How To Install GParted on Fedora 42
Disk partitioning remains one of the most critical aspects of Linux system administration, and Fedora 42 users require reliable tools to manage their storage effectively. GParted stands as the premier graphical partition editor for Linux distributions, offering an intuitive interface for complex disk operations that would otherwise require advanced command-line expertise.
This comprehensive guide addresses the specific needs of Fedora 42 users seeking to install and configure GParted on their systems. Whether you’re managing enterprise storage solutions or organizing personal data across multiple partitions, understanding proper GParted installation procedures ensures optimal system performance and data integrity. The latest Fedora 42 release introduces significant improvements including enhanced GNOME 48 integration and advanced BTRFS snapshot capabilities, making partition management more sophisticated than ever before.
Throughout this tutorial, you’ll discover multiple installation methods, troubleshooting solutions, and best practices that leverage Fedora 42’s cutting-edge features. Our approach emphasizes both safety and efficiency, ensuring your partition operations remain secure while maximizing system capabilities.
What is GParted and Why Use It on Fedora 42
Definition and Purpose
GParted, an acronym for GNOME Partition Editor, represents a powerful graphical frontend to the libparted library. This sophisticated tool transforms complex partition management tasks into accessible point-and-click operations, eliminating the steep learning curve associated with command-line utilities like fdisk or parted. The software provides comprehensive disk management capabilities while maintaining the robust functionality that system administrators demand.
As a cross-platform partition management solution, GParted supports virtually every filesystem type encountered in modern computing environments. From traditional ext4 and NTFS to advanced filesystems like BTRFS and ZFS, the application handles diverse storage scenarios with remarkable consistency.
Key Features and Capabilities
GParted excels in creating, resizing, moving, and copying partitions without data loss when operations are performed correctly. The software’s non-destructive approach means users can reorganize disk layouts while preserving existing data structures. Real-time partition preview functionality allows administrators to visualize changes before committing to potentially irreversible operations.
Advanced features include support for GUID Partition Table (GPT) and Master Boot Record (MBR) partition schemes. The application seamlessly handles filesystem checking, repair operations, and label modifications. Additionally, GParted provides comprehensive information about partition properties, including usage statistics, filesystem health, and allocation details.
The software’s queue-based operation system represents a significant safety feature, allowing users to plan multiple partition changes and review them collectively before execution. This approach minimizes risks associated with complex disk restructuring operations.
Fedora 42 Specific Benefits
Fedora 42’s integration with GNOME 48 desktop environment creates optimal conditions for GParted operations. The enhanced graphical interface provides improved accessibility features and streamlined workflow integration. Native package availability through Fedora repositories ensures seamless installation and automatic security updates.
The latest kernel versions included with Fedora 42 offer superior hardware compatibility and performance optimizations specifically beneficial for disk management operations. These improvements translate to faster partition operations and enhanced reliability during intensive storage tasks.
System Requirements and Prerequisites
Hardware Requirements
Fedora 42 establishes specific minimum system specifications that directly impact GParted performance. The operating system requires a 64-bit processor (x86_64 architecture) with at least 2GHz dual-core processing capability. While GParted itself maintains relatively modest resource requirements, partition operations benefit significantly from additional processing power.
Memory requirements begin at 2GB RAM minimum, though 4GB or more provides optimal performance for complex partition operations. Large partition resize operations or filesystem conversions may temporarily require substantial memory allocation, making adequate RAM crucial for smooth operations.
Storage considerations extend beyond simple installation space requirements. Fedora 42 needs approximately 15GB unallocated drive space for basic installation, but partition management activities require additional temporary space for operation buffers and filesystem manipulation.
Software Prerequisites
Successful GParted installation demands current Fedora 42 system packages and proper repository configurations. Users must verify their installation includes essential development tools and library dependencies that support graphical partition editing functionality.
