How To Install GParted on AlmaLinux 10
Managing disk partitions effectively is crucial for any Linux system administrator or power user. GParted (GNOME Partition Editor) stands out as one of the most reliable and user-friendly partition management tools available for Linux systems. This comprehensive guide walks you through multiple methods to install GParted on AlmaLinux 10, ensuring you have the knowledge and confidence to manage your disk partitions safely and efficiently.
AlmaLinux 10, released as a stable enterprise-grade replacement for CentOS, provides a robust foundation for both server and desktop environments. When combined with GParted’s powerful partition management capabilities, you gain access to professional-grade disk management tools that rival commercial solutions.
Understanding AlmaLinux 10 and GParted Compatibility
AlmaLinux 10 Architecture and Features
AlmaLinux 10 represents a significant evolution in enterprise Linux distributions. Built as a community-driven replacement for CentOS, it maintains binary compatibility with Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) while offering enhanced security features and improved hardware support. The distribution includes advanced architectural improvements such as x86_64_v2 and x86_64_v3 instruction set support, providing better performance on modern processors.
The operating system incorporates post-quantum cryptography support and enhanced SELinux policies, making it ideal for security-conscious environments. These features work seamlessly with GParted’s partition management capabilities, ensuring your disk operations remain secure and reliable.
GParted’s Role in Modern Linux Environments
GParted serves as an essential tool for disk management across various scenarios. Whether you’re configuring server storage, setting up development environments, or managing desktop systems, GParted provides a comprehensive solution for partition operations. The tool supports numerous file systems including ext4, NTFS, FAT32, XFS, and Btrfs, making it versatile enough for mixed-environment deployments.
The graphical interface eliminates the complexity often associated with command-line partition tools while maintaining the precision and safety required for professional use. GParted’s non-destructive operations ensure data integrity during resize, move, and copy operations.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Essential System Requirements
Before proceeding with GParted installation, ensure your AlmaLinux 10 system meets the following requirements:
- Operating System: AlmaLinux 10 with active installation and administrative access
- Memory: Minimum 1GB RAM (2GB recommended for large partition operations)
- Storage: At least 100MB free disk space for installation and dependencies
- Network: Active internet connection for package downloads
- Privileges: Root or sudo access for installation and execution
Pre-Installation Safety Checklist
Data safety should always be your primary concern when working with partition management tools. Create comprehensive backups of critical data before performing any partition operations. Verify your current partition layout using the lsblk command to understand your system’s storage configuration.
Test your network connectivity and ensure your system repositories are accessible. Update your package database to prevent dependency conflicts during installation. Consider documenting your current partition layout for reference during troubleshooting.
Method 1: Installing GParted via EPEL Repository
Step 1: Enable EPEL Repository
The Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL) repository provides access to additional software packages not included in AlmaLinux’s default repositories. Begin by installing the EPEL release package:
sudo dnf install -y epel-releaseThis command downloads and configures the EPEL repository for your AlmaLinux 10 system. The -y flag automatically confirms the installation, streamlining the process.
Step 2: Enable CodeReady Builder Repository
Many EPEL packages require dependencies from the CodeReady Builder (CRB) repository. Enable this repository using the following command:
sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled crbThe CRB repository contains development tools and libraries essential for many advanced packages, including those required by GParted’s dependencies.
Step 3: Update Package Repositories
Refresh your package database to ensure access to the latest package information:
sudo dnf clean all
sudo dnf updateThe clean all command removes cached package data, while update refreshes repository metadata and installs available system updates. This process ensures compatibility and reduces the likelihood of dependency conflicts.
Step 4: Install GParted Package
With repositories properly configured, install GParted using the DNF package manager:
sudo dnf install gpartedDNF automatically resolves dependencies and downloads required packages. The installation process typically includes libraries for partition detection, file system support, and graphical interface components. Installation time varies depending on your internet connection speed and system performance.
Step 5: Verify Installation Success
Confirm successful installation by checking the GParted version:
gparted --versionThis command displays the installed GParted version and confirms that the application is properly configured. You can also verify package installation using:
dnf info gpartedThis provides detailed information about the installed package, including version, dependencies, and installation size.
Method 2: Installing from Source Code
When to Choose Source Installation
Source code installation offers several advantages for advanced users and specific scenarios. You gain access to the latest features and bug fixes not yet available in repository packages. Custom compilation allows optimization for your specific hardware configuration and use case requirements.
This method proves particularly valuable in development environments where you need specific GParted features or modifications. However, source installation requires more technical expertise and ongoing maintenance responsibilities.
Installing Development Dependencies
Source compilation requires numerous development tools and libraries:
sudo dnf install gnome-common yelp-tools glib2-devel gcc-c++ libuuid-devel parted-devel gtkmm30-devel make polkit-devel gettext-develThese packages provide the compiler toolchain, development headers, and build utilities necessary for successful compilation. The installation process may take several minutes depending on your system’s current package set.
