How To Install GParted on Fedora 39
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install GParted on Fedora 39. GParted, short for GNOME Partition Editor, is a powerful and versatile open-source tool for managing disk partitions on Linux systems. It provides a user-friendly graphical interface for creating, resizing, copying, and moving partitions without data loss. GParted supports a wide range of file systems, including ext2, ext3, ext4, FAT16, FAT32, NTFS, and more.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the GParted on a Fedora 39.
Prerequisites
Before diving into the installation process, let’s ensure that you have everything you need:
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Fedora 39.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- While this guide is designed to be as straightforward as possible, some familiarity with the Linux command line will be beneficial.
- You will need access to the terminal to execute commands. Fedora 39 provides the Terminal application for this purpose. It can be found in your Applications menu.
- You’ll need an active internet connection to download GParted and its dependencies.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install GParted on Fedora 39
Step 1. To ensure that you have access to the latest packages and dependencies, it’s essential to update the Fedora repositories using the DNF package manager. Open the terminal and run the following commands:
sudo dnf clean all sudo dnf update
This ensures that you have the latest packages and dependencies required for a smooth installation.
Step 2. Installing the EPEL Repository.
Fedora 39 relies on the Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL) repository to provide additional packages that are not included in the default Fedora repositories. To enable the EPEL repository, run the following command in the terminal:
sudo dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-9.noarch.rpm
Step 3. Installing GParted on Fedora 39.
With the EPEL repository installed, you can now install GParted using the following command:
sudo dnf install gparted
DNF will handle the installation of GParted and its dependencies. Confirm the installation when prompted, and wait for the process to complete.
Step 4. Launch GParted on Fedora.
GParted needs root privileges to modify disk partitions. You can launch GParted with root privileges using the following command:
sudo gparted
Alternatively, you can also find GParted in your application menu under ‘System Tools’ or ‘Utilities’, depending on your desktop environment.
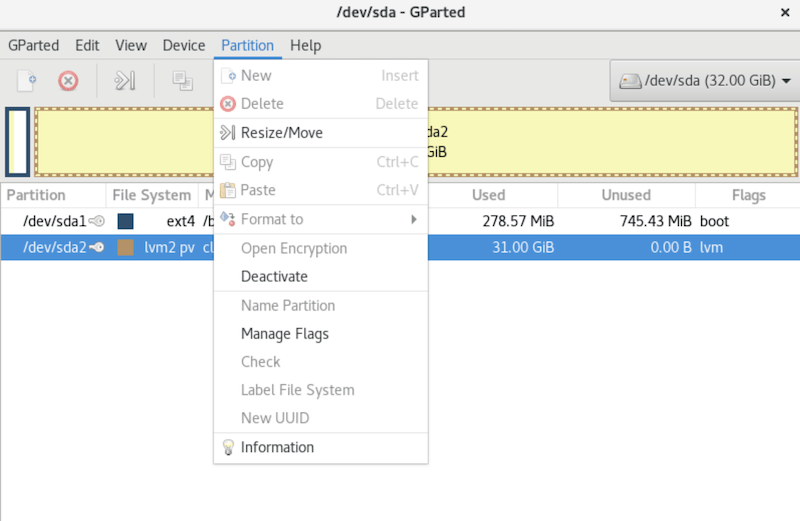
* Before making any changes to disk partitions, it’s crucial to back up any important data. While GParted is generally safe to use, there’s always a risk of data loss when dealing with disk partitions.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed GParted. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the GParted on your Fedora 39 system. For additional Apache or useful information, we recommend you check the official GParted website.