Administrative privileges represent a fundamental requirement for partition management operations. Users need either root access or sudo privileges to install software packages and execute disk modification commands. Terminal access capability ensures troubleshooting options remain available when graphical interfaces encounter difficulties.
System administrators should confirm DNF package manager functionality and network connectivity for repository access. Firewall configurations must permit package downloads and dependency resolution during installation procedures.
Pre-Installation System Preparation
Comprehensive system updates prevent compatibility conflicts during GParted installation. The process begins with repository cache cleanup and complete package updates to ensure optimal system stability. These preparatory steps eliminate potential dependency conflicts that could complicate installation procedures.
Data backup considerations become paramount before installing partition management software. While GParted installation itself poses minimal risks, subsequent partition operations could affect system stability if performed incorrectly. Creating comprehensive system backups provides essential recovery options for critical data protection.
Installation Methods on Fedora 42
Method 1: DNF Package Manager (Recommended)
The DNF package manager provides the most reliable and secure method for installing GParted on Fedora 42 systems. This approach ensures proper dependency resolution and seamless integration with system package management.
Begin the installation process with comprehensive system maintenance commands that prepare your environment for new software installation:
sudo dnf clean all
sudo dnf updateThe first command purges cached package files, eliminating potential corruption sources, while the second updates all installed packages to their latest stable versions. This preliminary step prevents compatibility issues and ensures optimal system performance.
Execute the GParted installation using Fedora’s native package repository:
sudo dnf install gpartedDNF automatically resolves dependencies and downloads required libraries, including gtk3, parted, and associated GNOME components. The installation process typically completes within minutes, depending on network connectivity and system performance.
Verify successful installation by checking the installed package version:
gparted --versionThis command confirms proper installation and displays version information for troubleshooting purposes.
Method 2: Graphical Package Manager
GNOME Software Center provides an alternative installation method for users preferring graphical interfaces over command-line operations. Access the Software Center through the Activities overview or application launcher.
Navigate to the search functionality and enter “GParted” to locate the partition editor package. The software center displays comprehensive package information, including descriptions, screenshots, and user reviews that inform installation decisions.
Click the Install button to initiate the installation process. The graphical interface handles authentication prompts and progress monitoring automatically. While this method offers user-friendly operation, command-line installation typically provides more detailed error reporting and troubleshooting information.
Method 3: Flatpak Installation
Flatpak installation offers containerized deployment for users requiring isolated application environments or systems with complex dependency conflicts. This method provides enhanced security through application sandboxing while maintaining full GParted functionality.
Enable Flatpak support if not already configured:
sudo dnf install flatpak
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoInstall GParted through Flatpak:
flatpak install flathub org.gnome.gpartedFlatpak installations maintain separation from system packages, preventing conflicts with existing software while providing consistent behavior across different Linux distributions.
Package Information and Versions
Current Fedora 42 repositories include GParted version 1.7.0-1.fc42, representing the latest stable release with comprehensive bug fixes and feature enhancements. Package maintainers ensure compatibility with Fedora’s six-month release cycle and provide timely security updates.
The official package maintainer contact information remains available through Fedora’s package database for reporting issues or requesting feature enhancements. Regular update cycles ensure users receive the latest functionality and security improvements through standard system update procedures.
Launching and Initial Setup
Starting GParted
GParted requires administrative privileges for all partition management operations due to the sensitive nature of disk modifications. Launch the application from terminal using:
sudo gpartedThis command provides root access necessary for disk device detection and partition manipulation. Password authentication ensures only authorized users can perform potentially destructive operations.
Alternative GUI launch methods include accessing GParted through the Activities overview or Applications menu under System Tools. When launched graphically, the system prompts for administrative credentials before granting disk access permissions.
Security considerations mandate careful privilege management during partition operations. Never grant unnecessary administrative access or leave GParted running unattended with elevated privileges.
