How To Install GNS3 on Debian 13

Network simulation has become an essential skill for IT professionals, network engineers, and certification candidates. GNS3 stands out as the premier network simulation platform, offering comprehensive virtualization capabilities for Cisco, Juniper, and other network devices. This detailed guide walks through the complete installation process of GNS3 on Debian 13, ensuring a smooth setup experience.
Debian 13 provides an excellent foundation for running GNS3 due to its stability, security, and extensive package repositories. Whether you’re preparing for CCNA certification, designing complex network topologies, or testing network configurations, this installation guide covers everything needed to get GNS3 running optimally on your Debian system.
Understanding GNS3 and Its Components
What is GNS3?
GNS3 (Graphical Network Simulator-3) represents a powerful network simulation tool that enables users to design, configure, and test network topologies without physical hardware. The platform supports multiple device types including routers, switches, firewalls, and virtual machines, making it invaluable for network professionals and students alike.
The simulator excels in providing hands-on experience with real network operating systems. Users can load actual Cisco IOS images, configure routing protocols, implement security policies, and troubleshoot network issues in a controlled virtual environment. This practical approach significantly enhances learning outcomes compared to theoretical study alone.
Network engineers utilize GNS3 for proof-of-concept deployments, testing network changes before production implementation, and creating training scenarios for team members. The platform’s flexibility allows integration with external networks, enabling hybrid physical-virtual topologies.
GNS3 Architecture Components
GNS3 operates through a modular architecture consisting of several interconnected components. The GNS3 GUI provides the graphical interface where users design network topologies, configure devices, and monitor network operations. This Qt-based application offers intuitive drag-and-drop functionality for rapid topology creation.
The GNS3 Server handles the backend processing, managing virtual machines, coordinating device interactions, and processing network traffic. The server can run locally on the same machine as the GUI or on remote systems for distributed computing scenarios.
Emulation engines form the core of GNS3’s functionality. QEMU provides virtual machine capabilities for running various operating systems, while Dynamips specifically emulates Cisco router hardware. VPCS (Virtual PC Simulator) creates lightweight endpoint devices for testing connectivity and basic network operations.
Supporting virtualization technologies include KVM for hardware acceleration and libvirt for virtual machine management. These components work together to deliver high-performance network simulation capabilities on Linux systems.
System Requirements and Prerequisites
Hardware Requirements
Successful GNS3 operation requires adequate system resources. The minimum CPU specification calls for a dual-core processor with virtualization support (Intel VT-x or AMD-V). However, quad-core or higher processors deliver significantly better performance, especially when running multiple virtual devices simultaneously.
RAM requirements start at 4GB minimum, though 8GB or more is strongly recommended for complex topologies. Each virtual router typically consumes 128-512MB of memory, while virtual machines may require 1-4GB depending on the operating system. Insufficient RAM leads to poor performance and system instability.
Storage considerations include at least 10GB free space for GNS3 installation and basic device images. Complex topologies with multiple VM images may require 50GB or more. SSD storage provides faster boot times and improved overall performance compared to traditional hard drives.
Verify virtualization support by running egrep -c '(vmx|svm)' /proc/cpuinfo. A non-zero result indicates hardware virtualization capabilities essential for optimal GNS3 performance.
Software Prerequisites
Debian 13 installation should be current and stable before proceeding with GNS3 setup. Verify the system version using cat /etc/debian_version to confirm Debian 13 installation.
Python 3.8 or newer is required for GNS3 operation. Check the installed version with python3 --version. Most Debian 13 installations include Python 3.10 or later by default, meeting GNS3 requirements.
Virtualization capabilities must be properly configured at the system level. The KVM kernel module should be available and loaded. Verify using lsmod | grep kvm to check for kvm_intel or kvm_amd modules.
Network interface configuration affects GNS3’s ability to connect simulated networks to external systems. Ensure the primary network interface is properly configured and functioning before beginning installation.
User Permissions and Groups
GNS3 requires specific user permissions for accessing virtualization resources. The current user must belong to the libvirt group to manage virtual machines through libvirt. Additionally, kvm group membership enables direct access to KVM acceleration features.
