
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install and configuration of Icinga 2 on your CentOS 7 server. For those of you who didn’t know, Icinga 2 is an open-source network monitoring system that checks the availability of your network resources, notifies users of outages, and generates performance data for reporting. It’s Scalable and extensible, Icinga2 can monitor large, complex environments across multiple locations.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of Icinga 2 on a CentOS 7 server.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: CentOS 7.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Icinga 2 Features
- Monitoring of network services (SMTP, POP3, HTTP, NNTP, ping, etc.)
- Monitoring of host resources (CPU load, disk usage, etc.)
- Monitoring of server components (switches, routers, temperature and humidity sensors, etc.)
- Simple plug-in design that allows users to easily develop their own service checks,
- Parallelized service checks.
- Ability to define network host hierarchy using “parent” hosts, allowing detection of and the distinction between hosts that are down and those that are unreachable.
- Ability to define event handlers to be run during service or host events for proactive problem resolution.
- Notification of contact persons when service or host problems occur and get resolved (via email, pager, or user-defined method).
- Escalation of alerts to other users or communication channels.
- Two optional user interfaces (Icinga Classic UI and Icinga Web) for visualization of host and service status, network maps, reports, logs, etc.
- Icinga Reporting module based on open source Jasper Reports for both Icinga Classic and Icinga Web user interfaces
- Capacity utilization reporting.
- Performance graphing via add-ons such as PNP4Nagios, NagiosGrapher, and InGraph.
Install Icinga 2 on CentOS 7
Step 1. First, let’s start by ensuring your system is up-to-date.
yum clean all yum -y update
Step 2. Next, you can add the EPEL repository before you can install Odoo using YUM:
Run the following command to do so:
yum install -y epel-release
Step 3. Installing Icinga 2.
First, enable the add-repository feature and add the repository for Icinga with the below commands:
rpm --import http://packages.icinga.org/icinga.key wget http://packages.icinga.org/epel/ICINGA-release.repo -O /etc/yum.repos.d/ICINGA-release.repo yum makecache
Now run the Icinga 2 Installation command as shown below:
yum install icinga2
Once the installation is complete. Make sure the service is up and running fine:
systemctl status icinga2.service systemctl enable icinga2.service systemctl start icinga2.service
By default, Icinga2 enables the following features. But we can confirm the enabled settings by running this command as below:
icinga2 feature list
Step 4. Installing the Icinga 2 plugin.
Icinga2 will collect the service information based on the monitoring plugins. So, we need to install the Nagios plugin using the below command:
yum install nagios-plugins-all
Next, you need to install the IDO module which is crucial for the Icinga 2 web interface. It will export all configuration and status information into its database. Execute the following command:
yum install icinga2-ido-mysql
Then restart Icinga 2 for the changes to take effect:
systemctl restart icinga2.service
Step 5. Configure the MySQL database for Icinga2.
Create a database for Icinga 2:
### Setting up the MySQL database Icinga2 ### # mysql -u root -p MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE icinga; MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, DROP, CREATE VIEW, INDEX, EXECUTE ON icinga.* TO 'icinga'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'icinga'; MariaDB [(none)]> exit # Importing the Icinga 2 IDO schema into database # mysql -u root -p icinga < /usr/share/icinga2-ido-mysql/schema/mysql.sql # Enabling the IDO MySQL module # icinga2 feature enable ido-mysql # For Systemd systems # systemctl restart icinga2.service
Step 6. Installing Icinga 2 Web.
First, setting up the external command pipe:
icinga2 feature enable command systemctl restart icinga2.service
Before you can send commands to Icinga 2 using a web interface, you need to add the “apache” user to the icingacmd group:
usermod -a -G icingacmd apache
Next, we can install the Web interface plugin and configure it one by one:
yum install icingaweb2 icingacli
Generate authentication token for later use in the web interface:
icingacli setup token create icingacli setup token show
Step 7. Setup Firewall Rules.
If you installed IPtables you have to allow the HTTP and its port to work outside the world:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https
Step 6. Accessing Icinga 2.
Icinga2 will be available on HTTP port 80 by default. Open your favorite browser and navigate to http://yourdomain.com/icingaweb2/setup or http://server-ip/icingaweb2/setup and complete the required steps to finish the installation. If you are using a firewall, please open port 80 to enable access to the control panel.
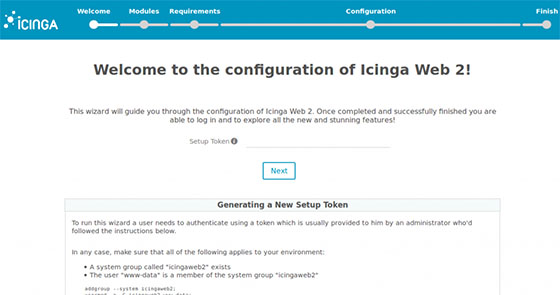
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Icinga 2. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Icinga 2 network monitoring on CentOS systems. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official Icinga 2 website.