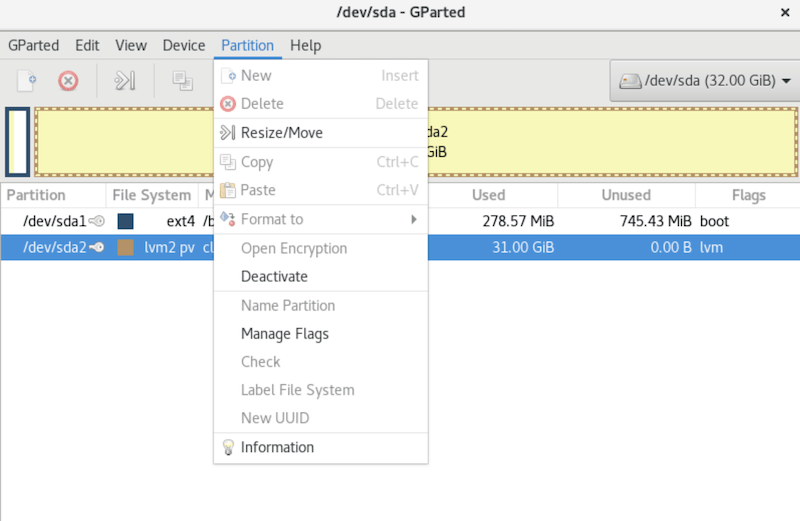
Understanding the Interface
GParted’s main window presents a comprehensive view of system storage devices and their partition layouts. The device selection dropdown menu at the top-right displays all detected storage devices, including internal drives, external USB devices, and network-attached storage systems.
The central partition list provides detailed information about each partition, including filesystem type, size, used space, and mount points. Color-coded graphical representation helps visualize partition layouts and identifies potential issues like fragmentation or space allocation problems.
Menu bar functionality includes options for device refresh, partition operations, and application preferences. The toolbar provides quick access to common operations like creating, deleting, and resizing partitions. Status bar information displays current operation progress and system messages.
Initial Configuration
Device detection operates automatically when GParted launches, scanning all available storage devices and building comprehensive partition maps. Refresh functionality allows manual rescanning when devices are connected or disconnected during operation.
Preference settings control display options, unit measurements, and warning thresholds for partition operations. Language and regional settings ensure proper localization for international users and compliance with local formatting standards.
Advanced configuration options include cylinder alignment settings, filesystem-specific parameters, and operation timeout values that optimize performance for specific hardware configurations.
Core Partition Management Operations
Creating New Partitions
Partition creation begins with selecting unallocated disk space within the GParted interface. Right-click the unallocated region to access the context menu containing partition creation options.
The New Partition dialog presents comprehensive configuration options including partition type (primary, extended, or logical), filesystem selection, and size specifications. Users can define exact partition boundaries using either graphical sliders or numerical input fields for precise control.
Filesystem selection encompasses all supported types including ext4, BTRFS, NTFS, FAT32, and specialized filesystems for specific applications. Label assignment helps identify partitions during system administration and simplifies mounting procedures.
Advanced options include partition alignment settings that optimize performance for solid-state drives and traditional hard disks. Proper alignment ensures optimal read/write performance and extends storage device lifespan.
Resizing and Moving Partitions
Partition resize operations require careful consideration of filesystem limitations and available free space. Select the target partition and access the Resize/Move option through the right-click context menu or Partition menu.
The resize dialog provides both graphical and numerical input methods for specifying new partition boundaries. Drag handles on the graphical representation allow intuitive size adjustments, while text fields enable precise measurements for exact specifications.
Moving partitions involves relocating data within the same storage device to optimize layout or consolidate free space. This operation requires significant time for large partitions and cannot be interrupted safely once initiated.
Safety considerations include verifying adequate free space for temporary data storage during move operations. Always ensure backup availability before attempting complex resize or move procedures on critical system partitions.
