How To Install Htop on CentOS Stream 10

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Htop on CentOS Stream 10. Monitoring system performance is crucial for maintaining optimal operation in any Linux environment. One of the most effective tools for this purpose is htop, an interactive process viewer that provides real-time insights into system resource usage. This article will guide you through the process of installing htop on CentOS Stream 10, ensuring you have the tools necessary to monitor and manage your system effectively.
Understanding Htop
What is Htop?
Htop is a powerful command-line utility that allows users to monitor system processes and resource usage in real-time. Unlike the traditional top command, htop offers a more user-friendly interface with color-coded metrics, making it easier to interpret data at a glance.
Advantages of Using Htop Over Top
- Enhanced User Interface: Htop features a visually appealing layout that displays CPU, memory, and swap usage in easy-to-read graphs.
- Real-Time Monitoring: It updates information dynamically, allowing users to see changes as they occur.
- Process Management: Users can easily manage processes, including killing or renicing them directly from the interface.
Use Cases for Htop
Htop is particularly beneficial for system administrators and developers who need to monitor server performance, troubleshoot resource-intensive processes, and ensure that applications run smoothly. Its intuitive design makes it an essential tool for anyone managing Linux systems.
Prerequisites for Installation
System Requirements
Before installing htop, ensure your system meets the following requirements:
- Operating System: CentOS Stream 10 must be installed and operational.
- Hardware: A minimum of 1 GB RAM is recommended for running htop alongside other applications.
User Permissions
You will need sufficient permissions, specifically sudo privileges, to install software on CentOS Stream 10. This ensures that you can execute commands that modify system files and install packages.
Updating the System
Before proceeding with the installation of htop, it’s essential to update your system to ensure all existing packages are current. Run the following command:
sudo dnf updateStep-by-Step Installation Guide
Step 1: Enable EPEL Repository
The Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL) repository contains additional packages that are not included in the standard CentOS repository. To enable EPEL on CentOS Stream 10, execute the following command:
sudo dnf install epel-releaseThis command installs the EPEL release package, which allows you to access a broader range of software, including htop.
Step 2: Install Htop
With the EPEL repository enabled, you can now install htop. Use the following command:
sudo dnf install htopThis command fetches the htop package from the EPEL repository and installs it on your system. During installation, you may be prompted to confirm the action; simply type ‘y’ and press Enter to proceed.
Step 3: Verify Installation
After installation is complete, it’s important to verify that htop was installed correctly. You can check its version by running:
htop --versionIf installed successfully, this command will display the version number of htop. If you encounter any errors at this stage, double-check your previous steps to ensure everything was executed correctly.
Step 4: Launching Htop
You can now start using htop by launching it from your terminal. Simply type:
htopThis command opens the htop interface, where you will see a colorful display of CPU usage, memory consumption, swap usage, and a list of running processes. Familiarize yourself with the interface as it provides various options for monitoring and managing processes.
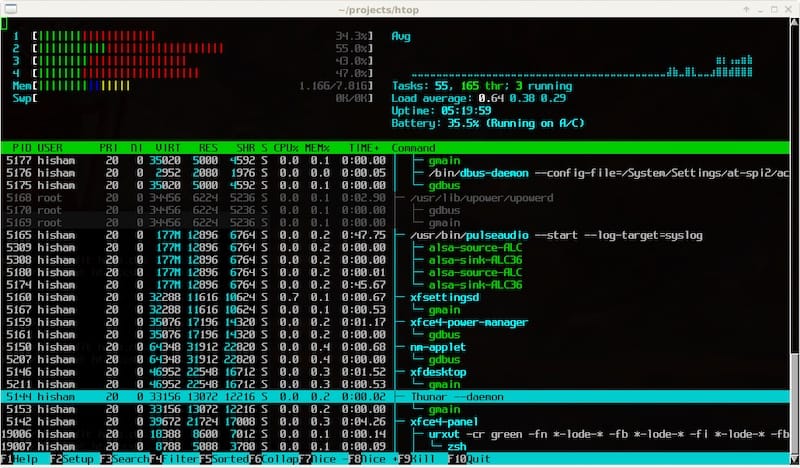
Using Htop Effectively
Navigating the Htop Interface
The htop interface is designed for ease of use. Here are some key features and navigation tips:
- Cores Display: The CPU usage is shown as bars representing each core’s activity.
- Memory Usage: Memory utilization is displayed graphically at the top of the screen.
- Selecting Processes: Use the arrow keys to navigate through processes. Highlight a process by selecting it with your keyboard.
- Killing Processes: To terminate a process, select it and press F9 (or ‘k’). You will be prompted to choose a signal (e.g., SIGTERM).
- S sorting Processes: Press F6 to sort processes by different criteria such as CPU or memory usage.
- S searching Processes: Press F3 and type in the name of a process to quickly locate it.
Managing Processes with Htop
The ability to manage processes directly from htop adds significant value. Here’s how you can effectively use this feature:
- Killing a Process: After selecting a process with arrow keys, press F9. Choose a signal like SIGTERM (15) or SIGKILL (9) based on your needs.
- Nicing a Process: To change a process’s priority, select it and press F7 (to increase priority) or F8 (to decrease priority).
- Paging Through Processes: If there are many processes running, use Page Up/Page Down keys to scroll through them efficiently.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Installation Issues
If you encounter problems during installation, consider these common issues:
- EPEL Repository Not Found: If you receive an error regarding missing repositories, ensure that your internet connection is active and try enabling EPEL again using the appropriate command.
- No Package Found Error: If DNF cannot find htop after enabling EPEL, run
sudo dnf clean all, followed bysudo dnf makecache, then attempt installation again.
Running Htop Issues
If htop does not launch or displays incorrectly:
- No Output or Blank Screen: If you see no output when launching htop, check if your terminal supports ANSI colors; try running in another terminal emulator.
- Error Messages Upon Launching: If error messages appear when starting htop, ensure that all dependencies were installed correctly during setup.
Congratulations! You have successfully install Htop. Thanks for using this tutorial to install Htop monitoring tool on your CentOS Stream 10 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Htop website.