How To Install Jenkins on AlmaLinux 10

Jenkins stands as the cornerstone of modern DevOps automation, enabling continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) workflows that streamline software development processes. AlmaLinux 10, the latest stable release of this enterprise-grade Linux distribution, provides an ideal foundation for running Jenkins with its robust security features and RHEL compatibility.
This comprehensive guide walks you through every step of installing and configuring Jenkins on AlmaLinux 10, from initial system preparation to advanced security hardening. Whether you’re a system administrator setting up your first CI/CD pipeline or a DevOps engineer migrating to AlmaLinux 10, this tutorial provides the detailed instructions and best practices you need for a successful deployment.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Hardware Requirements
Before beginning the Jenkins installation on AlmaLinux 10, ensure your system meets the minimum hardware specifications. Jenkins requires at least 2GB of RAM for basic operations, though 4GB or more is recommended for production environments. Your system should have a dual-core processor running at 2GHz or higher to handle build processes efficiently.
Disk space requirements vary based on your intended use. Allocate a minimum of 10GB of free storage for the Jenkins installation and initial configuration. However, production environments typically require 50GB or more to accommodate build artifacts, logs, and plugin data storage.
Software Prerequisites
Your AlmaLinux 10 installation must be fully updated with sudo privileges configured for the installation user. Ensure you have an active internet connection for downloading packages and dependencies. Basic command-line knowledge is essential for executing the installation commands and troubleshooting potential issues.
Verify your AlmaLinux 10 system is properly configured by running the system update command and confirming network connectivity to external repositories.
Initial Considerations
Plan your Jenkins deployment carefully by considering firewall configurations and network security requirements. If you intend to access Jenkins remotely, ensure your network infrastructure supports the necessary port access. Consider setting up a domain name or static IP address for consistent access to your Jenkins instance.
Review your organization’s security policies to determine appropriate authentication methods and access controls before proceeding with the installation.
Understanding Jenkins Architecture
Core Components
Jenkins operates on a master-agent architecture where the Jenkins controller (master) manages the overall system while agents (nodes) execute build jobs. The controller handles scheduling, plugin management, and the web interface, while agents provide distributed computing power for running builds across multiple environments.
The plugin ecosystem forms Jenkins’ greatest strength, offering thousands of integrations with development tools, version control systems, and deployment platforms. This extensible architecture allows teams to customize their CI/CD pipelines according to specific project requirements.
Why Choose Jenkins on AlmaLinux
AlmaLinux 10 provides enterprise-grade stability and security features that make it an excellent choice for hosting Jenkins instances. The distribution’s RHEL compatibility ensures access to a vast ecosystem of enterprise software and support resources while maintaining the open-source advantages.
Long-term support guarantees and regular security updates make AlmaLinux 10 particularly suitable for production Jenkins deployments where reliability and security are paramount concerns.
Step 1: System Preparation and Updates
Update System Packages
Begin the Jenkins installation process by updating your AlmaLinux 10 system to ensure all packages are current. Execute the following command to update and upgrade all installed packages:
sudo dnf update -y && sudo dnf upgrade -yThis command downloads and installs the latest security patches and package updates. The update process may take several minutes depending on your system’s current state and internet connection speed. Monitor the output for any error messages that might indicate repository connectivity issues.
After the update completes, verify the system is running the latest kernel version by checking the output of uname -r. A system reboot may be necessary if kernel updates were installed during the update process.
Configure System Settings
Set your system’s timezone to ensure accurate timestamps in Jenkins logs and build records. Use the timedatectl command to configure the appropriate timezone for your location:
sudo timedatectl set-timezone America/New_YorkConfigure your system’s hostname if needed for network identification and Jenkins instance management. A properly configured hostname helps with SSL certificate management and multi-instance deployments.
Verify network connectivity by testing DNS resolution and internet access. This verification step prevents installation failures due to network connectivity issues during package downloads.