Deleting and Formatting Partitions
Partition deletion removes both the partition structure and all contained data permanently. Select the target partition and choose Delete from the context menu, understanding that this operation cannot be reversed once applied.
Formatting operations recreate filesystem structures while preserving partition boundaries. This process removes all existing data while maintaining partition layout for data restoration or fresh filesystem deployment.
Filesystem conversion capabilities allow changing partition types without recreation, though this process may require multiple steps and intermediate conversions depending on source and target filesystem compatibility.
Data recovery considerations emphasize the importance of comprehensive backups before any destructive operations. While some specialized tools can recover deleted partitions, prevention through proper backup procedures remains the most reliable protection method.
Applying Changes Safely
GParted’s pending operations queue system allows comprehensive review of planned changes before execution. All partition modifications remain in pending status until explicitly applied, providing opportunities for revision and cancellation.
The operation queue displays all planned changes in chronological order with detailed descriptions of each modification. This transparency enables thorough review and helps identify potential conflicts or unintended consequences.
Apply button functionality executes all queued operations sequentially, providing progress indicators and status updates throughout the process. Once initiated, operations cannot be cancelled safely, emphasizing the importance of careful planning.
Rollback capabilities remain limited once operations begin execution. While some operations can be interrupted, data integrity cannot be guaranteed for partially completed modifications.
Advanced Features and Use Cases
Integration with Fedora 42 Installation
Fedora 42’s enhanced Anaconda installer includes improved partition management capabilities that complement GParted functionality. During system installation, users can create custom partition layouts incorporating BTRFS subvolumes and LUKS2 encryption for enhanced security and flexibility.
Manual partitioning during OS installation allows creation of specialized layouts including separate home partitions, swap configurations, and boot partition optimization. These advanced configurations benefit from GParted’s pre-installation preparation and post-installation maintenance capabilities.
BTRFS subvolume creation provides advanced snapshot and rollback functionality that integrates seamlessly with GParted’s partition management tools. This combination enables sophisticated storage management strategies for both desktop and server environments.
Dual-boot partition management requires careful coordination between operating systems and their respective storage requirements. GParted’s precise partition control enables creation of shared data partitions and proper boot loader configurations for multi-OS environments.
Snapshot and Rollback Support
BTRFS snapshot functionality provides point-in-time filesystem images that enable rapid system recovery from configuration errors or software conflicts. GParted’s subvolume management capabilities support comprehensive snapshot strategies for critical system protection.
Subvolume management extends beyond simple snapshots to include quota management, compression settings, and performance optimization. These advanced features require understanding of BTRFS architecture and careful planning for optimal implementation.
Integration with system backup procedures ensures snapshot functionality complements rather than replaces traditional backup strategies. Automated snapshot scheduling and retention policies provide ongoing protection without manual intervention requirements.
Advanced Filesystem Operations
Filesystem checking and repair capabilities within GParted provide comprehensive disk health monitoring and automated repair procedures for common corruption issues. These tools integrate with filesystem-specific utilities for thorough diagnostic and repair operations.
Partition table management includes conversion between MBR and GPT formats, essential for modern systems requiring large disk support or advanced boot configurations. These operations require careful planning and comprehensive backup procedures due to their fundamental nature.
UUID and label modification capabilities simplify system administration by providing human-readable identifiers for storage devices and partitions. Consistent labeling strategies improve system maintainability and reduce configuration errors.
Sector-level operations enable recovery from severe corruption scenarios and provide low-level disk analysis capabilities for advanced troubleshooting procedures.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Installation Problems
Repository access issues can prevent successful GParted installation on Fedora 42 systems. Verify network connectivity and DNS resolution before attempting package installation. Configure proxy settings if required for internet access in corporate environments.
Dependency conflicts may arise when installing GParted on systems with custom software installations or third-party repositories. Use DNF’s dependency resolution tools to identify and resolve conflicts:
sudo dnf check
sudo dnf repoquery --requires gpartedPermission-related errors during installation typically indicate insufficient administrative privileges or sudo configuration problems. Verify user membership in appropriate administrative groups and sudo policy configurations.