Security considerations include understanding that GNS3 operations require elevated privileges for certain functions. The installation process involves adding the current user to system groups that provide access to virtualization hardware and network interfaces.
Proper group membership ensures GNS3 can create and manage virtual networks, access hardware acceleration, and perform network bridge operations without requiring constant sudo elevation.
Pre-Installation System Preparation
System Updates
Begin the installation process by ensuring the Debian 13 system is fully updated. Execute sudo apt update to refresh package repository information and download the latest package lists from configured sources.
Follow with sudo apt upgrade -y to install available package updates. This process may take several minutes depending on the number of pending updates. System updates ensure compatibility with GNS3 components and resolve potential security vulnerabilities.
Consider rebooting the system after major updates, particularly if kernel updates were installed. A fresh boot ensures all updated components are properly loaded and configured.
Verify system stability by checking system logs using dmesg | tail -20 for any error messages or warnings that might affect the installation process.
Installing Essential Dependencies
GNS3 installation requires numerous supporting packages and libraries. Begin by installing Python development tools and package management utilities:
sudo apt install -y python3-dev python3-pip python3-venv python3-setuptoolsInstall PyQt5 libraries essential for the GNS3 graphical interface:
sudo apt install -y python3-pyqt5 python3-pyqt5.qtsvg python3-pyqt5.qtwebsocketsAdd virtualization components required for running virtual machines and network devices:
sudo apt install -y qemu-kvm qemu-utils libvirt-daemon-system libvirt-clients bridge-utilsInstall additional networking utilities for advanced GNS3 functionality:
sudo apt install -y uml-utilities virt-manager cpu-checkerThese packages provide the foundation for GNS3 operation, including virtual machine management, network bridging, and graphical interface components.
Configuring Virtualization Services
Enable and start the libvirtd service to manage virtual machines:
sudo systemctl enable libvirtd
sudo systemctl start libvirtdAdd the current user to required groups for virtualization access:
sudo usermod -aG libvirt,kvm $USERVerify KVM acceleration support using the cpu-checker utility:
sudo kvm-okA successful result indicates “KVM acceleration can be used,” confirming hardware virtualization support.
Configure the default virtual network bridge by starting libvirt’s default network:
sudo virsh net-autostart default
sudo virsh net-start defaultLog out and back in (or reboot) to ensure group membership changes take effect before proceeding with GNS3 installation.
Installing GNS3 Using pipx (Recommended Method)
Installing pipx Package Manager
The pipx package manager provides isolated Python environments for applications, preventing dependency conflicts with system packages. Install pipx using the system package manager:
sudo apt install -y pipxConfigure pipx for the current user and update the PATH environment:
pipx ensurepathRestart the terminal session or source the updated profile:
source ~/.bashrcVerify pipx installation by checking the version:
pipx --versionThe pipx approach offers significant advantages over traditional pip installation by maintaining separate virtual environments for each application, reducing the risk of dependency conflicts.
Installing GNS3 Server
Install the GNS3 server component using pipx:
pipx install gns3-serverThe installation process downloads and installs the GNS3 server along with its dependencies in an isolated virtual environment. This may take several minutes depending on internet connection speed.
Verify server installation by checking the installed version:
gns3server --versionTest basic server functionality by starting it in the foreground:
gns3serverThe server should start successfully and display binding information, typically showing it’s listening on localhost port 3080. Press Ctrl+C to stop the test server.
Installing GNS3 GUI
Install the GNS3 graphical user interface using pipx:
pipx install gns3-guiThe GUI installation includes the Qt-based graphical interface and associated dependencies. Pipx automatically manages the virtual environment and ensures compatibility between components.
Inject the GNS3 server into the GUI environment to ensure proper integration:
pipx inject gns3-gui gns3-serverVerify GUI installation by launching it from the command line:
gns3The GNS3 interface should open, displaying the main window with toolbar options and workspace area. Close the application to continue with additional component installation.
