How To Install Joplin on Fedora 42

Joplin is a powerful, free, and open-source note-taking application that helps you organize information securely across multiple devices. Unlike proprietary alternatives, Joplin emphasizes privacy with end-to-end encryption while offering robust features like Markdown support, cross-platform synchronization, and extensibility. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore multiple methods to install Joplin on Fedora 42, ensuring you can choose the approach that best suits your needs and preferences.
Understanding Joplin
Joplin stands out as a versatile note-taking solution designed for users who value both functionality and privacy. At its core, Joplin enables you to create, organize, and search through notes and to-do lists with ease. The application uses Markdown formatting, allowing for clean, structured documents that remain portable and accessible.
One of Joplin’s most compelling features is its strong focus on security. When synchronizing with cloud services, your notes can be protected with end-to-end encryption, ensuring your personal information remains private. This encryption works seamlessly with popular services including Dropbox, Nextcloud, OneDrive, and WebDAV.
The application also offers:
- Web clipper functionality for saving articles and screenshots from browsers
- Support for attachments, images, and other media
- Tagging and notebook organization systems
- Import capabilities from Evernote and other formats
- Cross-platform availability (desktop, mobile, and terminal interfaces)
For Fedora 42 users specifically, Joplin integrates well with the operating system and provides a native-feeling experience, regardless of which desktop environment you’re using.
Prerequisites for Installation
Before installing Joplin on your Fedora 42 system, you should prepare your environment to ensure a smooth installation process. Taking these preliminary steps will help avoid common issues later.
First, update your system to ensure you have the latest packages and security updates:
sudo dnf update -yNext, install the basic dependencies required by most installation methods:
sudo dnf install -y wget tar gzipIf you plan to use the desktop version with a graphical interface, you’ll also need these additional dependencies:
sudo dnf install -y xdg-utils libXScrnSaver libXss libgtk-3 libnotify libappindicator-gtk3 libsecretThese libraries provide essential functionality for the Joplin desktop application, including system notifications, application indicators, and secure credential storage.
Finally, if you’re migrating from another note-taking application, back up your existing notes before proceeding. While Joplin offers import capabilities, having a backup ensures your data remains safe during the transition.
Method 1: Installing Joplin via Official Bash Script
The official bash script installation method is recommended by the Joplin developers and provides a straightforward approach to getting Joplin working on Fedora 42. This method handles the installation process automatically, including desktop integration.
Start by opening your terminal and running the following command:
wget -O - https://raw.githubusercontent.com/laurent22/joplin/dev/Joplin_install_and_update.sh | bashThis command downloads and executes the installation script, which performs several important tasks:
- Checks your system for required dependencies
- Downloads the latest Joplin AppImage
- Creates the necessary directories for Joplin
- Sets up desktop integration with an application icon
- Makes the AppImage executable
During installation, you might see output indicating the download progress and setup steps. Once complete, the script will confirm that Joplin has been successfully installed.
You can now launch Joplin either by searching for it in your application menu or by running joplin in the terminal. The first time you run Joplin, you’ll be prompted to set up your profile and configure synchronization options if desired.
The bash script installation method offers several advantages:
- Simple one-line installation process
- Always installs the latest available version
- Automatic desktop integration
- Easy updates using the same command
However, since this method uses an AppImage, the application runs in a somewhat contained environment, which occasionally might cause integration issues with specific desktop environments or configurations.
Method 2: Installing Joplin via COPR Repository
For users who prefer to install Joplin through Fedora’s native package management system, the COPR repository method provides an excellent alternative. This approach integrates Joplin with your system’s package manager, allowing for streamlined updates and better system integration.
The Joplin COPR repository is maintained by a community member with the username “taw” and provides packages specifically built for Fedora and other RPM-based distributions.
To begin, install the DNF plugins core package if you haven’t already:
sudo dnf install -y dnf-plugins-coreNext, enable the Joplin COPR repository with the following command:
sudo dnf copr enable taw/joplinWhen prompted, confirm that you understand this repository is not officially supported by Fedora by typing ‘y’ and pressing Enter.
