How To Install Jellyfin on Debian 13

Setting up your own media streaming server has never been more accessible. Jellyfin stands as the premier open-source alternative to proprietary media servers, offering complete control over your entertainment library without subscription fees or limitations. This comprehensive guide walks you through installing Jellyfin on Debian 13 (Trixie), ensuring a smooth setup process for both beginners and experienced Linux users.
Whether you’re migrating from Plex or starting fresh with home media management, Jellyfin provides robust transcoding capabilities, multi-device support, and extensive customization options. The latest Debian 13 release offers enhanced stability and performance improvements that make it an ideal foundation for your media server infrastructure.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Hardware Requirements
Installing Jellyfin on Debian 13 requires careful consideration of your hardware specifications. Your system needs sufficient processing power to handle media transcoding, especially for 4K content streaming to multiple devices simultaneously.
Minimum specifications include a dual-core CPU with at least 2GB of RAM for basic functionality. However, recommended specifications suggest a quad-core processor with 8GB of RAM to ensure smooth operation during peak usage. Storage requirements vary significantly based on your media library size, but allocating at least 500GB for the operating system and initial media collection proves practical.
Network connectivity plays a crucial role in streaming performance. Gigabit ethernet provides optimal performance for local network streaming, while adequate upload bandwidth becomes essential for remote access scenarios.
Software Requirements
Before proceeding with the Jellyfin installation, verify your Debian 13 system meets all software prerequisites. Administrative privileges through sudo access remain mandatory for installing packages and configuring system services.
Your system requires an active internet connection for downloading packages and dependencies. The APT package manager should function correctly with updated repository information. Basic Linux command-line familiarity helps navigate the installation process, though this guide provides detailed explanations for each step.
Pre-Installation Checklist
System compatibility verification ensures smooth installation without unexpected complications. Check your Debian version using lsb_release -a to confirm you’re running Trixie (Debian 13). Verify available disk space with df -h ensuring adequate room for both the application and media storage.
Backup considerations become critical before making system modifications. Create system snapshots or backups of important configurations. Document current network settings and service configurations that might require adjustment during the setup process.
Security considerations include reviewing firewall configurations and planning network access patterns. Determine whether you need local-only access or remote streaming capabilities before beginning installation.
Preparing Your Debian 13 System
System Updates and Maintenance
Begin by updating your Debian 13 system to ensure all packages reflect the latest versions and security patches. Execute comprehensive system updates using the following command sequence:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -yThis command combination refreshes package repository information and upgrades all installed packages to their newest versions. System maintenance continues with removing unnecessary packages that accumulate over time:
sudo apt autoremove -y
sudo apt autocleanVerify your system version and codename to confirm proper Debian 13 installation:
lsb_release -a
cat /etc/debian_versionInstalling Essential Dependencies
Jellyfin installation requires several essential packages for proper functionality. Install the complete dependency stack using this comprehensive command:
sudo apt install software-properties-common apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release wget -yEach package serves specific purposes in the media server setup:
software-properties-commonprovides tools for managing software repositoriesapt-transport-httpsenables secure HTTPS repository accessca-certificatesensures SSL/TLS certificate validationcurlandwgetfacilitate file downloads from remote serversgnupghandles GPG key management for repository authenticationlsb-releaseprovides distribution information utilities
Verify successful installation by checking package versions:
curl --version
wget --version
gpg --versionSystem Security Preparation
Configure basic firewall settings to secure your media server while maintaining necessary access. Install and configure UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) if not already present:
sudo apt install ufw -y
sudo ufw enable
sudo ufw allow 8096/tcp
sudo ufw allow sshThe Jellyfin default port (8096) requires explicit firewall permission for web interface access. SSH access preservation ensures continued remote administration capabilities.
User permission setup involves creating dedicated service accounts if desired, though the default Jellyfin installation handles user management automatically. Review existing user groups and permissions to prevent conflicts during installation.
Method 1: Quick Installation Using Official Script
Official Jellyfin Installation Script
The official installation script provides the fastest path to a working Jellyfin installation on Debian 13. This method automatically handles repository configuration, GPG key management, and package installation in a single command execution.