Installing Required Emulation Components
Installing and Configuring Dynamips
Dynamips provides Cisco router emulation capabilities essential for many GNS3 topologies. Install Dynamips from the Debian repositories:
sudo apt install -y dynamipsVerify Dynamips installation and check the version:
dynamips -HThe command should display Dynamips help information and version details. Dynamips requires Cisco IOS images to function properly, which users must obtain separately according to Cisco licensing requirements.
Create a directory for storing IOS images:
mkdir -p ~/GNS3/images/IOSSet appropriate permissions for the images directory:
chmod 755 ~/GNS3/images/IOSTest Dynamips functionality by running it without arguments. It should display usage information without errors, confirming proper installation.
Setting Up VPCS (Virtual PC Simulator)
VPCS creates lightweight virtual PCs for testing network connectivity and basic operations. Install VPCS from the repository:
sudo apt install -y vpcsVerify VPCS installation:
vpcs -vCreate a working directory for VPCS configurations:
mkdir -p ~/GNS3/projects/vpcsTest VPCS by launching it interactively:
vpcsThe VPCS prompt should appear, allowing basic network commands. Type quit to exit the VPCS interface. This confirms successful installation and basic functionality.
Installing uBridge
uBridge facilitates network bridging between virtual and physical interfaces. Install required build dependencies:
sudo apt install -y git build-essential libpcap-devClone the uBridge source code:
git clone https://github.com/GNS3/ubridge.git
cd ubridgeCompile and install uBridge:
make
sudo make installSet proper permissions for uBridge:
sudo chmod +s /usr/local/bin/ubridgeVerify installation by checking the uBridge version:
ubridge -vReturn to the home directory and clean up the source:
cd ~
rm -rf ubridgeConfiguring QEMU and KVM
Ensure QEMU utilities are properly installed for virtual machine support:
sudo apt install -y qemu-system-x86 qemu-utilsVerify KVM acceleration is available and functioning:
sudo kvm-okCreate directories for VM storage:
mkdir -p ~/GNS3/images/QEMU
mkdir -p ~/GNS3/projects/qemuTest QEMU functionality by checking available machine types:
qemu-system-x86_64 -machine help | head -10This command should display available virtual machine types, confirming QEMU is properly installed and configured.
Initial GNS3 Configuration and Setup
First Launch and Setup Wizard
Launch GNS3 for the first time to initiate the setup wizard:
gns3The setup wizard guides through initial configuration options. Select “Run appliances on my local computer” for standalone operation, or choose remote server options for distributed setups.
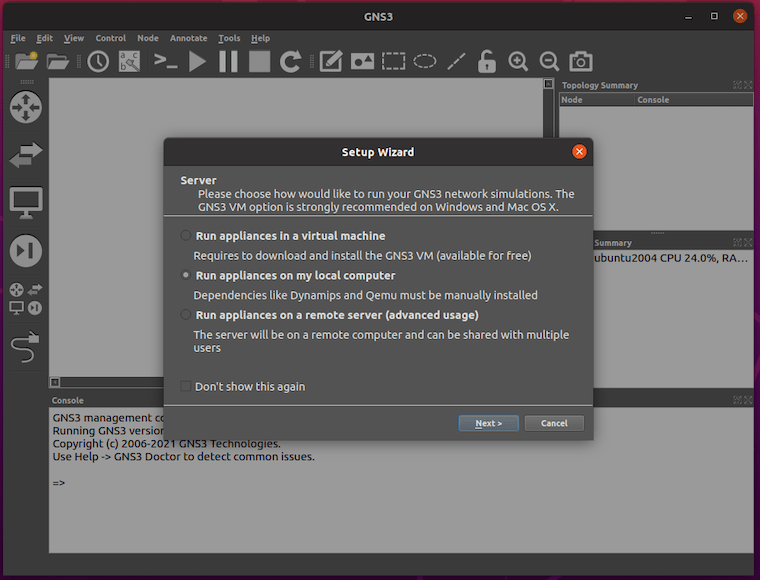
The wizard automatically detects installed emulation engines including Dynamips, VPCS, and QEMU. Verify all components appear in the detected software list before proceeding.
Configure the project location, typically defaulting to ~/GNS3/projects. This directory stores network topology files and associated configurations.