Step 2: Java Installation and Configuration
Install OpenJDK
Jenkins requires Java 11 or later to function properly. AlmaLinux 10 provides OpenJDK packages through its default repositories, making installation straightforward. Install OpenJDK 11 and its development tools using the DNF package manager:
sudo dnf install java-11-openjdk java-11-openjdk-devel -yThe installation includes both the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) and Java Development Kit (JDK). The development package provides additional tools that some Jenkins plugins may require for advanced functionality.
OpenJDK 11 represents the recommended Java version for Jenkins due to its long-term support status and optimal compatibility with Jenkins core and plugins. While newer Java versions work with Jenkins, Java 11 provides the best balance of features and stability.
Verify Java Installation
Confirm the Java installation completed successfully by checking the installed version:
java -versionThe command output should display OpenJDK version information, confirming the installation succeeded. Look for version numbers indicating Java 11 or higher to ensure compatibility with Jenkins requirements.
Set the JAVA_HOME environment variable if your system doesn’t automatically configure it. Add the following line to your system’s environment configuration:
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdkTest the Java installation by running a simple Java command to verify the runtime environment functions correctly.
Step 3: Adding Jenkins Repository
Download Jenkins Repository
Jenkins packages aren’t included in AlmaLinux’s default repositories, requiring the addition of the official Jenkins repository. Download the Jenkins repository configuration using wget:
sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.repoThis command downloads the repository configuration file and places it in the appropriate directory for DNF to recognize. The repository file contains the necessary information for accessing Jenkins packages and their dependencies.
The stable repository provides tested releases suitable for production environments. Avoid using development or weekly repositories for production Jenkins installations due to potential stability issues.
Import GPG Key
Security best practices require verifying package authenticity using GPG signatures. Import the Jenkins project’s GPG key to enable package verification:
sudo rpm --import https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.io.keyThis step ensures DNF can verify the authenticity of downloaded Jenkins packages. Package verification prevents installation of tampered or malicious software by confirming packages come from the official Jenkins project.
Update the package metadata to include the newly added Jenkins repository:
sudo dnf update -yThe update process downloads repository metadata and makes Jenkins packages available for installation.
Step 4: Installing Jenkins
Execute Installation Command
Install Jenkins using the DNF package manager now that the repository and GPG key are properly configured:
sudo dnf install jenkins -yDNF automatically resolves dependencies and installs required packages along with Jenkins. The installation process downloads approximately 200MB of packages, including Jenkins itself and any missing dependencies.
Monitor the installation output for error messages or warnings. Successful installation concludes with a “Complete!” message and package installation summary.
Verify Installation Success
Confirm Jenkins installed correctly by checking the package information:
rpm -qi jenkinsThis command displays detailed information about the installed Jenkins package, including version numbers and installation paths. Verify the installation directories exist and contain the expected Jenkins files.
Review the default configuration files located in /etc/sysconfig/jenkins to understand the initial system configuration. These files control Jenkins startup parameters and system integration settings.
Step 5: Starting and Enabling Jenkins Service
Start Jenkins Service
Jenkins installs as a systemd service, allowing standard service management commands. Start the Jenkins service using systemctl:
sudo systemctl start jenkinsThe startup process initializes the Jenkins environment and begins listening for web connections. Initial startup may take 1-2 minutes as Jenkins loads plugins and configures the runtime environment.
Enable automatic startup to ensure Jenkins starts automatically after system reboots:
sudo systemctl enable jenkinsThis configuration prevents manual intervention after system restarts and ensures continuous availability.
Check Service Status
Verify the Jenkins service started successfully and is running properly:
sudo systemctl status jenkinsThe status command displays service information including current state, startup time, and recent log entries. Look for “active (running)” status to confirm successful startup.
Review the service logs if startup issues occur. Common problems include Java version incompatibility, port conflicts, or insufficient system resources. Address any error messages before proceeding to the next configuration step.
Step 6: Firewall Configuration
Open Required Ports
AlmaLinux 10 includes firewall protection that blocks network access by default. Configure the firewall to allow access to Jenkins’ web interface on port 8080:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcpThis command creates a permanent firewall rule allowing TCP traffic on port 8080. The permanent flag ensures the rule persists after system restarts.