Script benefits include automated dependency resolution, proper repository configuration, and compatibility verification. The installation script detects your system architecture and selects appropriate packages automatically.
Download and execute the official script with this single command:
curl https://repo.jellyfin.org/install-debuntu.sh | sudo bashScript integrity verification ensures secure installation by validating the downloaded script before execution. While the single-line installation offers convenience, security-conscious administrators might prefer downloading and inspecting the script separately:
curl -o install-jellyfin.sh https://repo.jellyfin.org/install-debuntu.sh
less install-jellyfin.sh
sudo bash install-jellyfin.shStep-by-Step Script Installation
The installation script performs several automated tasks during execution. It begins by detecting your operating system version and architecture, followed by repository configuration and GPG key installation.
Package installation proceeds automatically after repository setup completion. The script installs core Jellyfin components including the server application, web interface, and optimized FFmpeg builds for media transcoding.
Monitor the installation progress for any error messages or dependency conflicts. The script provides verbose output indicating each completed step and any encountered issues.
Verification of Script Installation
Installation verification confirms proper setup and service functionality. Check the Jellyfin service status immediately after script completion:
sudo systemctl status jellyfinVerify service startup configuration to ensure automatic launching after system reboots:
sudo systemctl is-enabled jellyfinTest initial web interface connectivity by accessing the server through your web browser at http://localhost:8096. Successful connection indicates proper installation and service operation.
Method 2: Manual Repository Installation
Adding Jellyfin Repository Manually
Manual repository configuration provides greater control over the installation process and better understanding of system modifications. This method proves particularly valuable for administrators managing multiple systems or requiring custom configurations.
Begin GPG key import using modern keyring management practices. Debian 13 supports advanced keyring functionality that improves security over legacy methods:
curl -fsSL https://repo.jellyfin.org/jellyfin_team.gpg.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/jellyfin.gpgRepository configuration follows the new sources.list.d format for improved modularity:
echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/jellyfin.gpg arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture)] https://repo.jellyfin.org/debian $(lsb_release -cs) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jellyfin.sourcesAlternative Repository Setup Methods
Traditional sources.list method remains available for administrators preferring legacy configuration approaches:
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture)] https://repo.jellyfin.org/debian $(lsb_release -cs) main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.listModern sources.list.d format offers superior organization and management capabilities. Create a dedicated configuration file for Jellyfin repository management:
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jellyfin.listAdd the following repository configuration to the file:
deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/jellyfin.gpg arch=amd64] https://repo.jellyfin.org/debian trixie mainPackage Installation Process
Update package repository information after adding the Jellyfin repository:
sudo apt updateInstall core Jellyfin packages using APT package manager. The installation includes multiple components for complete functionality:
sudo apt install jellyfin jellyfin-server jellyfin-web -yFFmpeg installation requires special attention due to Jellyfin’s optimized builds. Search for available FFmpeg versions compatible with your system:
apt search jellyfin-ffmpeg
sudo apt install jellyfin-ffmpeg7 -yThe jellyfin-ffmpeg7 package provides hardware acceleration support and optimized encoding profiles for various media formats. This custom FFmpeg build significantly improves transcoding performance compared to standard repository versions.
Post-Installation Verification
Verify successful package installation by checking installed versions and dependencies:
dpkg -l | grep jellyfin
apt show jellyfinService status verification ensures proper installation and automatic startup configuration:
sudo systemctl status jellyfin
sudo systemctl enable jellyfin
sudo systemctl start jellyfinTest port connectivity and service binding:
sudo netstat -tlnp | grep 8096
ss -tlnp | grep 8096Service Configuration and Management
Systemd Service Management
Jellyfin service management utilizes systemd for reliable service control and monitoring. Understanding basic service operations enables effective media server administration.