With the repository enabled, install Joplin using DNF:
sudo dnf install -y joplinThis command will download and install the Joplin package along with any required dependencies that aren’t already on your system. The installation typically completes within a minute or two, depending on your internet connection speed.
After installation, you can launch Joplin from your application menu or by typing joplin in the terminal. The first-time setup experience is identical to other installation methods.
The COPR repository installation offers several benefits:
- Integration with Fedora’s native package management
- Automatic updates through regular system updates
- Better desktop environment integration
- Simplified removal if needed
The primary consideration when using this method is that the COPR repository might occasionally lag slightly behind the official releases, depending on the maintainer’s update schedule. However, the repository is generally kept up-to-date with recent Joplin versions.
Method 3: Installing Joplin via Flatpak
Flatpak provides a universal packaging system for Linux applications, offering sandboxed environments that help ensure compatibility across different distributions. Installing Joplin via Flatpak is a good option if you prefer containerized applications with isolated dependencies.
First, ensure Flatpak is installed on your Fedora 42 system. While it comes pre-installed on Fedora, you can verify and set up the Flathub repository with these commands:
sudo dnf install -y flatpak
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoNow, install Joplin using Flatpak:
flatpak install flathub net.cozic.joplin_desktopDuring the installation, you’ll be prompted to confirm the installation of Joplin and its dependencies. Type ‘y’ and press Enter when prompted.
After installation completes, you can launch Joplin from your application menu or using this command:
flatpak run net.cozic.joplin_desktopThe Flatpak version of Joplin runs in a sandboxed environment, which provides several advantages:
- Isolation from your system for enhanced security
- Self-contained dependencies to prevent conflicts
- Consistent behavior regardless of your system configuration
- Easy updates through the Flatpak system
However, there are some potential considerations with the Flatpak version:
- Possible Wayland compatibility issues, especially on newer Fedora versions with KDE Plasma 6
- Slightly larger disk space requirements due to bundled dependencies
- Potential permission limitations requiring additional configuration
If you encounter issues with Joplin not starting after installing via Flatpak, particularly on Wayland-based desktops, you might need to add the --ozone-platform=wayland parameter to the application. This can be done by creating an override:
flatpak override --user --env=JOPLIN_FLAGS="--ozone-platform=wayland" net.cozic.joplin_desktopMethod 4: Installing Joplin via Snap
Snap is another universal package system for Linux that provides containerized applications. While developed by Canonical (the company behind Ubuntu), Snap works well on Fedora 42 and provides another option for installing Joplin.
Start by installing the Snap system on your Fedora 42:
sudo dnf install -y snapd
sudo systemctl enable --now snapd.socket
sudo ln -s /var/lib/snapd/snap /snapThese commands install the Snap daemon, enable its service, and create a symbolic link for compatibility. After setting up Snap, it’s recommended to log out and log back in or restart your system to ensure all paths are properly updated.
Now, install Joplin with this command:
sudo snap install joplin-desktopOnce installed, you can launch Joplin from your application menu or by running:
snap run joplin-desktopThe Snap version of Joplin offers several benefits:
- Automatic background updates
- Isolated environment for improved security
- Consistent behavior across different Linux distributions
- All required dependencies included in the package
Some users have reported that the Snap version works well on newer Fedora versions with KDE Plasma 6, where the Flatpak version sometimes encounters issues. This makes it a good alternative if you’re experiencing problems with other installation methods.
However, be aware that Snap packages generally:
- Use more disk space than traditional packages
- May have slightly longer startup times on first launch
- Might have some limitations in system integration
Method 5: Installing Joplin Terminal Application
For users who prefer a command-line interface or need to run Joplin on a server without a graphical environment, Joplin offers a terminal version. This text-based interface provides most of the core functionality while being lightweight and keyboard-friendly.
To install the terminal version of Joplin, you first need to install Node.js and npm:
sudo dnf install -y nodejs npmAfter installing Node.js, you can install the Joplin terminal application with these commands:
NPM_CONFIG_PREFIX=~/.joplin-bin npm install -g joplin
sudo ln -s ~/.joplin-bin/bin/joplin /usr/bin/joplinThe first command installs Joplin to a directory in your home folder, while the second creates a symbolic link to make the joplin command available system-wide.