Accept default port settings (TCP 3080 for server communication) unless specific network requirements dictate otherwise. The wizard completes setup and presents the main GNS3 interface.
Server Configuration
Access server configuration through Edit > Preferences > Server. The local server configuration should show “Running” status with the correct host binding (127.0.0.1) and port (3080).
Review server settings to ensure proper binding configuration. For security reasons, the default localhost binding prevents external connections unless specifically configured.
Test server connectivity using the “Test Settings” button within the preferences dialog. Successful connection confirms proper server configuration and communication.
Advanced users may configure additional server instances or remote server connections through the same interface, enabling distributed GNS3 deployments across multiple systems.
Path Configuration
Configure GNS3 paths through Edit > Preferences > General. Set the projects directory to a location with adequate storage space:
/home/username/GNS3/projectsConfigure appliance storage directory:
/home/username/GNS3/appliancesSet up symbols directory for custom device icons:
/home/username/GNS3/symbolsEnsure all configured directories exist and have proper permissions:
mkdir -p ~/GNS3/{projects,appliances,symbols,configs}
chmod -R 755 ~/GNS3Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
Dependency Resolution Problems
Missing Dynamips Package Error: If Dynamips is not detected, verify installation:
which dynamipsIf the command returns no output, reinstall Dynamips:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install --reinstall dynamipsPyQt5 Dependency Conflicts: Resolve PyQt5 issues by ensuring system packages are current:
sudo apt install -y python3-pyqt5 python3-pyqt5.qtsvgLibvirt Installation Issues: If libvirt components are missing, install the complete package set:
sudo apt install -y qemu-kvm libvirt-daemon-system libvirt-clients virt-managerVPCS Version Mismatch: Reinstall VPCS if version conflicts occur:
sudo apt remove vpcs
sudo apt install vpcsPermission and Access Issues
Libvirt Group Membership Problems: Verify current user is in required groups:
groups $USERIf libvirt or kvm groups are missing, add them:
sudo usermod -aG libvirt,kvm $USERLog out and back in to apply group changes.
KVM Access Denied Errors: Ensure KVM modules are loaded:
lsmod | grep kvmIf modules are missing, load them manually:
sudo modprobe kvm-intel # For Intel CPUs
sudo modprobe kvm-amd # For AMD CPUsVirtual Bridge (virbr0) Issues: Restart libvirt networking:
sudo systemctl restart libvirtd
sudo virsh net-destroy default
sudo virsh net-start defaultFile Permission Problems: Set correct permissions on GNS3 directories:
chmod -R 755 ~/GNS3
chown -R $USER:$USER ~/GNS3GUI Launch Problems
PATH Environment Issues: If GNS3 command is not found, update PATH:
export PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$PATH"
echo 'export PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.bashrcPipx Virtual Environment Problems: Reinstall GNS3 GUI if environment corruption occurs:
pipx uninstall gns3-gui
pipx install gns3-guiDisplay and X11 Forwarding Issues: For remote installations, ensure X11 forwarding is enabled:
export DISPLAY=:0.0Desktop Integration Problems: Create a desktop entry manually:
cat > ~/.local/share/applications/gns3.desktop << EOF
[Desktop Entry]
Name=GNS3
Comment=Graphical Network Simulator
Exec=gns3
Icon=gns3
Terminal=false
Type=Application
Categories=Network;Education;
EOFPost-Installation Verification and Testing
Verifying Installation Components
Test GNS3 server startup by launching it independently:
gns3server --localThe server should start without errors and display listening information. Stop with Ctrl+C.
Launch the GNS3 GUI and verify all components are detected:
gns3Check Help > About to confirm version information and component status.
Navigate to Edit > Preferences and verify all emulation engines show as available in their respective sections.
Creating a Test Project
Create a new project to verify functionality:
- Click “New Project” or press Ctrl+N
- Name the project “GNS3-Test”
- Select the default project directory
- Click “OK” to create the project
Add devices to test basic functionality:
- From the device toolbar, drag a “VPCS” device to the workspace
- Add an “Ethernet Hub” from the network devices
- Connect the VPCS to the hub using the link tool
- Start all devices using the green play button
Test device connectivity by opening the VPCS console and configuring an IP address:
VPCS> ip 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0
VPCS> ping 192.168.1.1Successful project creation and device operation confirm proper GNS3 installation and configuration.
