How To Install GParted on Manjaro
GParted, short for GNOME Partition Editor, is a powerful and user-friendly tool for managing disk partitions on Linux systems. For Manjaro users, installing GParted can greatly simplify the process of creating, resizing, and managing partitions. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the installation process, usage tips, and alternatives to GParted on Manjaro Linux.
Understanding GParted and Its Importance
GParted is an open-source partition editor that allows users to efficiently manage their disk space. It provides a graphical interface for tasks such as creating, deleting, resizing, moving, and copying partitions. This tool is particularly useful for:
- Setting up dual-boot systems
- Resizing partitions to optimize disk space
- Creating new partitions for data organization
- Formatting partitions with various file systems
For Manjaro users, GParted offers a straightforward way to manage disk partitions without relying on command-line tools, making it an essential utility for both beginners and advanced users.
Prerequisites for Installing GParted on Manjaro
Before proceeding with the installation, ensure that:
- Your Manjaro system is up-to-date
- You have a stable internet connection
- You have sufficient disk space (GParted is relatively small, but it’s always good to check)
- You have administrative (sudo) privileges on your system
Step-by-Step Guide to Install GParted on Manjaro
Manjaro, being an Arch-based distribution, uses the pacman package manager. Follow these steps to install GParted:
1. Update Your System
First, ensure your system is up-to-date:
sudo pacman -SyuThis command synchronizes the package databases and upgrades all packages on the system.
2. Install GParted
Once your system is updated, install GParted using the following command:
sudo pacman -S gpartedPacman will calculate dependencies and ask for confirmation before installing. Type ‘Y’ and press Enter to proceed.
3. Verify the Installation
After the installation completes, you can verify it by checking the version:
gparted --versionThis command should display the installed version of GParted.
Launching and Using GParted
To launch GParted, you have two options:
- Use the application menu: Search for “GParted” in your desktop environment’s application launcher.
- Use the terminal: Simply type `
gparted` in the terminal and press Enter.
Note: GParted requires root privileges to make changes to disk partitions. When launched from the application menu, it will prompt for your password. If launched from the terminal, use:
sudo gparted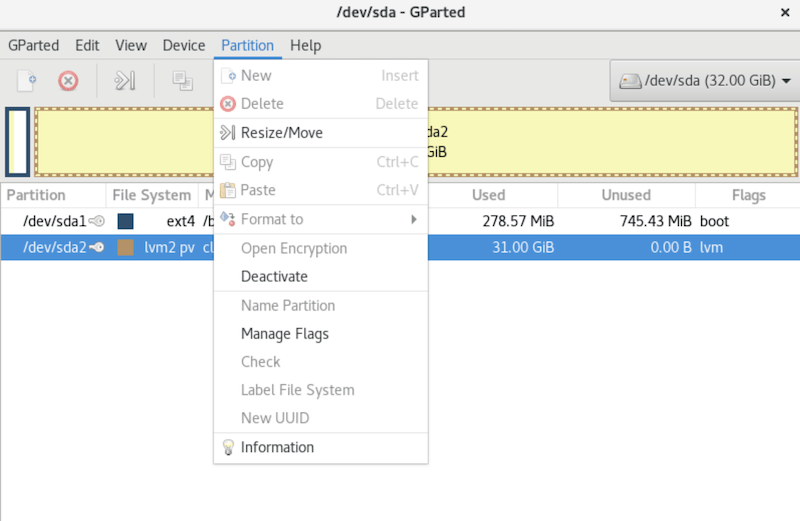
Basic Usage of GParted
Once launched, GParted presents a graphical interface showing all detected storage devices and their partitions. Here are some basic operations:
- Select a device: Use the dropdown menu in the top-right corner to choose the disk you want to work on.
- Create a new partition: Right-click on unallocated space and select “New”.
- Resize a partition: Right-click on a partition and select “Resize/Move”.
- Delete a partition: Right-click on a partition and select “Delete”.
- Format a partition: Right-click on a partition and select “Format to”.
Always remember to click the “Apply All Operations” button (green checkmark) to implement your changes.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While installing and using GParted on Manjaro, you might encounter some issues. Here are solutions to common problems:
1. Package Not Found Error
If pacman can’t find the GParted package, try updating the package databases:
sudo pacman -SyThen attempt the installation again.
2. Dependency Conflicts
In rare cases, you might face dependency conflicts. Try resolving them by updating your entire system:
sudo pacman -SyuIf the issue persists, you may need to investigate which packages are conflicting and update or remove them as necessary.
3. Permission Denied Errors
If you encounter “permission denied” errors when trying to modify partitions, ensure you’re running GParted with root privileges:
sudo gparted4. GParted Not Detecting All Drives
If GParted isn’t showing all your drives, it might be due to drive encryption or LVM (Logical Volume Management). In such cases, you may need to use specialized tools or decrypt the drives before using GParted.
Alternatives to GParted on Manjaro
While GParted is a popular choice, Manjaro offers several alternatives for disk partition management:
1. KDE Partition Manager
For users of the KDE desktop environment, KDE Partition Manager provides similar functionality to GParted with a Qt-based interface. Install it using:
sudo pacman -S partitionmanager2. GNOME Disks
GNOME users might prefer GNOME Disks (gnome-disk-utility), which offers a simpler interface for basic partition management. Install it with:
sudo pacman -S gnome-disk-utility3. Command-Line Tools
For advanced users comfortable with the terminal, Manjaro includes powerful command-line tools:
-
fdisk: A text-based partition table manipulator -
parted: The command-line version of GParted -
cfdisk: A curses-based variant of fdisk
These tools are typically pre-installed on Manjaro systems.
Best Practices for Partition Management
When using GParted or any partition management tool on Manjaro, keep these best practices in mind:
- Always backup your data before making changes to partitions.
- Use a live system (like a Manjaro live USB) when modifying system partitions to avoid conflicts with mounted filesystems.
- Verify your changes carefully before applying them, as partition modifications can lead to data loss if done incorrectly.
- For dual-boot setups, be cautious not to modify partitions of other operating systems unless you’re certain about the changes.
- Keep your system updated to ensure you have the latest version of GParted with bug fixes and improvements.
Advanced GParted Features for Manjaro Users
GParted offers several advanced features that Manjaro users might find useful:
1. LVM Support
GParted can handle Logical Volume Management (LVM) partitions, which are commonly used in more complex storage setups. However, for extensive LVM operations, specialized tools like system-config-lvm might be more appropriate.
2. RAID Configuration
While GParted can view and manage partitions on RAID arrays, it’s not designed for RAID configuration. For RAID setup and management, use dedicated tools like mdadm.
3. Disk Checks and Repairs
GParted can initiate filesystem checks and repairs for many filesystem types. This feature is particularly useful for troubleshooting disk issues on Manjaro systems.
Integrating GParted with Manjaro Workflow
To make the most of GParted on your Manjaro system:
- Create a desktop shortcut for quick access to GParted.
- Familiarize yourself with Manjaro’s default partitioning scheme to understand how your system is organized.
- Use GParted in conjunction with Manjaro’s built-in tools for a comprehensive disk management approach.
- Regularly check your disk usage and use GParted to optimize your partition layout as needed.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed GParted. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the GParted on your Manjaro system. For additional Apache or useful information, we recommend you check the official GParted website.