To start using the terminal version, simply open a terminal and type:
joplinOn first launch, you’ll be guided through an initial setup process where you can configure synchronization options and other settings. The interface is navigated primarily with keyboard commands, which are displayed at the bottom of the screen.
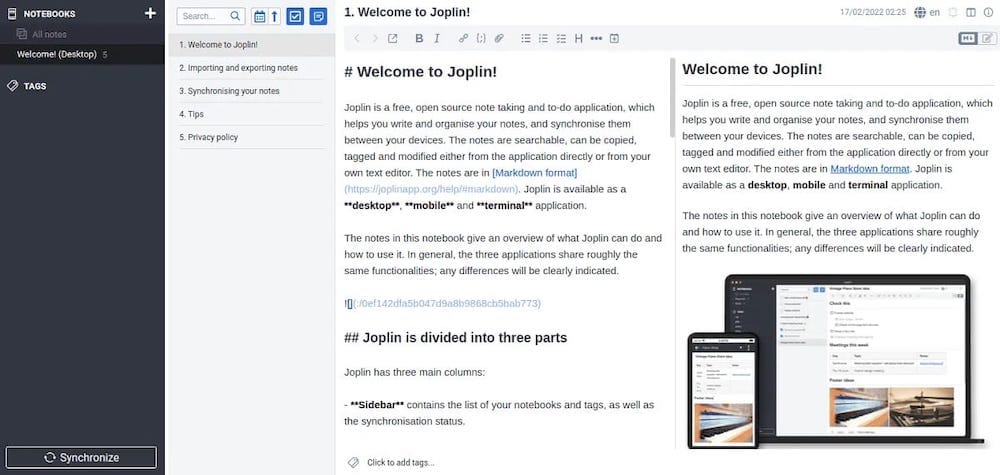
The terminal version includes most features of the desktop application:
- Note creation and editing with full Markdown support
- Organization with notebooks and tags
- Synchronization with the same services as the desktop version
- Search functionality
- Import/export capabilities
This version is particularly useful for:
- Server environments without graphical interfaces
- Remote work through SSH connections
- Resource-constrained systems
- Users who prefer keyboard-focused workflows
While the terminal version doesn’t support rich media as seamlessly as the desktop application, it provides a fast and efficient experience for text-based note-taking and organization.
Post-Installation Configuration
After installing Joplin, configuring it properly will enhance your experience and ensure your notes are secure and accessible across all your devices. Here are the essential configuration steps to consider:
Synchronization Setup:
Joplin’s synchronization capabilities allow you to access your notes from multiple devices. To configure synchronization:
- Go to Tools > Options > Synchronization
- Choose your preferred service:
- Dropbox
- OneDrive
- Nextcloud
- WebDAV
- File system (local or network drives)
- Follow the service-specific instructions to authenticate
- Set a synchronization interval (hourly is recommended for regular users)
Security Configuration:
If you’re synchronizing your notes, especially to third-party services, enabling encryption is crucial:
- In Synchronization settings, check “Encrypt sync data”
- Create a strong master password
- Store this password securely (if lost, your encrypted data cannot be recovered)
- Consider enabling application password protection for additional security
Appearance Customization:
Joplin offers various themes and layout options to match your preferences:
- Navigate to Tools > Options > Appearance
- Choose from available themes (Light, Dark, etc.)
- Adjust font size and family for better readability
- Configure the layout (notebook pane position, editor/viewer arrangement)
Web Clipper Extension:
The Web Clipper allows you to save web content directly to Joplin:
- Go to Tools > Options > Web Clipper
- Install the browser extension for your preferred browser
- Connect the extension using the service URL shown in Joplin (typically http://localhost:41184)
- Test the connection by clipping a web page
Plugins and Extensions:
Enhance Joplin’s functionality with community-developed plugins:
- Navigate to Tools > Options > Plugins
- Browse available plugins
- Install plugins that match your workflow needs
- Configure installed plugins according to their documentation
Keyboard Shortcuts:
Learning keyboard shortcuts can significantly improve your efficiency:
- Access Tools > Options > Keyboard Shortcuts
- Review the default shortcuts
- Customize shortcuts to match your preferences
- Print or save a cheat sheet until you’ve memorized the most important ones
After completing these configuration steps, create a few test notes to ensure everything is working correctly. Try synchronizing between devices if you plan to use multiple platforms, and verify that your notes appear as expected across all your Joplin installations.
