
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Gitea on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS. For those of you who didn’t know, Gitea is a free, open-source, and self-hosted version control system alternative to GitHub and GitLab. Gitea comes with a rich set of features including time tracking, repository branching, issues tracking, file locking, merging, and much more. Gitea can be installed on all popular operating systems like Windows, macOS, Linux, and ARM.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of Gitea on the Ubuntu 18.04 server.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Ubuntu 18.04, and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Gitea on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
Step 1. First, make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date by running the following apt commands in the terminal.
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade sudo apt install sqlite3
Step 2. Installing Git.
Install Git on your server using the following command:
sudo apt install git
Step 3. Installing Gitea on Ubuntu 18.04.
First, you will need to download the latest version of the Gitea binary from the Git repository. You can download it with the following command:
sudo wget -O /tmp/gitea https://dl.gitea.io/gitea/1.10.2/gitea-1.10.2-linux-amd64
Copy the binary to a global location:
sudo mv /tmp/gitea /usr/local/bin
Make the binary executable:
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/gitea
Next, create the directories and set the required permissions and ownership:
sudo mkdir -p /var/lib/gitea/{custom,data,indexers,public,log}
sudo chown git: /var/lib/gitea/{data,indexers,log}
sudo chmod 750 /var/lib/gitea/{data,indexers,log}
sudo mkdir /etc/gitea
sudo chown root:git /etc/gitea
sudo chmod 770 /etc/gitea
Step 4. Create Systemd Service file for Gitea.
Next, you will need to create a systemd service file to manage the Gitea service. You can create it with the following command:
sudo wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/go-gitea/gitea/master/contrib/systemd/gitea.service -P /etc/systemd/system/
Then, enable and start the Gitea service:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable --now gitea
Step 5. Accessing Gitea Web Interface.
By default, Gitea listens for connections on port 3000 on all network interfaces, Open your browser, type http://YOUR_DOMAIN_OR_IP_ADDRESS:3000
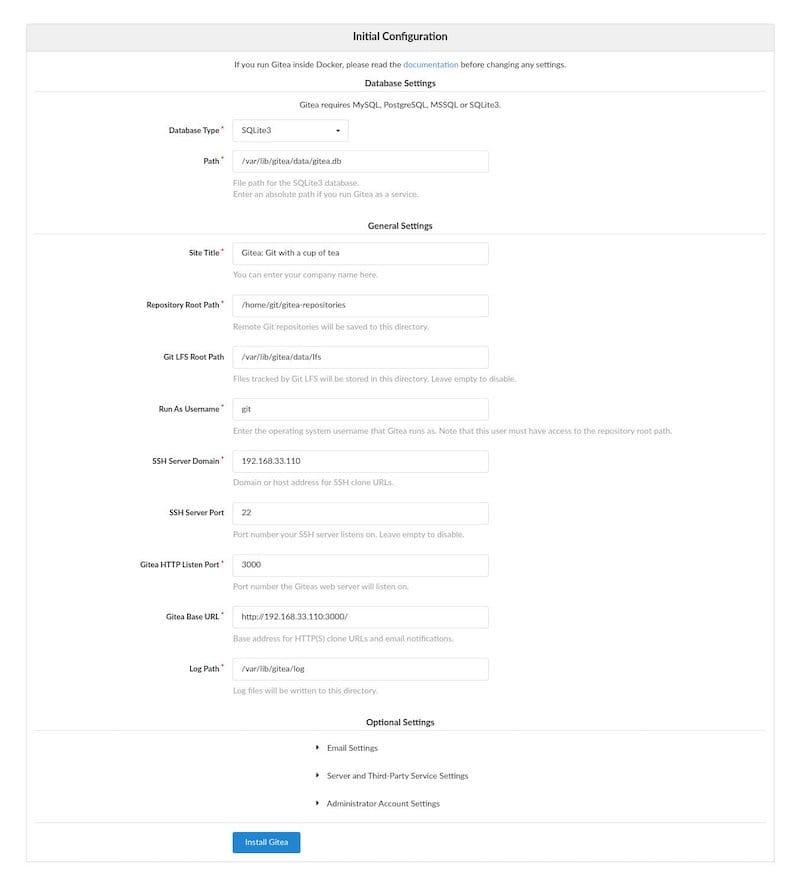
Database Settings:
- Database Type: SQLite3
- Path: Use an absolute path,
/var/lib/gitea/data/gitea.db
Application General Settings:
- Site Title: Enter your organization name.
- Repository Root Path: Leave the default
/home/git/gitea-repositories. - Git LFS Root Path: Leave the default
/var/lib/gitea/data/lfs. - Run As Username: git
- SSH Server Domain: Enter your domain or server IP address.
- SSH Port: 22, change it if SSH is listening on another Port
- Gitea HTTP Listen Port: 3000
- Gitea Base URL: Use HTTP and your domain or server IP address.
- Log Path: Leave the default
/var/lib/gitea/log
Once installation is complete, hit the “Install Gitea” button. The installation is instant. When completed you will be redirected to the login page.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Gitea. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Gitea on your Ubuntu 18.04 LTS system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official Gitea website.