Source Code Compilation Process
Download the latest GParted source code from the official repository:
git clone https://github.com/GNOME/gparted.git
cd gpartedConfigure the build environment with your preferred options:
./configure --disable-docThe --disable-doc option speeds up compilation by skipping documentation generation. For production environments, consider enabling additional features:
./configure --enable-libparted-dmraidCompile and install the software:
make
sudo make installThe compilation process utilizes multiple CPU cores automatically, optimizing build time. Installation places binaries in system directories and configures necessary permissions.
Source Installation Considerations
Source installations require manual maintenance for security updates and bug fixes. Monitor the GParted project for important releases and security announcements. Consider integrating source builds into your configuration management system for consistency across multiple systems.
Document your build configuration and compilation options for future reference. This information proves invaluable when troubleshooting issues or rebuilding on different systems.
Method 3: Using GParted Live
GParted Live Overview and Benefits
GParted Live provides a bootable Linux environment specifically designed for partition management tasks. This approach offers unique advantages for certain scenarios, particularly when modifying system partitions that cannot be unmounted during normal operation.
The live environment eliminates concerns about file system locking and provides access to all storage devices without operating system interference. This method proves essential for resizing root partitions, recovering corrupted systems, and performing maintenance on servers without local access.
Creating GParted Live Media
Download the latest GParted Live ISO from the official website. Verify the download integrity using provided checksums to ensure file authenticity.
Create bootable USB media using the dd command:
sudo dd if=gparted-live-x.x.x-x.iso of=/dev/sdX bs=4M status=progressReplace gparted-live-x.x.x-x.iso with the actual filename and /dev/sdX with your USB device identifier. Exercise extreme caution when specifying the target device to prevent data loss.
Using GParted Live Effectively
Boot from the created media and select appropriate language and keyboard settings. GParted Live automatically detects available storage devices and launches the partition editor interface.
The live environment provides access to additional tools including file managers, text editors, and network utilities. These tools facilitate data backup, file transfer, and system recovery operations alongside partition management tasks.
Launching and Using GParted
Command Line Launch
Execute GParted from the terminal with administrative privileges:
sudo gpartedThe application prompts for your password and launches the graphical interface. Root privileges are essential for disk device access and partition modification operations.
Desktop Environment Integration
GParted integrates seamlessly with major desktop environments including GNOME, KDE, and XFCE. Access the application through your desktop’s application menu, typically located in the “System Tools” or “Administration” section.
Modern desktop environments provide PolicyKit integration, allowing secure privilege escalation through graphical authentication dialogs. This approach enhances security by eliminating the need for command-line sudo access.
Interface Overview and Navigation
The GParted interface displays detected storage devices in a dropdown menu at the top-right corner. Select your target device to view its current partition layout. The main area shows a graphical representation of partitions, with colors indicating different file system types.
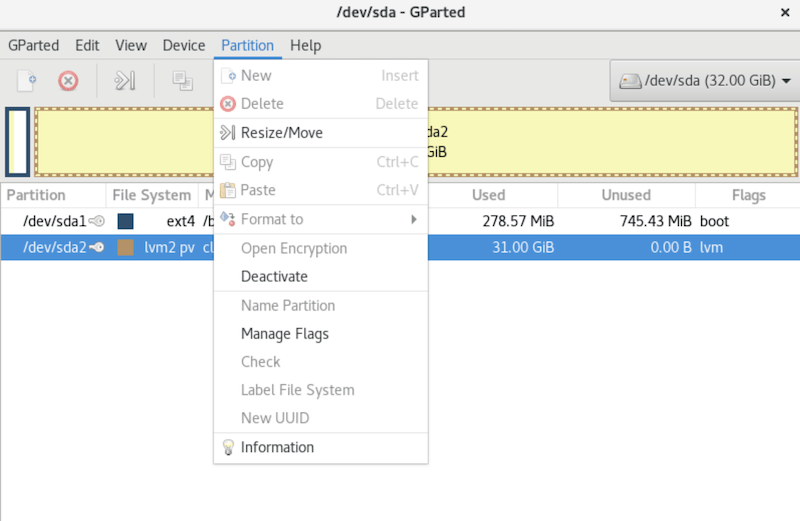
The toolbar provides quick access to common operations including create, delete, resize, and move functions. Menu options offer advanced features such as device information, partition checking, and label management.
Basic Partition Operations
Creating New Partitions: Right-click on unallocated space and select “New” to create a partition. Specify size, file system type, and label as needed. GParted validates your settings and warns about potential issues before applying changes.
Resizing Existing Partitions: Select a partition and choose “Resize/Move” from the context menu or toolbar. Drag partition boundaries or enter precise values in the dialog box. The interface shows available space and prevents invalid operations.
Moving Partitions: Use the resize dialog to reposition partitions within available space. Moving operations can be time-consuming for large partitions, particularly on traditional hard drives.
Formatting Partitions: Select an existing partition and choose your desired file system from the format menu. This operation destroys existing data, so ensure you have proper backups before proceeding.
Advanced Features and Optimization
Partition Alignment and Performance
Modern storage devices benefit from proper partition alignment, particularly SSDs and advanced format hard drives. GParted automatically aligns partitions to optimal boundaries, improving performance and extending device lifespan.
