How To Install Gitea on Rocky Linux 10

Managing your own Git repository infrastructure has become essential for developers and organizations seeking complete control over their source code. Gitea emerges as a powerful, lightweight alternative to hosted Git services, offering enterprise-grade features without the complexity of larger platforms. This comprehensive guide demonstrates how to install Gitea on Rocky Linux 10, transforming your server into a robust, self-hosted Git platform.
Rocky Linux 10 provides the perfect foundation for hosting Gitea, combining enterprise stability with cutting-edge performance. By following this detailed installation process, you’ll establish a production-ready Git server capable of supporting multiple users, repositories, and collaborative workflows. Whether you’re a system administrator, DevOps engineer, or development team lead, this tutorial provides everything needed to deploy Gitea successfully.
What is Gitea? Understanding the Self-Hosted Git Platform
Gitea represents a community-driven fork of Gogs, designed to provide a painless self-hosted Git service. Written entirely in Go programming language, Gitea delivers exceptional performance while maintaining minimal resource requirements. The platform offers comprehensive version control capabilities, including repository management, issue tracking, pull requests, wikis, and continuous integration support.
Unlike heavyweight alternatives such as GitLab, Gitea focuses on simplicity and speed. The lightweight architecture enables deployment on modest hardware configurations while supporting thousands of repositories. Key features include built-in package registry support, organizational structures, team management, and extensive API functionality for custom integrations.
The self-hosted approach provides complete data sovereignty, eliminating dependency on external services. Organizations benefit from enhanced security, customizable workflows, and unlimited private repositories without subscription costs. Gitea’s active development community ensures regular updates, security patches, and feature enhancements, making it an ideal choice for production environments.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Before beginning the Gitea installation process, ensure your Rocky Linux 10 system meets minimum requirements. A fresh installation with at least 2GB RAM and 20GB available storage provides adequate resources for small to medium deployments. Larger organizations should consider 4GB RAM and 100GB+ storage for optimal performance.
Administrative privileges are essential for completing this installation. Root access or sudo capabilities enable system-level configurations, service management, and security hardening. Verify your user account possesses necessary permissions before proceeding with the installation steps.
Network connectivity requirements include outbound internet access for downloading packages and Gitea binaries. The default Gitea installation utilizes port 3000 for web interface access, though this can be customized during configuration. If implementing reverse proxy configurations, ensure ports 80 and 443 remain available for HTTP/HTTPS traffic.
Database selection significantly impacts deployment complexity. SQLite provides the simplest setup option, requiring no additional database server installation. PostgreSQL offers superior performance for larger deployments, while MariaDB/MySQL provides familiar administration interfaces for many administrators. Consider your team’s expertise and expected repository volume when selecting database platforms.
Domain name configuration, while optional, enhances professional deployment aesthetics. Configure DNS records pointing to your server’s IP address before beginning installation. SSL certificate preparation streamlines post-installation security hardening processes.
Preparing the Rocky Linux 10 Environment
System preparation begins with comprehensive package updates ensuring the latest security patches and system libraries. Execute the following command to refresh package repositories and install available updates:
sudo dnf update -yThis process may require several minutes depending on system age and internet connectivity. Reboot your system if kernel updates were installed to ensure all changes take effect properly.
Essential dependency installation includes Git version control system, which Gitea requires for core functionality. Install Git and verify the installation using these commands:
sudo dnf install git wget curl tar -y
git --versionThe output should display Git version information, confirming successful installation. Additional packages including wget, curl, and tar support binary downloading and extraction processes required during Gitea installation.
Firewall configuration ensures proper network access while maintaining security. Rocky Linux 10 utilizes firewalld for network traffic management. Configure firewall rules to allow Gitea’s default port:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3000/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
sudo firewall-cmd --list-portsSELinux considerations require attention for proper Gitea operation. While disabling SELinux simplifies installation, production environments benefit from proper SELinux policy configuration. Temporarily set SELinux to permissive mode during installation:
sudo setenforce 0
sudo sed -i 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=permissive/' /etc/selinux/configCreating a dedicated system user enhances security by isolating Gitea processes from system-level privileges. Execute the following command to create the git user account:
sudo adduser --system --shell /bin/bash --comment 'Git Version Control' --create-home --home-dir /home/git gitThis command establishes a system account with restricted privileges specifically for running Gitea services. The dedicated user approach follows security best practices by limiting potential attack surfaces.
