How To Install Gitea on AlmaLinux 10

Gitea represents a powerful, lightweight solution for organizations seeking a self-hosted Git service that combines simplicity with enterprise-grade functionality. This modern version control system offers an compelling alternative to cloud-based platforms like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket, providing complete control over your code repositories while maintaining robust collaboration features.
Unlike heavyweight alternatives, Gitea delivers essential features including issue tracking, pull requests, code review, wikis, and continuous integration support within a minimal resource footprint. The platform’s Go-based architecture ensures exceptional performance and cross-platform compatibility, making it ideal for teams requiring reliable source code management without the overhead of complex enterprise solutions.
AlmaLinux 10 serves as an exceptional foundation for Gitea deployment, offering enterprise-grade stability through its Red Hat Enterprise Linux compatibility while maintaining open-source accessibility. This distribution provides long-term support, robust security features, and comprehensive package management that aligns perfectly with production Git hosting requirements.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the complete Gitea installation process on AlmaLinux 10, covering everything from initial system preparation through advanced configuration and security hardening. Following these detailed instructions will result in a fully functional, secure, and optimized Git service ready for production use.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Hardware Requirements
Successful Gitea deployment requires careful consideration of system resources to ensure optimal performance. For basic installations supporting small teams, allocate a minimum of 2GB RAM and 2 CPU cores with at least 20GB storage space. Production environments hosting multiple repositories and concurrent users should provision 4GB RAM or more, alongside 4+ CPU cores and 100GB+ SSD storage.
Storage requirements scale significantly with repository size and user activity. Plan for 10-50GB per active developer depending on project complexity and binary asset usage. SSD storage dramatically improves Git operations, particularly for large repositories with extensive history.
Software Prerequisites
AlmaLinux 10 installation with root access or sudo privileges forms the foundation for this deployment. Ensure your system includes Git version 2.0 or higher, typically available through standard package repositories. The installation process requires internet connectivity for downloading packages and the Gitea binary.
Database selection impacts both performance and maintenance requirements. SQLite offers simplicity for smaller deployments, while PostgreSQL or MySQL/MariaDB provide superior performance for larger installations. Consider your expected user base and repository volume when choosing database backends.
Network configuration must accommodate HTTP traffic on port 3000 (default) and SSH access on port 22. Firewall rules require adjustment to permit these connections while maintaining security boundaries.
Domain and SSL Planning
Production deployments benefit from proper domain configuration and SSL certificate implementation. Acquire a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) and configure DNS records pointing to your AlmaLinux server. SSL certificates from providers like Let’s Encrypt enhance security and user trust while enabling modern browser features.
Consider reverse proxy configuration using Nginx or Apache to handle SSL termination and provide additional security layers. This approach simplifies certificate management and enables advanced routing capabilities.
Pre-Installation System Setup
System Updates and Package Management
Begin with comprehensive system updates to ensure security patches and package compatibility. Execute the following commands to refresh your AlmaLinux 10 installation:
sudo dnf update -y
sudo dnf install epel-release -y
sudo dnf install wget curl git vim nano -yThe EPEL repository provides additional packages essential for Gitea operation. Verify Git installation and version compatibility:
git --versionEnsure the output displays Git version 2.0 or higher. Update Git if necessary using the package manager or compilation from source.
Database Setup
SQLite configuration requires minimal setup, making it ideal for development and small team environments. Create the database directory and set appropriate permissions:
sudo mkdir -p /var/lib/gitea/data
sudo chown -R git:git /var/lib/giteaFor PostgreSQL implementation, install the database server and create a dedicated user:
sudo dnf install postgresql postgresql-server -y
sudo postgresql-setup --initdb
sudo systemctl enable postgresql
sudo systemctl start postgresqlCreate a Gitea database and user with appropriate privileges:
sudo -u postgres psql
CREATE USER gitea WITH PASSWORD 'your_secure_password';
CREATE DATABASE gitea OWNER gitea;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE gitea TO gitea;
\qMySQL/MariaDB configuration follows similar patterns with database-specific commands. Choose the database system that aligns with your team’s expertise and infrastructure requirements.
User and Security Setup
Create a dedicated system user for Gitea operation, enhancing security through privilege separation:
sudo adduser --system --group --disabled-password --shell /bin/bash --home /home/git gitThis command creates a system user named git with restricted privileges and a home directory for SSH key management. The disabled password prevents direct login while maintaining system functionality.