Service control commands provide comprehensive management capabilities:
sudo systemctl start jellyfin # Start the service
sudo systemctl stop jellyfin # Stop the service
sudo systemctl restart jellyfin # Restart the service
sudo systemctl reload jellyfin # Reload configurationAutomatic startup configuration ensures your media server launches automatically during system boot:
sudo systemctl enable jellyfin
sudo systemctl disable jellyfin # Disable auto-start if neededService status monitoring provides detailed information about service health and recent activity:
sudo systemctl status jellyfin -l
journalctl -u jellyfin -f # Follow live logs
journalctl -u jellyfin --since "1 hour ago" # Recent logsService Configuration Files
Jellyfin configuration resides in several key locations within the Debian filesystem. Understanding these locations facilitates troubleshooting and customization:
/etc/jellyfin/– System configuration files/var/lib/jellyfin/– Database and metadata storage/var/log/jellyfin/– Application log files/etc/systemd/system/jellyfin.service.d/– Service customizations
Custom service parameters can be configured through systemd override files:
sudo systemctl edit jellyfinAdd custom environment variables or service parameters as needed:
[Service]
Environment="JELLYFIN_DATA_DIR=/custom/path"
Environment="JELLYFIN_CONFIG_DIR=/custom/config"User and Permission Management
Jellyfin service runs under a dedicated system user account for security isolation. The installation process automatically creates the jellyfin user with appropriate permissions.
File permission requirements ensure proper access to media libraries and configuration directories. Media files should remain readable by the jellyfin user:
sudo usermod -a -G your_media_group jellyfin
sudo chmod -R 755 /path/to/media/directorySecurity considerations include limiting unnecessary permissions while maintaining functionality. Avoid running Jellyfin as root or granting excessive filesystem access.
Initial Setup and Web Interface Configuration
Accessing the Web Interface
Jellyfin web interface becomes accessible immediately after successful service startup. Navigate to the setup wizard using your preferred web browser at http://your-server-ip:8096.
Browser compatibility encompasses all modern web browsers including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. Mobile browsers also provide full functionality for media server administration.
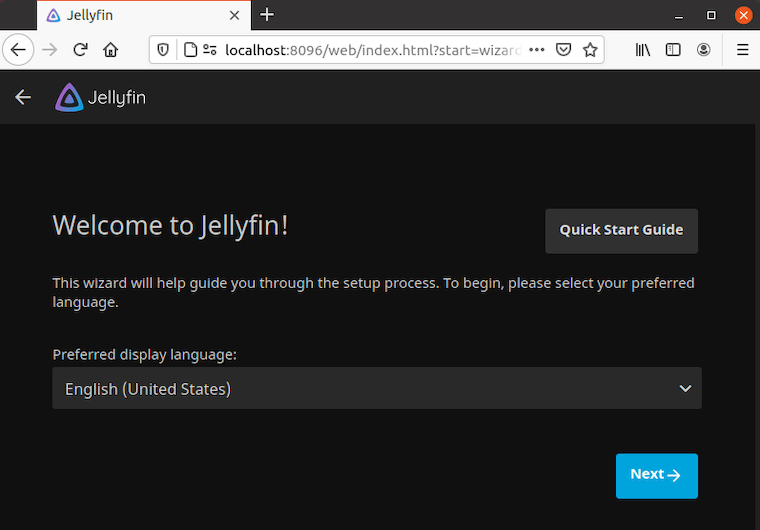
Network accessibility considerations include firewall configuration and local network routing. Ensure port 8096 remains open and accessible from client devices.
Setup Wizard Walkthrough
Welcome screen navigation initiates the initial configuration process. The setup wizard guides you through essential settings for immediate media server functionality.
Administrator account creation establishes primary administrative access. Choose a strong username and password combination following security best practices:
- Use unique usernames avoiding common defaults
- Implement complex passwords with mixed character types
- Consider password manager integration for secure storage
Language and regional settings configure localization options for optimal user experience. Select appropriate language, timezone, and cultural preferences matching your location.
Media Library Configuration
Media library setup forms the core of Jellyfin functionality. The wizard presents options for configuring different content types:
- Movies – Feature films and documentaries
- TV Shows – Series and episodic content
- Music – Audio collections and playlists
- Books – Digital publications and audiobooks
- Mixed Content – Multi-format libraries
Directory path configuration requires careful consideration of storage organization and access permissions. Ensure the jellyfin user maintains read access to all specified directories:
sudo chown -R jellyfin:jellyfin /media/library
sudo chmod -R 755 /media/libraryMetadata and indexing options affect library scanning performance and content organization. Enable automatic metadata retrieval for enhanced browsing experiences while considering bandwidth limitations.
