How To Install Gitea on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Gitea on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS. For those of you who didn’t know, Gitea is a free and open-source version control system similar to GitHub. However, it is more straightforward, lightweight, and easy to configure as compared to GitLab. One can use it across any major OS like Linux, Windows, macOS, etc.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Gitea open-source version control system on Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish). You can follow the same instructions for Ubuntu 22.04 and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint, Elementary OS, Pop!_OS, and more as well.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Ubuntu 22.04, 20.04, and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Gitea on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Jammy Jellyfish
Step 1. First, make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date by running the following apt commands in the terminal.
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade sudo apt install software-properties-common apt-transport-https wget ca-certificates gnupg2 ubuntu-keyring
Step 2. Installing MariaDB.
Gitea needs a server for storing the data or its content. To store data from Gitea, we will use MariaDB. Now run the following command below to install MariaDB to your Ubuntu system:
sudo apt install mariadb-server mariadb-client
After successfully installation, enable MariaDB (to start automatically upon system boot), start, and verify the status using the commands below:
sudo systemctl enable mariadb sudo systemctl start mariadb sudo systemctl status mariadb
Confirm the installation and check the installed build version of MariaDB:
mariadb --version
By default, MariaDB is not hardened. You can secure MariaDB using the mysql_secure_installation script. you should read each step carefully which will set a root password, remove anonymous users, disallow remote root login, and remove the test database and access to secure MariaDB:
mysql_secure_installation
Now log in to the MariaDB shell:
mysql -u root -p
Next, create a database using the following command:
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE giteadb; MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE USER 'giteauser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'your_strong_passwd'; MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL ON giteadb.* TO 'giteauser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'your_strong_passwd' WITH GRANT OPTION; MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; MariaDB [(none)]> EXIT;
Step 3. Installing Git.
By default, Git is available on Ubuntu 22.04 base repository. Now run the following command below to install the latest version of Git on your Ubuntu system:
sudo apt install git
Confirm the installation and check the installed build version of Git:
git --version
Next, we create a Git user to run Gitea services:
sudo adduser --system --group --disabled-password --shell /bin/bash --home /home/git --gecos 'Git Version Control' git
Step 4. Installing Gitea on Ubuntu 22.04.
By default, Gitea is not available on Ubuntu 22.04 base repository. Now run the following command below to download the latest version of Gitea to your Ubuntu system:
wget -O /tmp/gitea https://dl.gitea.io/gitea/1.16.8/gitea-1.16.8-linux-amd64
Move the Gitea binary file to ‘/usr/local/bin‘ and make the binary executable file:
mv /tmp/gitea /usr/local/bin chmod +x /usr/local/bin/gitea
Next, we create the directory structure and set the required permissions and ownership:
mkdir -p /var/lib/gitea/{custom,data,indexers,public,log}
chown git: /var/lib/gitea/{data,indexers,log}
chmod 750 /var/lib/gitea/{data,indexers,log}
mkdir /etc/gitea
chown root:git /etc/gitea
chmod 770 /etc/gitea
Step 5. Create Systemd Service File.
Now download the file to the “/etc/systemd/system/” directory using the following command below:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/go-gitea/gitea/main/contrib/systemd/gitea.service -P /etc/systemd/system/
Then, reload systemd and start the Gitea service with the following command:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable --now gitea sudo systemctl status gitea
Step 6. Configure Firewall.
Ubuntu 22.04 has ufw a firewall running by default. Now we enable connection through ports 3000:
sudo ufw allow 3000/tcp sudo ufw enable sudo ufw status
Step 7. Accessing Gitea Web Interface.
Once completely successful installed, now open your web browser and access the Gitea web UI using the URL http://your-ip-address:3000. You will be taken to the Gitea dashboard as shown below:
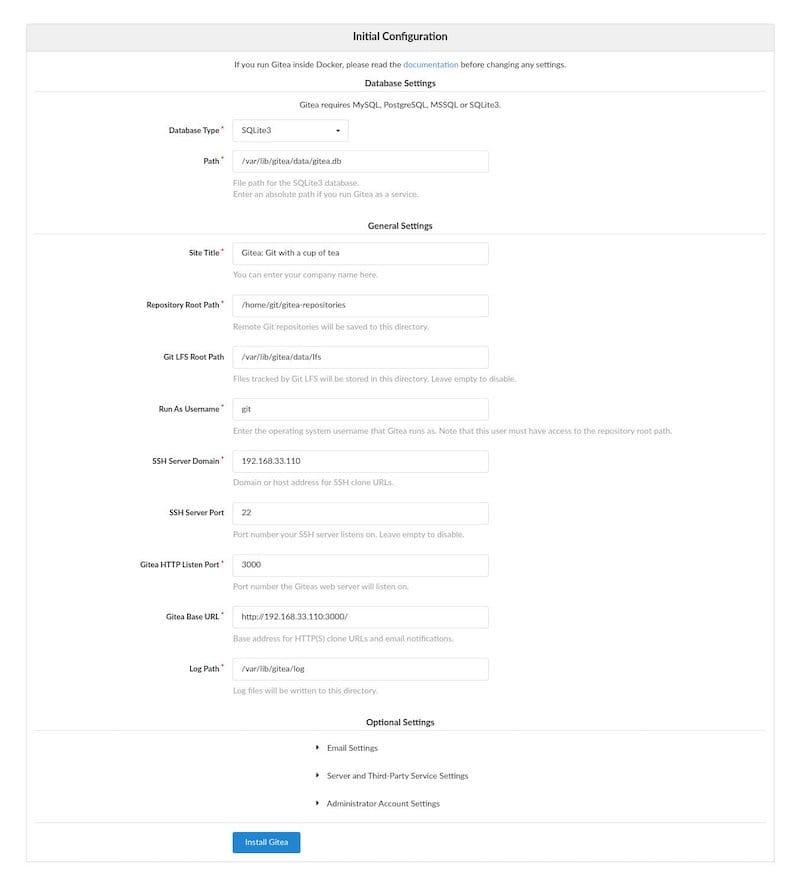
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Gitea. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Gitea open-source version control system on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Jammy Jellyfish system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Gitea website.