Network connectivity problems can interrupt package downloads and cause installation failures. Ensure stable internet connections and consider using local repository mirrors for improved reliability in bandwidth-constrained environments.
Runtime Issues
Device detection failures may occur with newer hardware or specialized storage controllers not fully supported by current kernel versions. Update system packages and kernel modules to ensure compatibility with latest hardware developments.
Permission denied errors during partition operations indicate insufficient privileges or security policy restrictions. Verify GParted launches with appropriate administrative credentials and check SELinux policies that might restrict disk access.
Partition lock situations arise when filesystems remain mounted during operation attempts. Unmount target filesystems before performing partition modifications, ensuring no active processes access the affected storage devices.
GUI display problems on systems with multiple graphics adapters or complex display configurations may prevent proper GParted operation. Configure appropriate display settings and verify graphics driver compatibility with GNOME 48 desktop environment.
Operation Failures
Insufficient disk space errors during partition operations require adequate free space for temporary data storage and operation buffers. Calculate space requirements before initiating complex operations and ensure adequate margins for unexpected overhead.
Filesystem corruption handling requires immediate attention to prevent data loss and system instability. Use filesystem-specific repair tools in conjunction with GParted for comprehensive corruption resolution procedures.
Interrupted operations recovery depends on the specific operation type and completion status when interruption occurs. Some operations can be safely resumed while others may require complete restart from backup restoration.
Hardware compatibility issues may affect operation reliability on older systems or specialized hardware configurations. Verify hardware support documentation and consider alternative approaches for unsupported configurations.
Best Practices and Safety Tips
Data Protection Strategies
Comprehensive backup creation before major partition operations provides essential protection against data loss from unexpected failures or user errors. Implement multiple backup strategies including full system images, incremental backups, and critical data copies stored on separate storage devices.
Testing procedures on non-critical systems validate operation procedures and identify potential issues before applying changes to production environments. Virtual machine testing provides safe environments for experimenting with complex partition layouts and advanced configurations.
Understanding irreversible operations helps users make informed decisions about partition modifications and their potential consequences. Document all planned changes and their expected outcomes before beginning complex procedures.
Recovery planning includes preparing bootable rescue media, backup restoration procedures, and emergency contact information for critical system recovery scenarios.
Performance Optimization
Optimal partition sizes and alignment ensure maximum storage performance and longevity, particularly for solid-state drives requiring specific alignment parameters for optimal operation. Research manufacturer recommendations for alignment settings and partition boundaries.
Filesystem selection guidelines help choose appropriate filesystems for specific use cases, considering factors like performance requirements, file size limitations, and feature needs. Match filesystem capabilities to application requirements for optimal performance.
Defragmentation considerations vary significantly between traditional hard drives and solid-state storage devices. Understand appropriate maintenance procedures for your specific storage technology to avoid performance degradation or hardware damage.
System resource management during partition operations requires adequate memory allocation and CPU availability for optimal performance. Schedule intensive operations during low-activity periods to minimize system impact.
Security Considerations
Running GParted with minimal required privileges reduces security exposure while maintaining necessary functionality for partition management operations. Use targeted sudo configurations that limit administrative access to specific commands and time periods.
Encryption best practices include proper key management, secure key storage, and comprehensive understanding of encryption limitations and recovery procedures. Document encryption configurations and recovery methods for emergency situations.
Secure deletion techniques ensure sensitive data cannot be recovered from deleted partitions or reformatted storage devices. Understand the difference between logical deletion and secure wiping procedures for appropriate data protection.
Access control management includes monitoring user activities during partition operations and maintaining audit trails for security compliance and troubleshooting purposes.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed GParted. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the GParted on your Fedora 42 Linux system. For additional or useful information, we recommend you check the official GParted website.