Database Setup and Configuration
SQLite Setup (Recommended for Beginners)
SQLite provides the simplest database option for Gitea installations, requiring no additional server configuration or maintenance. Rocky Linux 10 includes SQLite support in base repositories, making installation straightforward:
sudo dnf install sqlite -ySQLite stores data in single files, simplifying backup and migration processes. Performance remains excellent for repositories supporting up to 100 concurrent users. The embedded database approach eliminates network latency and reduces system complexity significantly.
Create the database directory structure with appropriate permissions:
sudo mkdir -p /var/lib/gitea/data
sudo chown -R git:git /var/lib/giteaPostgreSQL Setup (Advanced Option)
PostgreSQL offers superior scalability for larger Gitea deployments requiring robust concurrent access support. Install PostgreSQL server and client packages:
sudo dnf install postgresql postgresql-server postgresql-contrib -yInitialize the PostgreSQL database cluster and enable automatic startup:
sudo postgresql-setup --initdb
sudo systemctl enable postgresql
sudo systemctl start postgresqlCreate dedicated database and user for Gitea with appropriate privileges:
sudo -u postgres psql
CREATE DATABASE gitea;
CREATE USER gitea WITH PASSWORD 'secure_password_here';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE gitea TO gitea;
\qConfigure PostgreSQL authentication by editing /var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf:
sudo nano /var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.confAdd the following line for local Gitea connections:
local gitea gitea md5Restart PostgreSQL to apply configuration changes:
sudo systemctl restart postgresqlMariaDB/MySQL Alternative
MariaDB provides familiar MySQL-compatible database services for administrators comfortable with MySQL administration. Install MariaDB server packages:
sudo dnf install mariadb-server mariadb -y
sudo systemctl enable mariadb
sudo systemctl start mariadbSecure the MariaDB installation using the built-in security script:
sudo mysql_secure_installationFollow the prompts to set root password, remove anonymous users, and disable remote root access. Create Gitea database and user account:
sudo mysql -u root -p
CREATE DATABASE gitea CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
CREATE USER 'gitea'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'secure_password_here';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON gitea.* TO 'gitea'@'localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;Installing Gitea from Binary
Downloading the latest Gitea binary ensures access to newest features and security updates. Navigate to the Gitea releases page or use wget to download directly:
cd /tmp
wget -O gitea https://dl.gitea.io/gitea/1.21.1/gitea-1.21.1-linux-amd64Verify the downloaded binary integrity by checking file size and permissions. The binary should be approximately 100MB and executable:
ls -la gitea
file giteaInstall the Gitea binary to system-wide location with proper permissions:
sudo mv gitea /usr/local/bin/gitea
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/giteaVerify successful installation by checking Gitea version information:
gitea --versionThe output should display version details confirming proper binary installation and execution capabilities.
Create essential directory structure for Gitea data, configuration, and logging:
sudo mkdir -p /var/lib/gitea/{custom,data,log}
sudo mkdir -p /etc/gitea
sudo chown -R git:git /var/lib/gitea/
sudo chown -R git:git /etc/gitea/
sudo chmod -R 750 /var/lib/gitea/
sudo chmod 770 /etc/gitea/These directories organize Gitea files according to Linux Filesystem Hierarchy Standard, ensuring proper system integration and maintainability.
Systemd Service Configuration
Creating a systemd service enables automatic Gitea startup and proper process management. Create the service definition file:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/gitea.serviceInsert the following service configuration:
[Unit]
Description=Gitea (Git with a cup of tea)
After=syslog.target
After=network.target
After=postgresql.service
After=mariadb.service
After=mysqld.service
[Service]
Type=simple
User=git
Group=git
WorkingDirectory=/var/lib/gitea/
RuntimeDirectory=gitea
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/gitea web --config /etc/gitea/app.ini
Restart=always
Environment=USER=git HOME=/home/git GITEA_WORK_DIR=/var/lib/gitea
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetReload systemd configuration to recognize the new service:
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadEnable and start Gitea service:
sudo systemctl enable gitea
sudo systemctl start giteaVerify service status and troubleshoot any startup issues:
sudo systemctl status gitea
sudo journalctl -u gitea --no-pagerSuccessful startup should display active (running) status with no error messages in the service logs.
