How To Install JupyterLab on Fedora 39

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install JupyterLab on Fedora 39. JupyterLab is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents containing live code, equations, visualizations, and narrative text. It’s widely used for data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, machine learning, and much more.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the JupyterLab computational environment on a Fedora 39.
Prerequisites
Before diving into the installation process, let’s ensure that you have everything you need:
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Fedora 39.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- You will need access to the terminal to execute commands. Fedora 39 provides the Terminal application for this purpose. It can be found in your Applications menu.
- A network connection or internet access to download the JupyterLab repository.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install JupyterLab on Fedora 39
Step 1. Before diving into the installation process, it’s crucial to prepare your Fedora system. Start by updating your system to ensure all existing packages are up to date, using the command:
sudo dnf clean all sudo dnf update
Step 2. Installing Python.
JupyterLab requires Python 3.3 or greater. Fedora 39 comes with Python 3 installed by default, but you can verify or install Python 3 using the following command:
sudo dnf install python3
Ensure pip, Python’s package installer is up to date:
python3 -m pip install --user --upgrade pip
Step 3. Installing JupyterLab on Fedora 39.
With pip, you can easily install JupyterLab:
pip install jupyterlab --user
To enable JupyterLab extensions and other Jupyter customizations, it’s recommended to also install Node.js:
sudo dnf install nodejs
Once installed, you can start JupyterLab by running:
jupyter lab
Step 3. Create a Virtual Environment (Optional but recommended).
Isolate project dependencies by creating a Python virtual environment:
python3 -m venv myenv source myenv/bin/activate
Step 4. Installing Essential JupyterLab Extensions.
Extend JupyterLab’s functionality with extensions, such as the GitHub extension:
jupyter labextension install @jupyterlab/github
Step 5. Configure JupyterLab.
Generate and customize the JupyterLab configuration file:
jupyter lab --generate-config
Then, edit ~/.jupyter/jupyter_lab_config.py to customize JupyterLab settings according to your preferences.
Now execute the command below to open port 8888 for JupyterLab. Then, start your JupyterLab on local IP 192.168.77.20, and Make sure to change the IP address:
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=8888/tcp jupyter lab --ip 192.168.77.20
Finally, open your web browser and visit your local IP address with port 8888, http://192.168.77.20:8888/. You will be prompted with the JupyterLab login page.
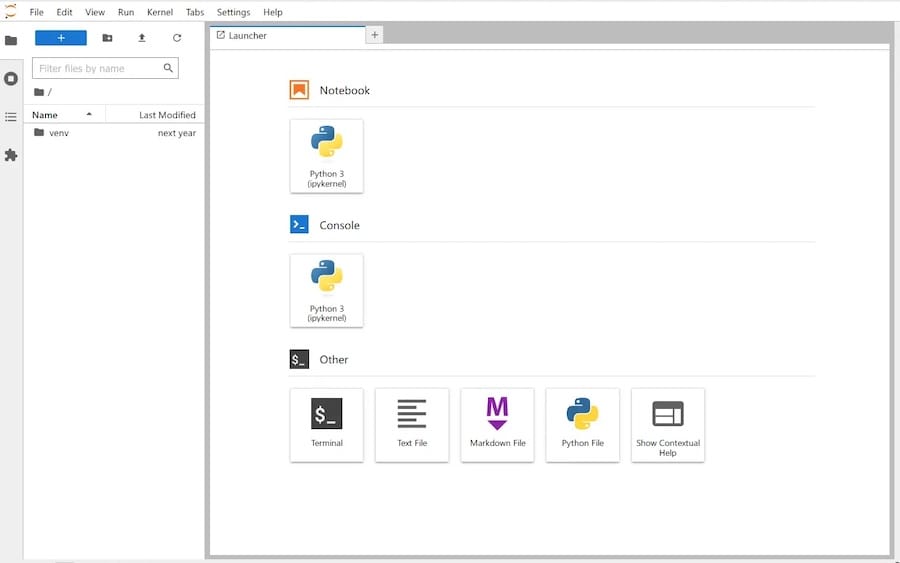
Step 6. Secure JupyterLab.
If you plan to access JupyterLab over a network, it’s important to secure it. Set up a password for JupyterLab by running:
jupyter notebook password
Congratulations! You have successfully installed JupyterLab. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the JupyterLab computational environment on your Fedora 39 system. For additional or useful information, we recommend you check the official Jupyter website.