The alignment options in partition dialogs allow fine-tuning for specific hardware configurations. “MiB alignment” works well for most modern devices, while “Cylinder alignment” may be appropriate for older hardware.
File System Optimization
Choose appropriate file systems based on your specific use case requirements. Ext4 provides excellent performance and reliability for Linux systems, while XFS excels with large files and high-performance storage.
For mixed environments, NTFS support enables compatibility with Windows systems. Ensure you install the ntfs-3g package for full NTFS functionality:
sudo dnf install ntfs-3gBatch Operations and Efficiency
Queue multiple operations before applying changes to minimize disk activity and reduce total operation time. GParted displays pending operations in a dedicated pane, allowing review and modification before execution.
Consider the order of operations when planning complex partition layouts. Efficient sequencing can significantly reduce total operation time and minimize data movement.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Installation and Repository Problems
If EPEL repository installation fails, verify your network connectivity and DNS resolution. Check firewall settings that might block repository access:
sudo firewall-cmd --list-allFor persistent repository issues, manually download and install the EPEL release package:
wget https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-10.noarch.rpm
sudo dnf install epel-release-latest-10.noarch.rpmRuntime and Permission Issues
Permission denied errors typically indicate insufficient privileges or PolicyKit configuration problems. Ensure your user account has sudo access and try launching from the command line:
sudo gpartedFor desktop environment integration issues, install the appropriate PolicyKit authentication agent:
sudo dnf install polkit-gnomeDevice Detection and Hardware Issues
If storage devices don’t appear in GParted, check system logs for hardware errors:
sudo dmesg | grep -i error
sudo journalctl -xeVerify device recognition using standard Linux tools:
lsblk
sudo fdisk -lThese commands help identify hardware problems or driver issues affecting device detection.
Performance and Stability Optimization
Large partition operations may require significant time and system resources. Monitor system performance during operations and ensure adequate free memory. Consider closing unnecessary applications to free system resources.
For operations on large partitions, using command-line tools may provide better performance than the graphical interface:
sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdXNThis approach bypasses GUI overhead and may complete faster than equivalent GParted operations.
Security Considerations and Best Practices
Data Protection Strategies
Always create comprehensive backups before performing partition operations. Even non-destructive operations carry inherent risks, and hardware failures can occur during any disk activity.
Test backup integrity by attempting to restore files to a temporary location. Verify that your backup strategy covers all critical data and system configurations.
System Security and Access Control
Limit GParted access to authorized users only. Consider using dedicated administrative accounts for partition management tasks rather than everyday user accounts.
Document all partition changes for security auditing and compliance requirements. Maintain logs of who performed operations, when they occurred, and what changes were made.
Production Environment Guidelines
Implement change management procedures for production systems. Schedule partition operations during maintenance windows to minimize service disruption.
Develop rollback procedures for failed operations. While GParted operations are generally reliable, having contingency plans reduces downtime and data loss risks.
Performance Optimization and Best Practices
Hardware Considerations for Optimal Performance
Storage device type significantly impacts GParted operation speed. SSDs provide much faster performance for most operations compared to traditional hard drives. USB 3.0 connections offer substantial speed improvements over USB 2.0 for external device management.
System memory affects performance during large partition operations. Ensure adequate RAM availability by closing unnecessary applications before starting intensive operations.
Optimization Techniques
Defragment NTFS partitions before resizing to improve operation speed and success rates. Boot into Windows Safe Mode for optimal defragmentation results when working with dual-boot systems.
Leave adequate free space in partitions to prevent performance degradation. The general recommendation suggests maintaining at least 10-15% free space for optimal file system performance.
Planning Efficient Operations
Design partition layouts to minimize future reorganization needs. Consider your long-term storage requirements when initially configuring systems.
Plan operation sequences to reduce data movement. Expanding partitions into adjacent free space requires minimal time, while moving partitions across the disk can take hours.
Integration with AlmaLinux 10 Ecosystem
Package Management Integration
GParted integrates seamlessly with AlmaLinux’s DNF package manager. Updates arrive through normal system update processes, ensuring you receive security patches and feature improvements automatically.
Monitor package dependencies during system updates to prevent conflicts with custom installations. Repository-installed versions typically provide better long-term stability than source builds.
Desktop Environment Compatibility
GParted works excellently across different desktop environments common on AlmaLinux 10. GNOME provides the most integrated experience, while KDE Plasma and XFCE offer excellent functionality with minor interface differences.
Wayland display server compatibility ensures future-proofing as Linux distributions transition away from X11. GParted operates reliably under both display systems.
Enterprise Features and Compliance
SELinux integration ensures GParted operations comply with security policies required in enterprise environments. The application respects system security contexts and operates within defined security boundaries.
Systemd integration provides proper service management and logging capabilities. Operation logs integrate with standard system logging infrastructure for monitoring and compliance purposes.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed GParted. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing GParted (GNOME Partition Editor) on your AlmaLinux OS 10 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official GParted website.