Initial Gitea Configuration via Web Interface
Access the Gitea web interface by opening your browser and navigating to http://your-server-ip:3000. The initial setup wizard guides you through essential configuration options.
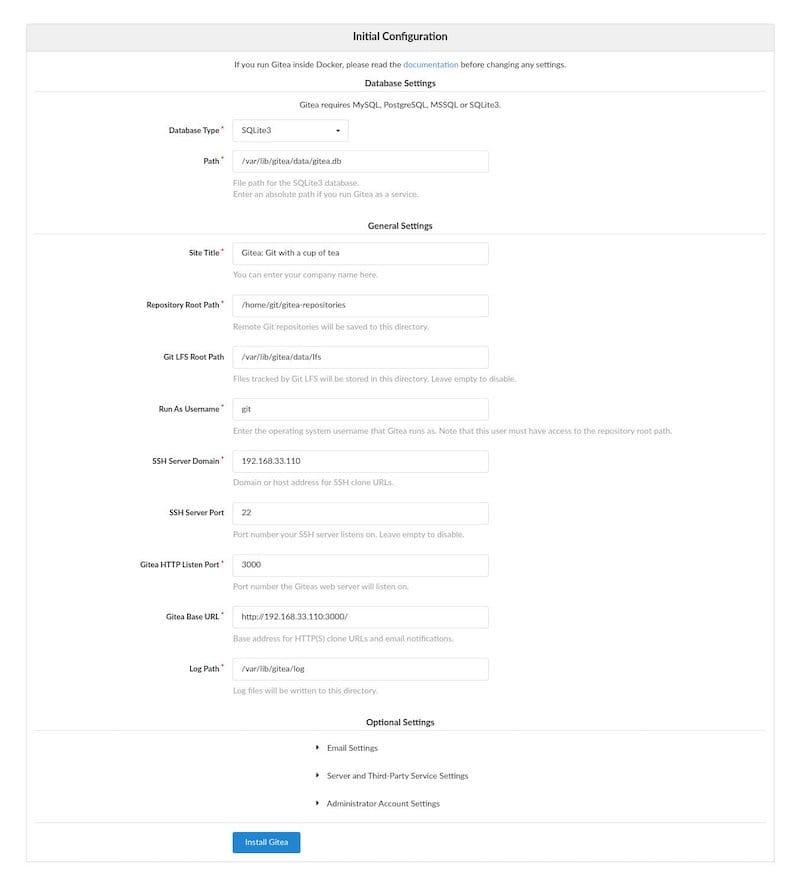
Database configuration represents the first critical setup step. Select your chosen database type from the dropdown menu:
- SQLite3: Select for simple installations, specify
/var/lib/gitea/data/gitea.dbas the database path - PostgreSQL: Enter
127.0.0.1:5432for host,giteafor database name, username, and the password created earlier - MySQL/MariaDB: Use
127.0.0.1:3306for host, with appropriate database credentials
General settings configuration customizes your Gitea installation for organizational requirements:
- Site Title: Enter your organization or project name
- Repository Root Path: Verify
/var/lib/gitea/data/gitea-repositoriesis correct - Git LFS Root Path: Set to
/var/lib/gitea/data/lfsfor large file support - SSH Server Domain: Enter your server’s domain name or IP address
- SSH Port: Confirm port 22 or specify custom SSH port
- HTTP Port: Verify port 3000 or customize as needed
Administrator account creation establishes initial administrative access. Choose a strong username and password for the administrative account. This account possesses system-wide privileges for user management, repository administration, and system configuration.
Security settings enhance installation protection:
- Disable Self-Registration: Prevents unauthorized account creation
- Enable Captcha: Reduces automated spam registrations
- Require Sign-In to View Pages: Restricts anonymous access
- Default Branch: Set to
mainfollowing modern Git practices
Email configuration enables notification functionality. Configure SMTP settings for your email provider or leave blank for local-only installations without email notifications.
Complete the installation by clicking the “Install Gitea” button. The process may take several minutes as Gitea initializes the database and creates initial configuration files.