Performance Optimization and Best Practices
System Optimization
CPU Affinity Configuration: For systems with multiple cores, configure CPU affinity to dedicate specific cores to GNS3 operations. Edit GNS3 server configuration to limit CPU usage:
echo 'taskset -c 0,1 gns3server' > ~/.gns3server_optimizedMemory Allocation Recommendations: Configure adequate RAM for device operations. Set device memory limits in GNS3 preferences:
- Cisco routers: 128-256MB for basic routing
- Virtual machines: 512MB-2GB depending on OS
- Reserve 2GB system memory for host operations
Storage Optimization: Use SSD storage for improved performance. Configure separate directories for different image types:
mkdir -p ~/GNS3/images/{IOS,QEMU,Docker}Network Interface Optimization: Configure dedicated network interfaces for GNS3 traffic when using complex topologies with external connectivity.
Security Considerations
User Permission Best Practices: Run GNS3 with minimal required privileges. Avoid unnecessary sudo usage during normal operation.
Network Isolation Strategies: Use libvirt’s default network for isolated testing. Create separate networks for different project types:
virsh net-define custom-network.xml
virsh net-start custom-networkFirewall Configuration: Configure iptables rules to control GNS3 network access:
sudo iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.122.0/24 -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A OUTPUT -d 192.168.122.0/24 -j ACCEPTSecure Image Management: Store device images in restricted directories with appropriate permissions. Maintain separate directories for different device types and versions.
Adding Network Appliances and Images
Using GNS3 Marketplace
Access the built-in marketplace through File > Import Appliance. The marketplace provides free appliances including:
- Network operating system templates
- Pre-configured virtual machines
- Docker containers for modern applications
- Open-source network tools
Download appliances directly within GNS3 by selecting desired templates and clicking “Download.” The system automatically configures appliance settings and creates appropriate device templates.
Popular free appliances include:
- OpenWrt for wireless router simulation
- pfSense for firewall testing
- Ubuntu and CentOS virtual machines
- Network monitoring tools
Custom Image Installation
Adding Router Images: Place Cisco IOS images in the appropriate directory:
cp c7200-adventerprisek9-mz.152-4.S7.bin ~/GNS3/images/IOS/Configuring Appliance Templates: Create custom templates through Edit > Preferences > Dynamips > IOS Routers. Configure:
- Platform type (c7200, c3745, etc.)
- Memory allocation
- Network adapters
- Startup configuration
Docker Container Integration: Modern GNS3 versions support Docker containers for current network applications:
docker pull nginxConfigure Docker templates in GNS3 preferences to utilize containerized applications within network topologies.
Image Licensing Requirements: Ensure compliance with vendor licensing when using commercial network operating systems. Cisco IOS images require appropriate licensing for legal use.
Maintenance and Updates
Regular maintenance ensures optimal GNS3 performance and security. Update GNS3 components using pipx:
pipx upgrade gns3-server
pipx upgrade gns3-guiUpdate system packages monthly:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeManaging Pipx Package Updates: List installed packages and versions:
pipx listUpgrade all pipx packages simultaneously:
pipx upgrade-allSystem Maintenance Recommendations:
- Clean temporary files monthly:
rm -rf ~/.gns3/tmp/* - Archive old projects:
tar -czf old_projects.tar.gz ~/GNS3/projects/archived/ - Monitor disk usage:
du -sh ~/GNS3/*
Backup and Restore Procedures: Regular backups prevent data loss:
tar -czf gns3-backup-$(date +%Y%m%d).tar.gz ~/GNS3/Restore from backup when needed:
tar -xzf gns3-backup-20250901.tar.gz -C ~/Congratulations! You have successfully installed GNS3. Thanks for using this tutorial to install the latest version of GNS3 open-source network simulation software on Debian 13 “Trixie”. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official GNS3 website.