
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Icinga 2 on Debian 11. For those of you who didn’t know, Icinga 2 is an open-source monitoring solution that is used to monitor the availability of various network resources including host metrics such as system uptime, load, memory, disk space, running processes, network, and many more. Icinga 2 has a user-friendly web interface, but it also comes with a command-line interface that can be used to monitor networks, servers, and services with specific commands.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you through the step-by-step installation of the Icinga open-source network monitoring on a Debian 11 (Bullseye).
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Debian 11 (Bullseye).
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Icinga 2 on Debian 11 Bullseye
Step 1. Before we install any software, it’s important to make sure your system is up to date by running the following apt commands in the terminal:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Step 2. Installing LAMP stack.
A Debian 11 LAMP server is required. If you do not have LAMP installed, you can follow our guide here.
Step 3. Installing Icinga 2 on Debian 11.
By default, the Icinga2 package is available on the Debian 11 base repository. You can install it using the following command below:
sudo apt install icinga2 monitoring-plugins
After installation, enable Icinga 2 to start on server boot:
sudo systemctl start icinga2 sudo systemctl enable icinga2
Step 4. Configure MariaDB.
Now we create a database and user for Icinga:
mysql -u root -p
This will prompt you for a password, so enter your MariaDB root password and hit Enter. Once you are logged in to your database server you need to create a database for Icinga 2 installation:
MariaDB [(none)]> create database icingaweb2; MariaDB [(none)]> grant all privileges on icingaweb.* to icingaweb2@localhost identified by 'strong-your-passwd'; MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges; MariaDB [(none)]> exit;
Once done, now we install the MariaDB plugin for Icinga 2 using the following command:
sudo apt install icinga2-ido-mysql
Output:
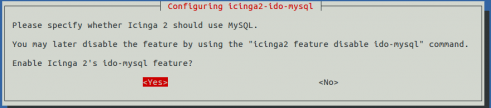
Next, select yes and hit enter. You will be prompt to configure the database icinga2-ido-mysql with dbconfig-common as shown in the following screen:
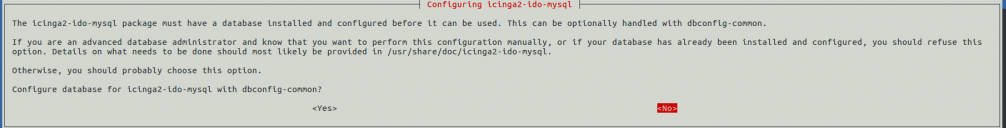
Next, enable the ido-mysql module with the following command:
icinga2 feature enable ido-mysql
Finally, restart the Icinga 2 service to apply all the configuration changes:
sudo systemctl restart icinga2
Step 5. Configure Icinga Web.
Icinga provides a web interface to monitor Icinga 2. You can install it with the following command below:
sudo apt install icingaweb2 icingacli
Then, generate a secrete token with the following command:
icingacli setup token create
Step 6. Accessing Icinga 2 Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, open your favorite browser and navigate to http://your-ip-address/icingaweb2/setup and complete the required steps to finish the installation. If you are using a firewall, please open port 80 to enable access to the control panel.
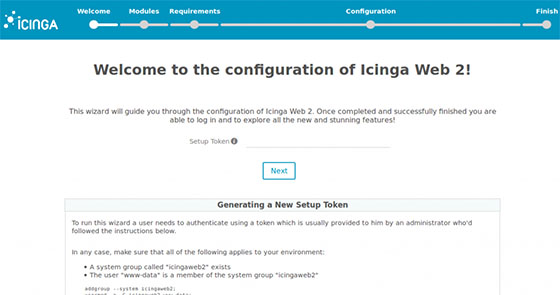
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Icinga. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the latest version of the Icinga 2 network monitoring on Debian 11 Bullseye. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Icinga website.