Managing Joplin Updates
Keeping Joplin updated ensures you have access to the latest features, security improvements, and bug fixes. The update process varies depending on your installation method.
For Bash Script Installations:
If you installed Joplin using the official bash script, update by running the same command again:
wget -O - https://raw.githubusercontent.com/laurent22/joplin/dev/Joplin_install_and_update.sh | bashThis will download and install the latest version while preserving your data and settings. Alternatively, you can navigate to the Joplin directory and update the AppImage directly:
cd ~/.joplin/
./Joplin.AppImage updateFor COPR Repository Installations:
When installed via the COPR repository, Joplin updates through the standard system update process:
sudo dnf updateTo update only Joplin without updating other packages:
sudo dnf update joplinFor Flatpak Installations:
Update Joplin installed via Flatpak with:
flatpak update net.cozic.joplin_desktopOr update all Flatpak applications at once:
flatpak updateFor Snap Installations:
Snap packages typically update automatically in the background. To manually trigger an update:
sudo snap refresh joplin-desktopFor Terminal Application:
Update the terminal version by running the same npm install command used during installation:
NPM_CONFIG_PREFIX=~/.joplin-bin npm install -g joplinRegardless of your installation method, it’s good practice to:
- Check for updates monthly
- Back up your data before major version updates
- Review the release notes for significant changes
- Verify synchronization is working after updates
Your Joplin data is stored separately from the application itself, so updates generally don’t affect your notes. However, it’s always wise to ensure your notes are properly synchronized before performing major updates.
Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
Even with careful installation, you might encounter some challenges when setting up Joplin on Fedora 42. Here are solutions to common problems:
Application Fails to Start:
If Joplin doesn’t launch after installation, try these fixes:
- Missing dependencies: Install required libraries:
sudo dnf install -y libXScrnSaver libXss libgtk-3 libnotify libappindicator-gtk3 libsecret - Flatpak on Wayland issues: For Flatpak installations (especially with KDE Plasma), add the Wayland parameter:
flatpak override --user --env=JOPLIN_FLAGS="--ozone-platform=wayland" net.cozic.joplin_desktop - Permission problems: Check AppImage permissions:
chmod +x ~/.joplin/Joplin.AppImage
Missing libfuse2 Error:
If you see errors about missing libfuse2 when using AppImage installations:
sudo dnf install fuse-libsSUID Sandbox Helper Error:
For AppImage “SUID sandbox” errors, try running with the no-sandbox parameter:
~/.joplin/Joplin.AppImage --no-sandboxSynchronization Issues:
If you have problems with synchronization:
- Verify internet connectivity and firewall settings
- Double-check authentication credentials
- For Dropbox/OneDrive issues, regenerate access tokens
- Check that the service URL is correct in Web Clipper settings
Performance Problems:
For slow performance or high resource usage:
- Check if you have thousands of notes (consider splitting across multiple profiles)
- Disable unused plugins temporarily to identify resource-heavy extensions
- Ensure your system meets minimum specifications
- Close other resource-intensive applications while using Joplin
Installation Dependency Errors:
If package managers report dependency resolution errors:
- Update your system completely:
sudo dnf update -y - Clear DNF cache:
sudo dnf clean all - Try an alternative installation method (e.g., switch from COPR to AppImage)
Desktop Integration Issues:
If Joplin doesn’t appear in application menus or has icon problems:
- For AppImage installations, run the bash script again
- For other methods, try updating desktop database:
sudo update-desktop-database
Remember that your Joplin data is stored separately from the application in ~/.config/joplin-desktop/ (for desktop) or ~/.config/joplin/ (for terminal). This means you can safely remove and reinstall the application without losing your notes, as long as you don’t delete these directories.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Joplin. Thanks for using this tutorial to install the latest version of the Joplin on Fedora 42 Linux. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Joplin website.