Reload the firewall configuration to activate the new rule:
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadThe reload operation applies configuration changes without interrupting existing connections.
Security Considerations
Production environments require careful firewall configuration to balance accessibility with security. Consider restricting access to specific IP addresses or network ranges using the --source parameter in firewall rules.
Implement additional security measures such as fail2ban for protection against brute force attacks. Configure reverse proxy servers with SSL termination for enhanced security and performance in production deployments.
Review your organization’s network security policies to ensure Jenkins firewall configuration aligns with established security standards and compliance requirements.
Step 7: Initial Jenkins Setup and Configuration
Access Web Interface
Navigate to Jenkins’ web interface using your system’s IP address or hostname. Open a web browser and visit http://your_server_ip:8080. The initial setup wizard appears automatically on first access.
The unlock screen displays instructions for retrieving the initial administrator password. This security measure prevents unauthorized access during the setup process.
Retrieve Initial Password
Jenkins generates a unique administrator password during installation. Retrieve this password using the cat command:
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPasswordCopy the displayed password exactly as shown. The password contains alphanumeric characters and symbols that must be entered precisely for successful authentication.
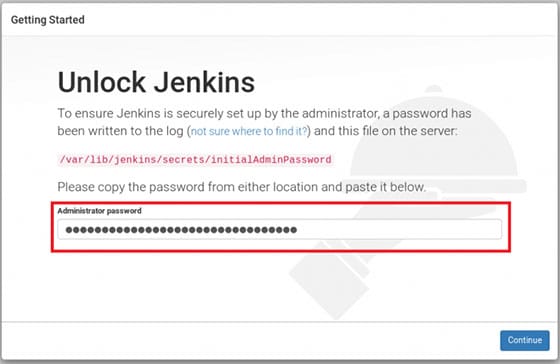
The initial password provides temporary administrative access for completing the setup wizard. Change this password immediately after setup completion to maintain security.
Complete Setup Wizard
Enter the initial password in the unlock screen to proceed with configuration. The setup wizard presents plugin installation options including recommended plugins or custom plugin selection.
Choose “Install suggested plugins” for most installations, as these provide essential functionality for common use cases. The installation process downloads and configures plugins automatically, which may take several minutes depending on internet connection speed.
Create an administrator account with a secure password during the final setup step. Configure the Jenkins URL to match your intended access method, whether using IP addresses or domain names.
Step 8: Essential Plugin Installation
Recommended Plugins
The suggested plugins installation includes essential tools for most Jenkins deployments. Key plugins include Git integration for version control, Pipeline plugins for advanced workflow management, and Build plugins for various programming languages and frameworks.
Additional recommended plugins provide notification capabilities, security enhancements, and reporting features. These plugins extend Jenkins functionality beyond basic CI/CD operations to support comprehensive DevOps workflows.
Custom Plugin Selection
Access the plugin manager through the Jenkins web interface to install additional plugins after initial setup. Navigate to “Manage Jenkins” → “Manage Plugins” to browse available plugins by category or search functionality.
Install plugins individually based on your specific requirements. Popular additions include Docker integration, Kubernetes deployment, Slack notifications, and code quality analysis tools.
Monitor plugin compatibility and update frequency when selecting additions. Well-maintained plugins with regular updates provide better security and compatibility with Jenkins core updates.
Post-Installation Configuration and Security
User Management Setup
Configure additional user accounts through the Jenkins security settings. Navigate to “Manage Jenkins” → “Manage Users” to create accounts for team members and automated systems.
Implement role-based access control (RBAC) using plugins like Role-based Authorization Strategy. This approach ensures users have appropriate permissions based on their responsibilities and reduces security risks from excessive privileges.
Consider integrating with existing authentication systems such as LDAP, Active Directory, or Single Sign-On (SSO) solutions for centralized user management and improved security compliance.
Security Hardening
Disable unnecessary features and plugins to reduce the attack surface. Review enabled plugins regularly and remove unused components that might introduce security vulnerabilities.