Security Hardening and Best Practices
Firewall optimization restricts network access to essential services only. If implementing reverse proxy configurations, close direct access to port 3000:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-port=3000/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=80/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=443/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadSSL/TLS certificate implementation encrypts client-server communications. Consider using Let’s Encrypt for free SSL certificates or upload commercial certificates to your reverse proxy configuration.
SSH key management enhances authentication security. Configure SSH keys for Git operations while disabling password authentication:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_configSet PasswordAuthentication no and restart SSH service:
sudo systemctl restart sshdRegular backup strategies protect against data loss. Create automated backup scripts for Gitea data and database:
#!/bin/bash
BACKUP_DIR="/backup/gitea/$(date +%Y%m%d)"
mkdir -p $BACKUP_DIR
tar -czf $BACKUP_DIR/gitea-data.tar.gz /var/lib/gitea/
tar -czf $BACKUP_DIR/gitea-config.tar.gz /etc/gitea/Update procedures maintain security and feature currency. Monitor Gitea releases and establish update schedules for critical security patches.
Access control configuration implements least-privilege principles. Review user permissions regularly and implement organizational structures for complex team environments.
Post-Installation Tasks and Configuration
Creating your first repository validates installation success. Navigate to the Gitea interface and click “New Repository.” Configure repository name, description, and visibility settings according to project requirements.
User registration management controls access to your Gitea instance. Navigate to Admin Panel > Users to review registration policies and manage user accounts. Implement organizational structures for team-based development workflows.
Git hooks configuration enables custom automation triggers. Create server-side hooks in repository directories for automated testing, deployment, or notification systems.
Webhook integration connects Gitea with external services like continuous integration platforms, notification systems, or project management tools. Configure webhooks in repository settings for automated workflow triggers.
Branch protection rules enforce code quality standards. Configure protected branches requiring pull request reviews, status checks, or administrative overrides for critical repositories.
Performance optimization includes adjusting worker processes, cache settings, and database connections based on expected usage patterns. Monitor resource utilization and adjust configuration accordingly.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Service startup failures often indicate permission or configuration problems. Check systemd logs for specific error messages:
sudo journalctl -u gitea -fDatabase connection issues require verification of credentials and network connectivity. Test database connections manually using command-line clients.
Permission problems frequently affect file access and repository operations. Verify ownership and permissions for Gitea directories:
sudo chown -R git:git /var/lib/gitea/
sudo chown -R git:git /etc/gitea/Port accessibility issues may indicate firewall blocks or service binding problems. Verify port binding using netstat:
sudo netstat -tlnp | grep :3000Log analysis provides detailed error information for complex troubleshooting scenarios. Gitea logs are located in /var/lib/gitea/log/ directory.
Configuration file corruption can prevent proper startup. Review /etc/gitea/app.ini for syntax errors or restore from backup copies.
Maintenance and Updates
Backup scheduling ensures data protection through automated procedures. Implement weekly full backups and daily incremental backups using cron jobs:
0 2 * * 0 /usr/local/bin/gitea-backup.shUpdate procedures require careful planning to prevent service disruption. Always backup data before updating Gitea binaries. Test updates in development environments before production deployment.
Database maintenance includes regular optimization, index rebuilding, and cleanup procedures. PostgreSQL and MariaDB require periodic vacuum and optimization operations.
Log rotation prevents disk space exhaustion from extensive logging. Configure logrotate for Gitea log files:
sudo nano /etc/logrotate.d/giteaSecurity monitoring includes regular vulnerability assessments, access log review, and security patch application. Subscribe to Gitea security announcements for prompt update notifications.
Alternative Installation Methods
Docker deployment simplifies installation and management for containerized environments. Docker provides consistent deployment across different Linux distributions:
docker run -d --name=gitea -p 3000:3000 -p 222:22 -v gitea-data:/data gitea/gitea:latestPackage manager installations utilize distribution-specific packages when available. Some third-party repositories provide RPM packages for Rocky Linux installations.
Comparison of methods reveals trade-offs between simplicity, control, and maintenance requirements. Binary installations provide maximum control, while Docker offers simplified management and updates.
Container orchestration using Kubernetes or Docker Compose enables scalable, production-ready deployments with automated failover and load balancing capabilities.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Gitea. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Gitea on your Rocky Linux 10 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Gitea website.