Configure SSH key storage for Git operations:
sudo mkdir -p /home/git/.ssh
sudo chmod 700 /home/git/.ssh
sudo chown git:git /home/git/.sshGitea Installation Process
Downloading Gitea Binary
Gitea binary installation provides the most straightforward deployment method for AlmaLinux 10. Navigate to the official Gitea releases page to identify the latest stable version, then download the appropriate binary:
cd /tmp
wget https://dl.gitea.com/gitea/1.24.2/gitea-1.24.2-linux-amd64Replace the version number with the current stable release. Verify download integrity using provided checksums:
wget https://dl.gitea.com/gitea/1.24.2/gitea-1.24.2-linux-amd64.sha256
sha256sum -c gitea-1.24.2-linux-amd64.sha256Successful verification confirms file integrity and prevents corruption-related issues during installation.
Binary Installation and Permissions
Move the downloaded binary to the system path and configure executable permissions:
sudo mv gitea-1.24.2-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/gitea
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/giteaTest the Gitea binary to ensure proper installation:
gitea --versionThe command should display version information confirming successful installation. Create a symbolic link if desired for easier access:
sudo ln -s /usr/local/bin/gitea /usr/bin/giteaDirectory Structure Creation
Gitea requires specific directories for configuration, data storage, and logging. Create the necessary directory structure with appropriate permissions:
sudo mkdir -p /var/lib/gitea/{custom,data,log}
sudo chown -R git:git /var/lib/gitea
sudo chmod -R 750 /var/lib/giteaCreate the configuration directory with restricted access:
sudo mkdir /etc/gitea
sudo chown root:git /etc/gitea
sudo chmod 770 /etc/giteaThese permission settings ensure security while allowing Gitea to function properly. The configuration directory requires write access during initial setup but should be restricted afterward.
Systemd Service Configuration
Systemd integration enables automatic startup and service management. Create a service file for Gitea:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/gitea.serviceAdd the following configuration:
[Unit]
Description=Gitea (Git with a cup of tea)
After=syslog.target
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=git
Group=git
WorkingDirectory=/var/lib/gitea/
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/gitea web -c /etc/gitea/app.ini
Restart=always
Environment=USER=git HOME=/home/git GITEA_WORK_DIR=/var/lib/gitea
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetEnable and start the Gitea service:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable gitea
sudo systemctl start giteaVerify service status and troubleshoot any startup issues:
sudo systemctl status gitea
sudo journalctl -u gitea -fInitial Configuration and Setup
Firewall Configuration
AlmaLinux 10 firewall configuration requires opening specific ports for Gitea operation. Configure firewalld to permit HTTP and SSH traffic:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=3000/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=22/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadVerify firewall rules are active:
sudo firewall-cmd --list-allFor production deployments, consider restricting access to specific IP ranges or implementing port knocking for enhanced security.
Web-Based Initial Setup
Access the Gitea web interface using your server’s IP address and port 3000:
http://your-server-ip:3000The initial setup wizard guides you through essential configuration steps. Configure database settings according to your chosen backend:
