
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Gitlab on your CentOS 7. For those of you who didn’t know, GitLab is a powerful, open-source platform that provides a complete solution for version control, collaboration, and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) for software development teams. By self-hosting GitLab on CentOS 7, you can enjoy the benefits of a secure, scalable, and customizable platform tailored to your organization’s needs.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of Gitlab on a CentOS 7 server.
GitLab Features
- GitLab provides you a web interface to edit files, and directories and create merge requests.
- It is self-hosted, hence you have full control over your server and the source code hosted inside.
- It provides LDAP user authentication and has a two-factor authentication system which makes the application very secure.
- You can insert your own branding on the login page and it also supports project import from GitHub and other sources to GitLab.
- It has lots of features like code reviews, issue tracking, activity feeds, and an inbuilt wiki.
- It provides fine workflow management which gives you the ability to create groups for a project, the ability to fork a repository as well as it provides the ability to manage large binaries with git LFS.
- GitLab comes with GitLab CI for continuous integration. You can also Docker with GitLab CI.
- It’s free and open source hence you won’t have to deal with any licensing issues.
Install Gitlab on CentOS 7
Step 1. Start by updating your system’s packages to ensure you have the latest security patches and bug fixes. Open a terminal and run the following command:
yum clean all yum -y update
This command will update all installed packages on your system.
Step 2. Install and Configure the necessary dependencies.
GitLab requires several dependencies to be installed before proceeding with the installation. Run the following command to install the necessary packages:
yum install postfix openssh-server
Now enable and start the ssh and post-fix services as follows:
systemctl enable sshd postfix systemctl start sshd postfix
Step 3. Installing GitLab.
Use the following command to install GitLab packages on the server:
curl -s https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/gitlab/gitlab-ce/script.deb.sh | sudo bash
Next, install the GitLab Community Edition (CE) package:
sudo yum install gitlab-ce
If you are not comfortable installing the repository through a piped script, you can find the entire script here.
During the installation process, you’ll be prompted to specify the external URL for your GitLab instance. Enter the domain name or IP address of your server, followed by the default GitLab port (80 for HTTP or 443 for HTTPS).
Step 4. Configure GitLab on the Server.
Now start the configuration by using the gitlab-ctl command:
gitlab-ctl reconfigure
Step 5. C9nfigure Firewall.
Next, configure the firewall to allow SSH, HTTP, and HTTPS traffic:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=ssh sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Step 6. Accessing Gitlab Web UI.
Gitlab will be available on HTTP port 80 by default. Open your favorite browser and navigate to http://yourdomain.com/ or http://server-ip and then login with a “root” user and with an initial password “5iveL!fe”. If you are using a firewall, please open port 80 to enable access to the control panel.
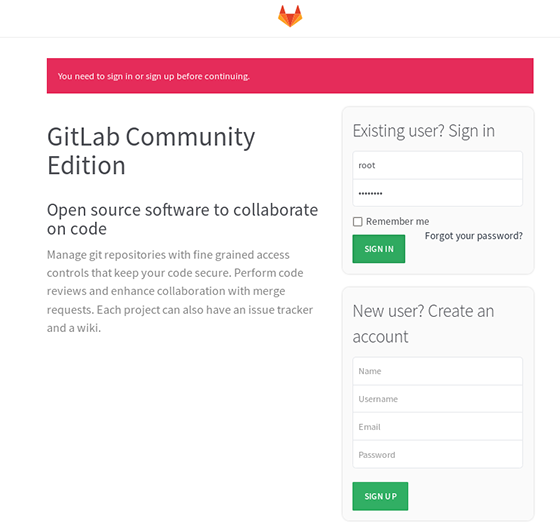
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Gitlab. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Gitlab on CentOS 7 server. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official Gitlab website.