How To Install GParted on Fedora 40
Fedora 40, the latest release of the popular Linux distribution, offers a robust and user-friendly environment for both desktop and server users. With its cutting-edge features and stability, Fedora 40 has become a preferred choice for many Linux enthusiasts. As a Linux user, effective disk management is crucial for optimizing system performance and ensuring data integrity. GParted, a powerful and versatile disk partitioning tool, is an essential utility for managing disk space on Fedora 40. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the process of installing GParted on Fedora 40, providing step-by-step instructions, troubleshooting tips, and best practices for efficient disk management.
What is GParted?
GParted, short for GNOME Partition Editor, is a free and open-source disk partitioning tool that allows users to create, resize, move, and delete disk partitions. It supports a wide range of file systems, including ext2, ext3, ext4, FAT16, FAT32, and NTFS. GParted provides a user-friendly graphical interface that makes disk management tasks intuitive and accessible to both novice and advanced users. With its powerful features and reliability, GParted has become an indispensable tool for Linux users worldwide.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with the installation of GParted on Fedora 40, ensure that your system meets the following requirements:
- A running Fedora 40 installation with a stable internet connection.
- Root or sudo privileges to execute administrative commands.
- Sufficient disk space for installing GParted and its dependencies.
It is crucial to back up your important data before performing any disk partitioning operations. While GParted is a reliable tool, it is always better to have a backup to prevent data loss in case of any unforeseen issues.
Updating Fedora 40 System
Before installing GParted, it is recommended to update your Fedora 40 system to ensure that you have the latest packages and security patches. Updating the system helps prevent potential compatibility issues and enhances overall system stability. To update your Fedora 40 system, follow these steps:
- Open the terminal on your Fedora 40 system.
- Clean the DNF cache by running the following command:
sudo dnf clean all - Update the system packages by executing the command:
sudo dnf update - Wait for the update process to complete. The terminal will display the progress and prompt you for confirmation if necessary.
- Once the update is finished, restart your system to apply the changes:
sudo reboot
Installing GParted on Fedora 40
Now that your Fedora 40 system is up to date, let’s proceed with installing GParted. Fedora 40 provides an easy way to install GParted using the DNF package manager. Here’s how you can install GParted on your Fedora 40 system:
- Open the terminal on your Fedora 40 system.
- Run the following command to install GParted:
sudo dnf install gparted - DNF will resolve the dependencies and prompt you to confirm the installation. Press “y” and hit Enter to proceed.
- Wait for the installation process to complete. DNF will download and install GParted along with its necessary dependencies.
If you encounter any issues during the installation process, such as missing dependencies or conflicts, DNF will provide appropriate error messages. In such cases, you can try resolving the issues by running sudo dnf update again and then retrying the GParted installation command.
Launching and Using GParted
Once GParted is successfully installed on your Fedora 40 system, you can launch it from the terminal using the following command:
sudo gpartedGParted requires root privileges to make changes to disk partitions, so it is necessary to run it with sudo.
Upon launching GParted, you will be presented with its intuitive graphical interface. The main window displays a list of available disk devices and their partitions. You can select a disk device from the drop-down menu located in the top-right corner of the window.
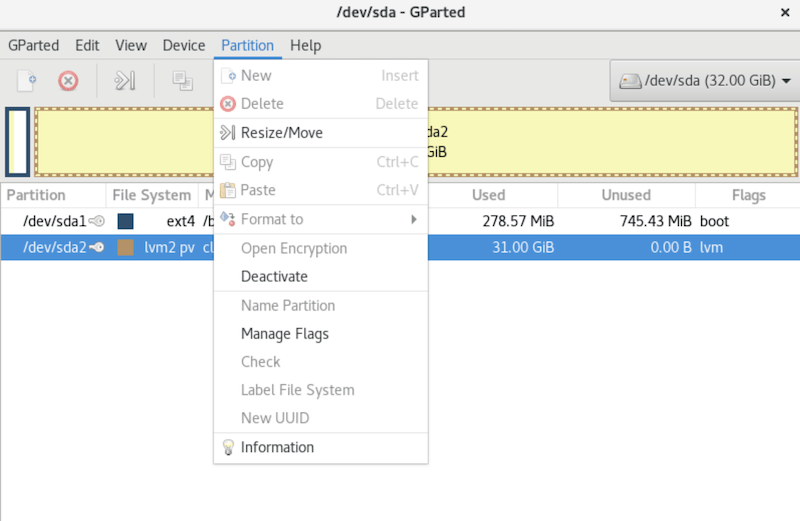
GParted provides various options for managing disk partitions, including:
- Creating a new partition: Right-click on the unallocated space and select “New” to create a new partition. Specify the partition size, file system, and label.
- Resizing a partition: Right-click on an existing partition and select “Resize/Move.” Adjust the partition size by dragging the handles or entering the desired values.
- Deleting a partition: Right-click on a partition and select “Delete” to remove it from the disk.
- Formatting a partition: Right-click on a partition and select “Format” to change its file system or label.
After making the desired changes, click on the “Apply” button to execute the pending operations. GParted will display a confirmation dialog, showing the actions to be performed. Review the changes carefully and click “Apply” to proceed.
Common Issues and Solutions
While using GParted on Fedora 40, you may encounter some common issues. Here are a few scenarios and their solutions:
Permission denied error: If you receive a “Permission denied” error when launching GParted, ensure that you are running it with sudo privileges. Launch GParted using the command sudo gparted instead of just gparted.
Partition busy or mounted: If you are unable to modify a partition because it is busy or mounted, unmount the partition first. Right-click on the partition and select “Unmount.” If the partition is in use by the system, you may need to boot into a live Linux environment to perform the desired operations.
Insufficient space for partition: When creating or resizing partitions, ensure that there is enough unallocated space available on the disk. If necessary, consider deleting or shrinking existing partitions to free up space.
Best Practices for Disk Management with GParted
To ensure safe and effective disk management with GParted on Fedora 40, follow these best practices:
- Backup important data: Always backup your critical data before performing any disk partitioning operations to prevent data loss in case of accidents or errors.
- Plan your partitions: Before making changes, carefully plan your disk partitions based on your storage requirements and intended usage.
- Avoid excessive partitioning: While partitioning can help organize your data, having too many partitions can lead to fragmentation and reduced performance.
- Use appropriate file systems: Choose the appropriate file system for your partitions based on your needs. For example, ext4 is commonly used for Linux systems, while FAT32 is compatible with various operating systems.
- Regularly maintain your system: Perform periodic disk maintenance tasks, such as disk cleanup and error checking, to keep your Fedora 40 system running smoothly.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed GParted. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the GParted on your Fedora 40 system. For additional or useful information, we recommend you check the official GParted website.