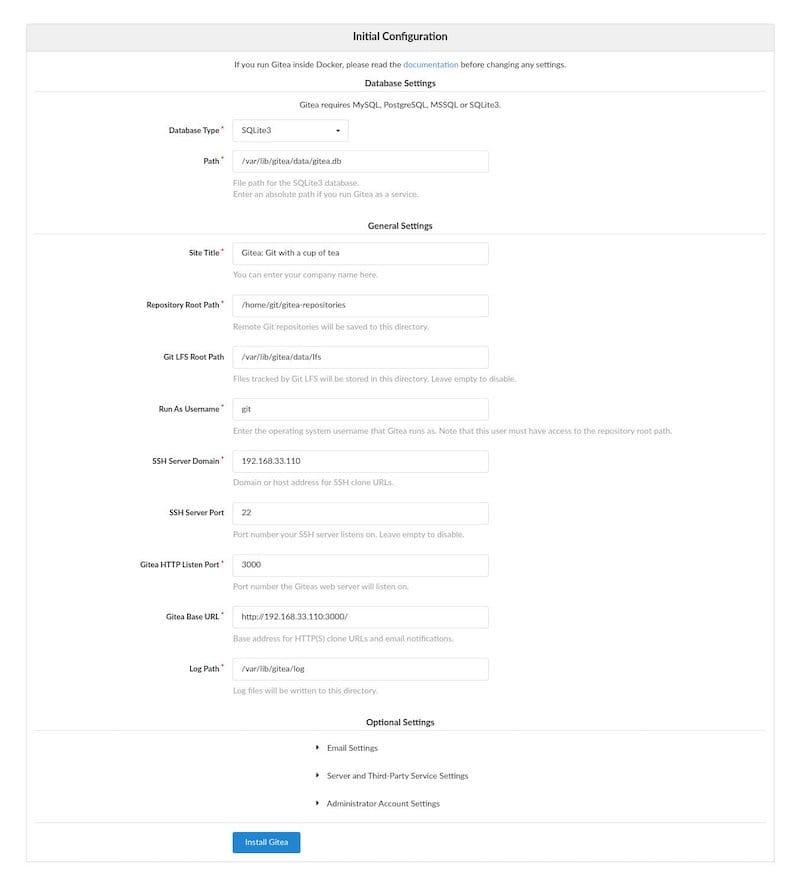
For SQLite:
- Database Type: SQLite3
- Path:
/var/lib/gitea/data/gitea.db
For PostgreSQL:
- Database Type: PostgreSQL
- Host:
127.0.0.1:5432 - Database Name:
gitea - Username:
gitea - Password:
your_secure_password
Configure application settings:
- Site Title: Your organization name
- Repository Root Path:
/var/lib/gitea/repositories - Git LFS Root Path:
/var/lib/gitea/lfs - Run As Username:
git - SSH Server Domain: Your server’s domain or IP
- SSH Port:
22 - HTTP Port:
3000 - Application URL:
http://your-domain:3000
Create an administrator account with strong credentials. This account will have full system access and should be secured appropriately.
Configuration File Customization
The app.ini configuration file controls Gitea behavior and security settings. After initial setup, modify critical security parameters:
sudo nano /etc/gitea/app.iniKey configuration adjustments include:
[security]
INSTALL_LOCK = true
SECRET_KEY = your-secret-key-here
[server]
DOMAIN = your-domain.com
HTTP_PORT = 3000
ROOT_URL = http://your-domain.com:3000/
DISABLE_SSH = false
SSH_PORT = 22
[database]
DB_TYPE = sqlite3
PATH = /var/lib/gitea/data/gitea.db
[log]
MODE = file
LEVEL = Info
ROOT_PATH = /var/lib/gitea/logRestart Gitea to apply configuration changes:
sudo systemctl restart giteaSecurity Hardening and Best Practices
Post-Installation Security
Security hardening begins with changing default ports and implementing access controls. Modify the HTTP port to reduce automated attacks:
[server]
HTTP_PORT = 8080Implement SSL/TLS encryption using Let’s Encrypt certificates:
sudo dnf install certbot python3-certbot-nginx -y
sudo certbot --nginx -d your-domain.comConfigure Nginx reverse proxy for SSL termination:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/gitea.confAdd the following configuration:
server {
listen 80;
server_name your-domain.com;
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name your-domain.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/your-domain.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/your-domain.com/privkey.pem;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
}Firewall and Network Security
Implement advanced firewall rules for enhanced security:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --remove-port=3000/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadConfigure fail2ban for brute force protection:
sudo dnf install fail2ban -y
sudo systemctl enable fail2ban
sudo systemctl start fail2banCreate a Gitea-specific fail2ban filter:
sudo nano /etc/fail2ban/filter.d/gitea.confAdd the following configuration:
[Definition]
failregex = .*Failed authentication attempt for .* from <HOST>
ignoreregex =Backup and Maintenance
Establish regular backup procedures for both data and configuration:
#!/bin/bash
# Gitea backup script
BACKUP_DIR="/backup/gitea"
DATE=$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S)
mkdir -p $BACKUP_DIR
# Backup database
sudo -u git /usr/local/bin/gitea dump -c /etc/gitea/app.ini -f $BACKUP_DIR/gitea-$DATE.zip
# Backup configuration
sudo cp /etc/gitea/app.ini $BACKUP_DIR/app.ini-$DATE
# Remove old backups (keep 30 days)
find $BACKUP_DIR -name "*.zip" -mtime +30 -deleteSchedule automatic backups using cron:
sudo crontab -e
0 2 * * * /path/to/backup-script.shAdvanced Configuration Options
Database Optimization
SQLite optimization for better performance:
[database]
DB_TYPE = sqlite3
PATH = /var/lib/gitea/data/gitea.db
SQLITE_TIMEOUT = 500
SQLITE_JOURNAL_MODE = WALPostgreSQL optimization for larger deployments:
[database]
DB_TYPE = postgres
