How To Install GParted on Fedora 41
GParted, short for GNOME Partition Editor, is a versatile and powerful tool for managing disk partitions on Linux systems. Whether you need to resize, move, or create new partitions, GParted simplifies the process while minimizing the risk of data loss. In this guide, we will take you through the detailed steps to install GParted on Fedora 41, one of the most cutting-edge Linux distributions available today.
By the end of this article, you’ll have GParted installed and ready to use on your system. We’ll also cover some troubleshooting tips and best practices for using this essential partition management tool safely and effectively.
Prerequisites Before Installation
Before diving into the installation process, there are a few things you need to prepare to ensure a smooth experience when installing GParted on Fedora 41.
System Requirements
Fedora 41 is a modern Linux distribution that requires certain minimum system specifications to run efficiently. While GParted itself is lightweight, you should ensure that your system meets the following requirements:
- Processor: 64-bit processor (x86_64)
- RAM: At least 1 GB of RAM (2 GB or more recommended)
- Disk Space: Sufficient free space for partitioning operations (at least 500 MB)
Access to Terminal
The installation process requires using the terminal in Fedora 41. Ensure you have terminal access and are comfortable running commands in it. This guide will provide all necessary commands in detail.
User Privileges
You must have root or sudo privileges to install software and manage disk partitions on Fedora. If you’re not logged in as root, prepend all commands with sudo.
Backup Recommendation
Partitioning operations can be risky if not done carefully. It’s highly recommended that you back up any important data before proceeding with installation and partition management using GParted. While GParted is reliable, unexpected issues like power outages or hardware failures can result in data loss.
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing GParted on Fedora 41
Now that you’ve prepared your system, let’s move on to the installation process. Follow these steps carefully to install GParted on your Fedora 41 system.
Step 1: Update System Packages
The first step before installing any new software is to ensure that your system packages are up-to-date. This ensures compatibility and prevents potential issues during installation.
sudo dnf clean all
sudo dnf update
The first command clears cached package files, while the second updates all installed packages to their latest versions. This step is crucial for maintaining system stability.
Step 2: Enable EPEL Repository
The Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL) repository provides additional software packages not included in the default Fedora repositories. While GParted is available in the default repositories, enabling EPEL ensures access to other useful tools that might be required later.
sudo dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-9.noarch.rpm
This command installs the EPEL repository. Once enabled, it allows you to install a broader range of software packages on your Fedora system.
Step 3: Install GParted
Now that your system is updated and EPEL is enabled, you’re ready to install GParted. The installation process is straightforward using DNF, Fedora’s package manager.
sudo dnf install gparted
This command will automatically download and install GParted along with any required dependencies. DNF handles dependency resolution seamlessly, so there’s no need for manual intervention unless an error occurs.
Troubleshooting Installation Issues
- Error: Missing Dependencies: If you encounter missing dependency errors during installation, ensure that all repositories are enabled and that your system is fully updated by running
sudo dnf update. - Error: Conflicting Packages: If DNF reports conflicting packages during installation, try resolving them by removing older versions of conflicting packages using
sudo dnf remove [package-name].
Step 4: Verify Installation
After installing GParted, it’s a good idea to verify that it has been installed correctly by checking its version number.
gparted --version
If installed successfully, this command will display the version of GParted installed on your system.
Step 5: Launching GParted
You can launch GParted either from the terminal or through the graphical user interface (GUI). Since managing partitions requires administrative privileges, you’ll need root access regardless of how you launch it.
Launching via Terminal
sudo gparted
This command opens GParted with root privileges directly from the terminal. You’ll be prompted for your password if you’re not logged in as root.
Launching via GUI
If you prefer using a graphical interface, you can find GParted in the Applications menu under “System Tools” or “Utilities.” When launched from the GUI, it will still prompt you for administrative privileges before allowing any partition modifications.
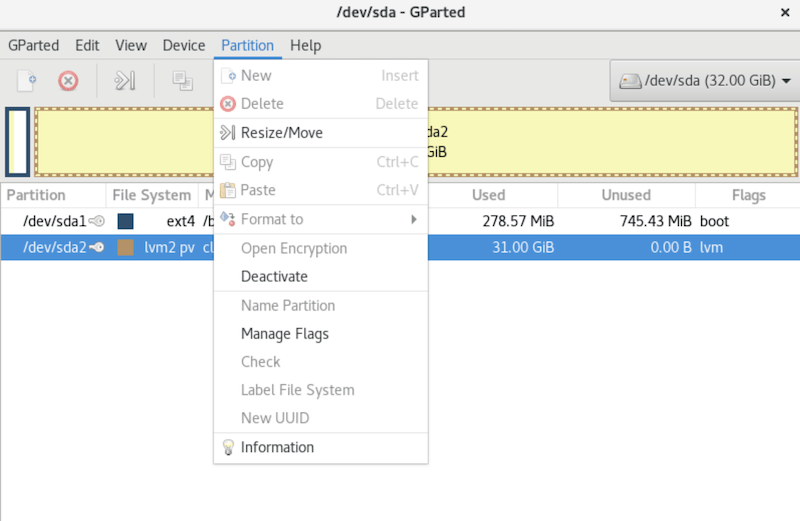
Using GParted Safely
Once you’ve installed and launched GParted successfully on Fedora 41, it’s important to understand how to use it safely and effectively for disk partition management.
Basic Operations in GParted
- Create Partition: Select unallocated space from your disk and click “New” to create a new partition. You can specify the file system type (e.g., ext4) and size here.
- Resize Partition: Right-click an existing partition and select “Resize/Move.” Adjust the size slider or enter specific values to resize it without losing data.
- Delete Partition: Select a partition you no longer need and click “Delete.” Be careful as this action cannot be undone once applied.
- Move Partition: Similar to resizing, moving partitions allows you to rearrange them without altering their contents.
The Importance of Data Backup Before Partitioning
No matter how experienced you are with partitioning tools like GParted, there’s always a risk of data loss when modifying disk partitions. Always back up important files before making changes. This ensures that even if something goes wrong during partitioning operations—such as power failure or hardware malfunction—you won’t lose critical data.
Potential Risks and How To Mitigate Them
- Avoid Power Interruptions: Ensure your computer is connected to an uninterrupted power supply (UPS) while performing partition operations.
- Avoid Overlapping Partitions: When resizing or moving partitions, double-check that no partitions overlap each other as this can lead to file system corruption.
- Create Recovery Media: Consider creating a bootable recovery USB drive just in case something goes wrong during partition changes.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Error: Missing Dependencies During Installation
If you encounter missing dependencies during installation of GParted on Fedora 41, ensure that all necessary repositories are enabled by running:
sudo dnf repolist
sudo dnf update
Error: GUI Fails To Launch Properly
If launching via GUI doesn’t work as expected (e.g., no prompt appears asking for root privileges), try launching directly from terminal using:
sudo gparted
Uninstalling GParted from Fedora 41
If at any point you wish to remove GParted from your system entirely—perhaps after completing your partitioning tasks—you can uninstall it easily using DNF:
sudo dnf remove gparted
Congratulations! You have successfully installed GParted. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the GParted on your Fedora 41 system. For additional or useful information, we recommend you check the official GParted website.