How To Install LEMP Stack on Fedora 40

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install LEMP Stack on Fedora 40. The LEMP stack, comprising Linux, Nginx (pronounced “Engine-X”), MariaDB, and PHP, is a powerful combination for hosting dynamic websites and web applications.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the LEMP Stack on Fedora 40.
Prerequisites
Before we dive into the installation process, ensure that you have the following prerequisites in place:
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Fedora 40.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- You will need access to the terminal to execute commands. Fedora provides the Terminal application for this purpose. It can be found in your Applications menu.
- A stable internet connection to download the necessary packages.
- A non-root sudo user or access to the root user. We recommend acting as a non-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install LEMP Stack on Fedora 40
Step 1. Update the System.
Keeping your system up-to-date is crucial for security and stability. Run the following command to ensure your Fedora 40 installation is fully updated:
sudo dnf clean all sudo dnf update
The package manager will retrieve the latest package information and prompt you to confirm the update. Press “y” and hit Enter to proceed with the update process. Depending on the number of updates available, this step may take a few minutes to complete.
Step 2. Installing Nginx on Fedora.
Nginx is a high-performance web server known for its efficiency and low resource consumption. To install Nginx on Fedora 40, run the following command:
sudo dnf install nginx
After the installation is complete, start and enable the Nginx service to run at system boot:
sudo systemctl start nginx sudo systemctl enable nginx
Verify that Nginx is running by accessing http://your_server_ip in a web browser. You should see the default Nginx welcome page.
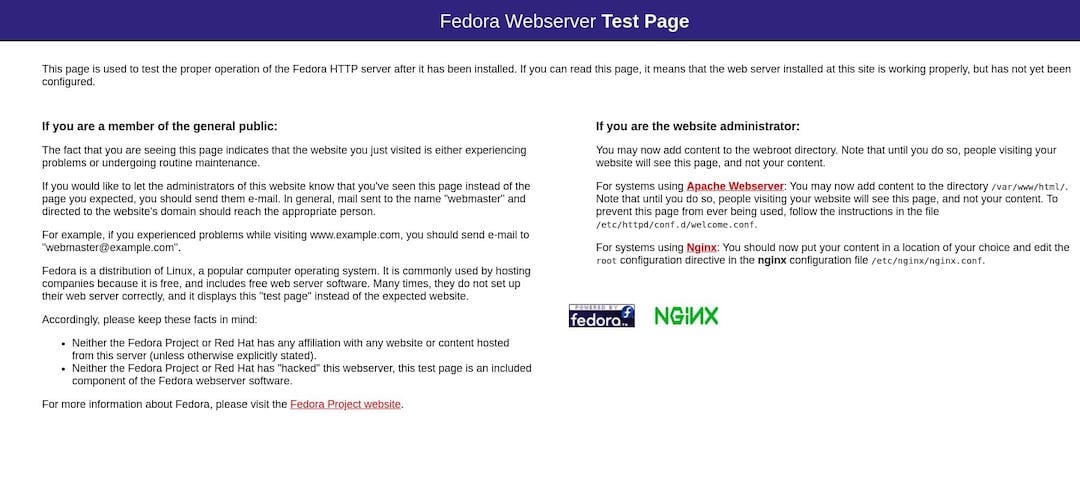
Don’t forget to open the firewall for Nginx traffic:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Step 3. Installing MariaDB.
MariaDB is a popular open-source database management system, a drop-in replacement for MySQL. Install MariaDB with the following command:
sudo dnf install mariadb-server
After the installation, start and enable the MariaDB service:
sudo systemctl start mariadb sudo systemctl enable mariadb
Secure your MariaDB installation by running the security script:
sudo mysql_secure_installation
This script will prompt you to set a root password, remove anonymous users, disable remote root login, remove test databases, and reload privilege tables.
Step 4. Installing PHP.
PHP is a server-side scripting language widely used for web development. Install PHP and the PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) package with the following command:
sudo dnf install php php-fpm php-mysqlnd
Start and enable the PHP-FPM service:
sudo systemctl start php-fpm sudo systemctl enable php-fpm
Configure PHP-FPM to work with Nginx by creating a new configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
Add the following lines to the file:
user = nginx group = nginx listen = /run/php-fpm/www.sock listen.owner = nginx listen.group = nginx pm = dynamic pm.max_children = 50 pm.start_servers = 5 pm.min_spare_servers = 5 pm.max_spare_servers = 35
Save the file and exit the editor. Restart the PHP-FPM service for the changes to take effect:
sudo systemctl restart php-fpm
Step 5. Configure Nginx to Use a PHP Processor.
To enable Nginx to process PHP files, create a new server block configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
Paste the following configuration into the file:
server {
listen 80;
server_name your_domain.com www.your_domain.com;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
include fastcgi.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php-fpm/www.sock;
}
}
Replace your_domain.com with your actual domain name or server IP address. Save the file and exit the editor.
Test the Nginx configuration for syntax errors:
nginx -t
If no errors are reported, reload Nginx for the changes to take effect:
sudo systemctl reload nginx
Step 6. Secure the LEMP Stack.
Securing your web server is crucial to protect against potential threats and vulnerabilities. Follow these steps to enhance the security of your LEMP stack:
- Configure UFW Firewall: Install and configure the Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) to allow only necessary traffic:
sudo dnf install ufw sudo ufw default deny incoming sudo ufw allow ssh sudo ufw allow http sudo ufw enable
- Enable HTTPS with Let’s Encrypt SSL: Secure your website with a free SSL/TLS certificate from Let’s Encrypt. Follow the official Let’s Encrypt documentation for your specific setup.
sudo dnf install certbot python3-certbot-nginx
Obtain and install the SSL certificate:
sudo certbot --nginx -d your_domain -d www.your_domain
Follow the prompts to complete the installation. Certbot will automatically configure Nginx to use the SSL certificate.
- Regular Updates and Maintenance: Keep your LEMP stack components up-to-date by regularly running
sudo dnf upgrade. Monitor logs and perform necessary maintenance tasks to ensure optimal performance and security.
Step 7. Testing the LEMP Stack.
To verify that your LEMP stack is working correctly, create a PHP info file:
sudo nano /usr/share/nginx/html/info.php
Add the following code to the file:
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Save the file and exit the editor, then access the PHP info file in your web browser by visiting http://your_server_ip/info.php. You should see detailed information about your PHP installation and configuration.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed LEMP. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the LEMP Stack on Fedora 40 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the Fedora website.