HOST = 127.0.0.1:5432
NAME = gitea
USER = gitea
PASSWD = your_secure_password
MAX_IDLE_CONNS = 30
MAX_OPEN_CONNS = 300
CONN_MAX_LIFETIME = 3600Integration and Customization
LDAP integration for enterprise authentication:
[auth]
LDAP_ENABLED = true
LDAP_HOST = ldap.example.com
LDAP_PORT = 389
LDAP_BIND_DN = cn=admin,dc=example,dc=com
LDAP_USER_SEARCH_BASE = ou=users,dc=example,dc=com
LDAP_USER_FILTER = (&(objectClass=inetOrgPerson)(uid=%s))Webhook configuration for continuous integration:
[webhook]
ALLOWED_HOST_LIST = localhost,127.0.0.1,*.example.com
SKIP_TLS_VERIFY = false
DELIVER_TIMEOUT = 30Performance Tuning
Cache optimization for improved response times:
[cache]
ENABLED = true
ADAPTER = memory
INTERVAL = 60
HOST = 127.0.0.1:6379Session management configuration:
[session]
PROVIDER = file
PROVIDER_CONFIG = /var/lib/gitea/data/sessions
COOKIE_SECURE = true
COOKIE_NAME = gitea_session
GC_INTERVAL_TIME = 86400Troubleshooting Common Issues
Installation Problems
Binary compatibility issues often stem from architecture mismatches. Verify your system architecture:
uname -mDownload the appropriate binary for your architecture (amd64, arm64, etc.). Permission errors typically indicate incorrect ownership or file permissions:
sudo chown -R git:git /var/lib/gitea
sudo chmod -R 750 /var/lib/giteaDatabase connection failures require verification of database service status and credentials:
sudo systemctl status postgresql
sudo -u postgres psql -c "SELECT 1;"Configuration Issues
Web interface accessibility problems often relate to firewall or port binding issues. Check if Gitea is listening on the correct port:
sudo netstat -tlnp | grep gitea
sudo ss -tlnp | grep giteaSSH key authentication failures require proper key format and permissions:
sudo -u git ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -f /home/git/.ssh/id_rsa
sudo chmod 600 /home/git/.ssh/id_rsa
sudo chmod 644 /home/git/.ssh/id_rsa.pubPerformance and Maintenance Issues
Slow performance may indicate resource constraints or database optimization needs. Monitor system resources:
sudo htop
sudo iotop
sudo systemctl status giteaLog file management prevents disk space issues:
sudo logrotate -f /etc/logrotate.d/giteaCreate a logrotate configuration:
sudo nano /etc/logrotate.d/giteaAdd the following configuration:
/var/lib/gitea/log/*.log {
daily
missingok
rotate 52
compress
delaycompress
notifempty
create 640 git git
postrotate
systemctl reload gitea
endscript
}Testing and Validation
Functional Testing
Create test repositories to verify core functionality:
# As git user
sudo -u git git init --bare /var/lib/gitea/repositories/test.gitTest SSH access with your private key:
ssh -T git@your-domain.comSuccessful authentication should display a welcome message from Gitea.
Clone and push operations validate repository functionality:
git clone git@your-domain.com:username/repository.git
cd repository
echo "# Test Repository" > README.md
git add README.md
git commit -m "Initial commit"
git push origin mainSecurity Validation
Access control testing ensures proper user permissions and repository visibility. Create test users with different permission levels and verify access restrictions.
SSL certificate validation confirms proper encryption:
openssl s_client -connect your-domain.com:443 -servername your-domain.comRun security scans using tools like nmap or nessus to identify potential vulnerabilities:
nmap -sS -O your-domain.comCongratulations! You have successfully installed Gitea. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Gitea on your AlmaLinux OS 10 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Gitea website.