Network and Remote Access
Local network configuration establishes basic connectivity for household devices. The default settings usually accommodate standard home network environments without modification.
Remote access setup enables media streaming from external networks. Configure dynamic DNS services or static IP addresses for reliable external connectivity:
# Configure UFW for remote access
sudo ufw allow from any to any port 8096
sudo ufw reloadSecurity considerations become paramount for internet-exposed services. Implement strong authentication, consider VPN access, and monitor access logs regularly.
Port forwarding configuration on your router directs external traffic to your Jellyfin server. Forward TCP port 8096 to your server’s internal IP address for remote access functionality.
Advanced Configuration Options
Server Settings Optimization
Transcoding configuration significantly impacts media server performance and compatibility across different devices. Hardware acceleration utilizes GPU resources for efficient video processing:
# Check available GPU acceleration options
sudo lspci | grep VGA
sudo apt install intel-media-va-driver-non-free # For Intel GPUsQuality and performance balance requires careful tuning based on your hardware capabilities and client device requirements. Bandwidth limitations help manage network usage during concurrent streaming sessions.
Buffer settings optimization reduces playback interruptions and improves user experience. Adjust buffer sizes based on network performance and storage capabilities.
User Management
Additional user account creation enables family sharing and content access control. Navigate to the administration panel for comprehensive user management functionality.
Permission levels provide granular control over user capabilities:
- Administrator – Full system access and configuration
- User – Standard media access with limited settings
- Guest – Temporary access with restricted permissions
Parental controls facilitate content filtering based on ratings and categories. Configure age-appropriate restrictions for younger family members.
Plugin Management
Plugin repository access expands Jellyfin functionality through community-developed extensions. Popular plugins include:
- Trakt integration for viewing history synchronization
- OpenSubtitles for automated subtitle downloading
- MusicBrainz for enhanced music metadata
- TMDb Box Sets for movie collection organization
Installation and configuration processes vary by plugin complexity. Most plugins require simple installation through the web interface followed by basic configuration.
Security Hardening
SSL/TLS certificate installation encrypts web interface communications and protects sensitive data transmission. Obtain certificates through Let’s Encrypt or commercial providers:
sudo apt install certbot -y
sudo certbot certonly --standalone -d your-domain.comReverse proxy configuration using Nginx or Apache provides additional security layers and enables advanced routing capabilities:
sudo apt install nginx -y
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/jellyfinAccess control implementation restricts unauthorized access through IP filtering, geographic restrictions, and authentication requirements.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Installation Problems
Repository access issues frequently occur due to network connectivity or GPG key problems. Verify internet connectivity and DNS resolution:
ping -c 4 repo.jellyfin.org
nslookup repo.jellyfin.orgGPG key problems manifest as authentication failures during package installation. Re-import keys using updated procedures:
sudo rm /etc/apt/keyrings/jellyfin.gpg
curl -fsSL https://repo.jellyfin.org/jellyfin_team.gpg.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/jellyfin.gpg
sudo apt updatePackage dependency conflicts may arise from mixed repository sources or outdated package versions. Resolve conflicts through careful dependency management:
sudo apt --fix-broken install
sudo apt autoremove
sudo apt cleanService and Connectivity Issues
Service startup failures require systematic troubleshooting through log analysis and dependency verification. Examine systemd logs for detailed error information:
journalctl -u jellyfin -n 50
systemctl --failedCommon error messages include port binding failures, permission errors, and missing dependencies. Address each category systematically:
# Check port availability
sudo netstat -tlnp | grep 8096
sudo lsof -i :8096
# Verify permissions
sudo ls -la /var/lib/jellyfin
sudo ls -la /etc/jellyfinWeb interface access problems often stem from firewall restrictions or incorrect network configuration. Verify service binding and firewall rules:
sudo systemctl status jellyfin
sudo ufw status verbosePerformance and Media Issues
Transcoding problems significantly impact media streaming quality and server performance. FFmpeg configuration issues require attention to codec support and hardware acceleration:
# Test FFmpeg functionality
ffmpeg -version
ffmpeg -codecs | grep h264Hardware acceleration troubleshooting involves verifying driver installation and device access permissions:
# Check GPU driver status
sudo lspci -k | grep -A 2 VGA
ls -la /dev/dri/Media library scanning issues prevent content discovery and organization. Permission problems with media directories require systematic resolution:
# Fix media directory permissions
sudo find /media -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
sudo find /media -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;
sudo chown -R jellyfin:jellyfin /mediaSystem-Specific Debian 13 Considerations
Package availability for newer Debian versions occasionally presents challenges due to repository update cycles. Testing repository compatibility may require manual intervention:
# Check package availability
apt policy jellyfin
apt search jellyfinCompatibility with testing repositories requires careful version management to prevent system instability. Monitor package versions and dependencies during updates.