Configure HTTPS access using SSL/TLS certificates for encrypted communication. Production deployments should never use unencrypted HTTP connections for Jenkins access.
Implement regular backup procedures for Jenkins configuration and job data. Automated backups ensure quick recovery from system failures or security incidents while maintaining business continuity.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Service Startup Problems
Jenkins startup failures often result from Java compatibility issues or insufficient system resources. Verify Java installation and version compatibility if Jenkins fails to start properly.
Check for port conflicts with other services using the same network ports. Use netstat -tlnp | grep 8080 to identify processes using port 8080 and resolve conflicts appropriately.
Permission problems can prevent Jenkins from accessing necessary files and directories. Ensure the jenkins user has appropriate permissions for the installation directory and workspace locations.
Web Interface Access Issues
Network connectivity problems may prevent access to the Jenkins web interface. Verify firewall configuration and ensure the correct ports are open for external access.
Browser compatibility issues occasionally affect Jenkins interface functionality. Test access using different browsers and clear browser caches if interface problems persist.
DNS resolution problems can cause access issues when using hostnames instead of IP addresses. Verify DNS configuration or use IP addresses temporarily to isolate connectivity problems.
Performance Optimization
Memory allocation tuning improves Jenkins performance for larger deployments. Configure JVM parameters in /etc/sysconfig/jenkins to optimize memory usage based on available system resources.
Monitor system resource usage during build operations to identify performance bottlenecks. Adjust JVM parameters, build concurrency settings, and workspace cleanup policies to optimize performance.
Implement build agent distribution to spread computational load across multiple systems. This approach improves build performance and provides redundancy for critical CI/CD operations.
Best Practices and Maintenance
Regular Updates
Maintain Jenkins security and functionality through regular updates. Schedule weekly or monthly update cycles depending on your organization’s change management policies and risk tolerance.
Test updates in staging environments before applying them to production systems. This practice identifies compatibility issues and prevents disruptions to active development workflows.
Backup Jenkins configuration before applying updates to enable quick rollback if problems occur. Automated backup procedures ensure consistent protection without manual intervention.
Monitoring and Logging
Configure log rotation to prevent disk space issues from excessive log accumulation. Jenkins generates substantial log data during normal operations that requires proper management.
Implement performance monitoring to track system resource usage, build queue lengths, and plugin performance. Monitoring helps identify optimization opportunities and prevents system overload.
Set up alerting mechanisms for critical system events such as disk space shortages, service failures, or security incidents. Proactive monitoring enables rapid response to potential problems.
Advanced Configuration Options
Reverse Proxy Setup
Configure Apache or Nginx as a reverse proxy for enhanced security and performance. Reverse proxies provide SSL termination, load balancing, and additional security features for production deployments.
Implement security headers and rate limiting through the reverse proxy configuration. These measures protect against common web attacks and improve overall system security.
Configure SSL certificates through the reverse proxy for encrypted communications. Use certificates from recognized certificate authorities for production systems to ensure client compatibility.
Scaling Considerations
Plan for master-agent architecture as your Jenkins usage grows. Distributed builds across multiple agents improve performance and provide redundancy for critical build operations.
Configure build agents on different operating systems to support diverse development environments. Mixed-platform agents enable comprehensive testing and deployment capabilities.
Implement high availability configurations for critical Jenkins deployments. Clustered setups with shared storage provide redundancy and minimize downtime during maintenance or failures.
Uninstallation Process
Service Shutdown
Stop the Jenkins service before beginning uninstallation procedures:
sudo systemctl stop jenkinsBackup important data including job configurations, build artifacts, and custom plugins before proceeding with removal. Uninstallation is irreversible without proper backups.
Package Removal
Remove the Jenkins package using DNF package manager:
sudo dnf remove jenkinsClean up configuration files and user data manually if complete removal is desired. System directories may contain additional files not removed by package uninstallation.
Remove the jenkins user account and associated files if no longer needed. Consider preserving configuration files for potential future reinstallation needs.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Jenkins. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Jenkins on your AlmaLinux OS 10 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Jenkins website.