTimeSync %f
Terminal=false
Type=Application
Icon=RealTimeSync
Categories=Utility;FileTools;GTK;
MimeType=application/x-freefilesync-real
StartupNotify=true
EOF5. Add to PATH
Add FreeFileSync to your PATH to run it from any terminal:
echo "PATH=\$PATH:\$HOME/Software/FreeFileSync" >> ~/.bashrc
echo "PATH=\$PATH:\$HOME/Software/FreeFileSync" >> ~/.profile
source ~/.bashrcLog out and log back in to apply these changes.
Post-Installation Configuration
After installation, a few additional steps will ensure FreeFileSync runs optimally.
Enable Desktop Icons
The desktop icons may not be usable due to permission issues. To fix this:
- Right-click on each desktop icon
- Select “Allow Launching”
Alternatively, you can delete the desktop icons since FreeFileSync is accessible from the application menu.
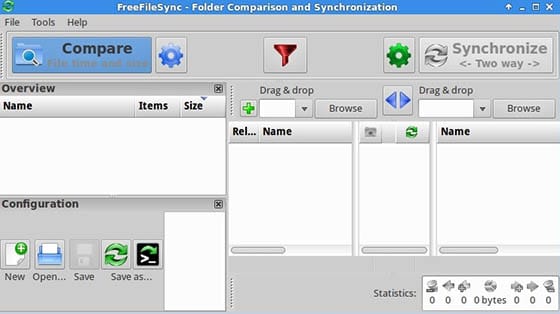
First-Time Configuration
When first launching FreeFileSync, consider configuring these recommended settings:
- Default comparison settings (binary or content)
- Default synchronization mode (Mirror, Two-Way, or Custom)
- Filter preferences for excluding unnecessary files
- Language and interface preferences
Basic Usage Tutorial
Now that FreeFileSync is installed, let’s learn how to use it for basic file synchronization.
Setting Up Source and Target Directories
- Launch FreeFileSync from the application menu or desktop icon
- Click the “Browse” button in the left panel to select your source directory
- Click the “Browse” button in the right panel to select your target directory
- The middle dropdown lets you select your synchronization method:
- Two-way: Updates both folders with the newest files
- Mirror: Makes the right folder identical to the left
- Update: Copies new/updated files from left to right
Comparing Folders
After selecting your directories, click the “Compare” button. FreeFileSync will analyze both locations and display differences between them.
The comparison results show:
- New files (files that exist in one location but not the other)
- Modified files (files that exist in both locations but have different content)
- Deleted files (files that were removed from one location)
Executing Synchronization
- Review the comparison results
- Adjust any specific file actions if needed
- Click the “Synchronize” button
- In the confirmation dialog, click “Start” to begin the synchronization
- A progress dialog will show the status of the operation
Once complete, both directories will be synchronized according to your chosen method.
Advanced Features
FreeFileSync offers several advanced features for power users:
Creating Batch Jobs
Batch jobs allow you to save your synchronization settings for future use:
- Set up your synchronization as usual
- Click “Save as Batch Job” from the File menu
- Choose a location to save the .ffs_batch file
- This file can be executed directly to run the same synchronization
Scheduling Automated Synchronization
You can schedule FreeFileSync batch jobs to run automatically:
- Create a batch job as described above
- Use Ubuntu’s built-in task scheduler (cron) to run it periodically:
crontab -eThen add a line like:
0 14 * * * env DISPLAY=:0 /path/to/FreeFileSync /path/to/your/job.ffs_batchThis will run your synchronization daily at 2:00 PM.
Cloud Storage Integration
FreeFileSync supports synchronization with various cloud storage services:
- Google Drive (via mounted folders)
- FTP/FTPS servers
- SFTP connections
- Network shares
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Here are solutions to common problems you might encounter:
Permission Problems
If you encounter permission errors during synchronization:
- Verify that you have read/write permissions for both source and target directories
- For system directories, you may need to run FreeFileSync with sudo
- Check file ownership and adjust if necessary
Application Crashes After Comparison
If FreeFileSync crashes after comparison, try removing the configuration file:
rm ~/.config/FreeFileSync/GlobalSettings.xmlThis often resolves the “std::bad_alloc” error.
Desktop Icons Not Working
If desktop icons don’t work:
- Right-click on the icon
- Select “Allow Launching”
- If that doesn’t work, try recreating the desktop entry files as shown in the manual installation section
Updating FreeFileSync
To update FreeFileSync to a newer version:
- Download the latest version from the official website
- Follow the same installation steps as before
- The new version will replace the old one, preserving your settings
For system-wide installations, use:
sudo ./FreeFileSync_NewVersion_Install.runFor manual installations, replace the entire directory and update desktop entries if necessary.
Uninstalling FreeFileSync
If you need to remove FreeFileSync:
For Official Installer Installations:
- The installer doesn’t provide a built-in uninstaller
- Remove the installation directory:
sudo rm -rf /opt/FreeFileSync - Remove desktop entries:
rm ~/.local/share/applications/freefilesync.desktop rm ~/.local/share/applications/realtimesync.desktop
For Manual Installations:
- Remove the FreeFileSync directory:
rm -rf ~/Software/FreeFileSync - Remove desktop entries:
rm ~/.local/share/applications/freefilesync.desktop rm ~/.local/share/applications/realtimesync.desktop - Remove icons:
rm ~/.local/share/icons/hicolor/256x256/apps/FreeFileSync.png rm ~/.local/share/icons/hicolor/256x256/apps/RealTimeSync.png
Congratulations! You have successfully installed FreeFileSync. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing FreeFileSync on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official FreeFileSync website.