Performance Optimization and Best Practices
Hardware Optimization
CPU and memory allocation directly impacts concurrent streaming capabilities and transcoding performance. Monitor resource utilization during peak usage periods:
htop
iostat -x 1Storage configuration recommendations include SSD deployment for metadata and database storage while utilizing traditional drives for media archives. Network optimization involves gigabit ethernet deployment and QoS configuration for consistent streaming performance.
Software Configuration
Optimal transcoding settings balance quality requirements with hardware limitations. Configure hardware acceleration when available and adjust quality profiles based on client device capabilities.
Library organization strategies improve scanning performance and user navigation. Implement consistent naming conventions and directory structures for optimal metadata detection.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Performance monitoring tools provide insights into system health and resource utilization. Regular maintenance tasks include database optimization, log rotation, and temporary file cleanup:
# Monitor Jellyfin logs
tail -f /var/log/jellyfin/jellyfin.log
# Clean temporary files
sudo find /var/lib/jellyfin/transcodes -type f -mtime +1 -deleteUpdate procedures require careful scheduling to minimize service interruptions. Plan maintenance windows and create configuration backups before major updates.
Security Considerations
Network Security
Firewall configuration provides the first line of defense against unauthorized access. Implement restrictive rules allowing only necessary traffic:
sudo ufw default deny incoming
sudo ufw default allow outgoing
sudo ufw allow ssh
sudo ufw allow 8096/tcp
sudo ufw enableVPN integration offers secure remote access without exposing services directly to the internet. Popular solutions include WireGuard and OpenVPN for encrypted tunneling.
Authentication and Access Control
Strong password policies prevent unauthorized access through credential compromise. Implement two-factor authentication when available and regularly audit user accounts for unnecessary access.
User permission management follows the principle of least privilege, granting only necessary access levels for each account type.
Maintenance and Updates
Regular Maintenance Tasks
System update procedures ensure security patches and bug fixes reach your media server promptly:
sudo apt update
sudo apt list --upgradable | grep jellyfin
sudo apt upgrade jellyfinJellyfin update management requires attention to changelog notifications and compatibility requirements. Database optimization maintains performance as your media library grows:
# Stop Jellyfin service
sudo systemctl stop jellyfin
# Backup database
sudo cp -r /var/lib/jellyfin/data /backup/jellyfin-data-$(date +%Y%m%d)
# Restart service
sudo systemctl start jellyfinBackup Strategies
Configuration backup procedures preserve customizations and user settings. Essential directories for backup include:
/etc/jellyfin/– System configuration/var/lib/jellyfin/data/– User data and settings/var/lib/jellyfin/root/default/– Server configuration
Automated backup solutions reduce administrative overhead and ensure consistent protection:
#!/bin/bash
# Jellyfin backup script
DATE=$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S)
BACKUP_DIR="/backup/jellyfin"
mkdir -p $BACKUP_DIR
sudo systemctl stop jellyfin
sudo tar -czf $BACKUP_DIR/jellyfin-config-$DATE.tar.gz /etc/jellyfin /var/lib/jellyfin/data
sudo systemctl start jellyfinCongratulations! You have successfully installed Jellyfin. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Jellyfin software media system on Debian 13 “Trixie” system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Jellyfin website.