How To Install LocalSend on Linux Mint 22

LocalSend revolutionizes file sharing across devices within your local network, offering a seamless alternative to proprietary solutions like AirDrop. This comprehensive guide walks you through every installation method available for Linux Mint 22, ensuring you can choose the approach that best fits your technical expertise and system requirements.
Whether you’re a seasoned Linux administrator or a newcomer to the platform, this tutorial provides detailed instructions for installing LocalSend using multiple methods. You’ll discover four distinct installation approaches, each with unique advantages and specific use cases.
The cross-platform nature of LocalSend makes it an invaluable tool for mixed-device environments. Linux Mint 22 users can effortlessly share files with Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS devices without relying on cloud services or external servers. This local network approach ensures maximum privacy and security while maintaining impressive transfer speeds.
Understanding LocalSend
LocalSend stands out as an open-source, cross-platform file sharing application that operates entirely within your local network. Unlike cloud-based solutions, LocalSend maintains complete user privacy by avoiding external servers and internet dependencies.
The application supports multiple operating systems including Linux distributions, Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and Fire OS. This universal compatibility makes LocalSend particularly valuable for households and offices with diverse device ecosystems.
Security remains paramount in LocalSend’s design philosophy. The application implements HTTPS encryption with auto-generated TLS/SSL certificates, ensuring all file transfers remain secure and private. Users maintain complete control over their data throughout the entire sharing process.
LocalSend’s intuitive interface requires minimal configuration while offering powerful features. The application automatically discovers devices on your network, streamlining the file sharing process to just a few clicks or taps.
System Requirements and Prerequisites
Linux Mint 22 Compatibility Requirements
Linux Mint 22 users need a minimum of 2GB RAM for optimal LocalSend performance, though 4GB is recommended for handling large file transfers efficiently. The system requires approximately 20GB of available disk space to accommodate the application and temporary transfer files.
All Linux Mint 22 desktop environments support LocalSend installation, including Cinnamon, MATE, and Xfce variants. The application integrates seamlessly with each environment’s native file manager and notification system.
Network Configuration Requirements
LocalSend requires an active Wi-Fi or Ethernet connection for device discovery and file transfers. All participating devices must connect to the same local network segment to communicate effectively.
The application utilizes port 53317 for both TCP and UDP protocols. Network administrators should ensure this port remains accessible through firewall configurations and router settings.
Pre-Installation System Preparation
Before installing LocalSend, update your Linux Mint 22 system packages to ensure compatibility and security. Execute the following commands in your terminal:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade -yVerify your network connectivity by testing communication with other devices on your local network. This preliminary check prevents potential connectivity issues during the installation process.
Installation Methods Overview
Available Installation Options
Linux Mint 22 offers four primary methods for installing LocalSend, each catering to different user preferences and technical requirements. Understanding these options helps you select the most appropriate installation approach.
Snap Package Installation provides the simplest method with automatic updates and sandboxed security. This approach suits users who prioritize convenience and automated maintenance.
Flatpak Installation offers enhanced security through advanced sandboxing while maintaining access to the latest features. This method appeals to security-conscious users who value isolation and permission control.
DEB Package Installation delivers traditional Linux package management with native system integration. This approach provides optimal performance and direct control over the installation process.
AppImage Installation creates a portable solution requiring no system modifications. This method benefits users who need flexibility or want to test LocalSend without permanent installation.
Installation Method Comparison
| Method | Installation Complexity | Update Management | Security Level | System Integration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snap | Beginner-friendly | Automatic | High (sandboxed) | Good |
| Flatpak | Moderate | Automatic | Very High | Excellent |
| DEB | Advanced | Manual | Standard | Native |
| AppImage | Simple | Manual | Standard | Minimal |
Choose your installation method based on your technical comfort level, security requirements, and system management preferences. Each approach successfully installs LocalSend while offering distinct advantages.
Method 1: Installing LocalSend via Snap Package
Prerequisites and Snap Verification
Linux Mint 22 includes Snap support by default, eliminating the need for additional configuration. Verify your Snap installation by opening a terminal and executing:
snap --versionIf Snap appears unavailable, enable it through the Software Manager settings. Navigate to Edit > Preferences > Snap Support and ensure the option is activated.
Step-by-Step Snap Installation Process
Terminal-Based Installation
Open your terminal using the Ctrl+Alt+T keyboard shortcut. Execute the following command to install LocalSend:
sudo snap install localsendThe system prompts for your administrator password. Enter your credentials and wait for the download and installation process to complete. Snap automatically handles all dependencies and configurations.
GUI Installation via Software Manager
Alternative installation through the graphical interface provides a user-friendly approach. Open the Software Manager application from your system menu.
Search for “LocalSend” in the application search bar. Select the LocalSend application from the results and click the Install button. Authenticate with your administrator credentials when prompted.
Post-Installation Verification
Confirm successful installation by checking your installed Snap packages:
snap list | grep localsendLaunch LocalSend from your application menu or execute the following terminal command:
localsendSnap-Specific Configuration Options
Snap installations operate within a confined environment that enhances security but may limit file access. By default, LocalSend can access files within your home directory and connected storage devices.
To expand file access permissions, use the following command:
sudo snap connect localsend:removable-mediaThis connection allows LocalSend to access external storage devices and network shares.
Method 2: Installing LocalSend via Flatpak
Setting Up Flatpak Environment
Linux Mint 22 includes Flatpak support, but you may need to add the Flathub repository for application access. Execute these commands to ensure proper configuration:
sudo apt install flatpak
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoRestart your system to complete the Flatpak setup process.
Installing LocalSend from Flathub
Command Line Installation
Install LocalSend using the Flatpak command-line interface:
flatpak install flathub org.localsend.localsend_appConfirm the installation when prompted and wait for the download to complete. Flatpak automatically manages dependencies and runtime requirements.
Software Manager Installation
Open the Software Manager and ensure Flatpak support is enabled in the preferences. Search for “LocalSend” and select the version from Flathub.
Click Install and authenticate with your administrator credentials. The Software Manager handles the entire installation process automatically.
Launching and Configuring Flatpak LocalSend
Launch LocalSend using the following command:
flatpak run org.localsend.localsend_appCreate a desktop shortcut by right-clicking the application in your menu and selecting Add to Desktop.
Managing Flatpak Permissions
Install Flatseal to manage LocalSend’s permissions granularly:
flatpak install flathub com.github.tchx84.FlatsealUse Flatseal to customize file system access, network permissions, and other security settings according to your requirements.
Method 3: Installing LocalSend via DEB Package
Downloading the Official DEB Package
Visit the LocalSend official website and navigate to the Downloads section. Select the Linux DEB package compatible with your system architecture (typically amd64 for modern systems).
Save the DEB file to your Downloads folder or another accessible location. Note the exact filename for command-line installation.
GUI Installation Process
Navigate to your Downloads folder using the file manager. Double-click the LocalSend DEB file to launch the Software Manager installer.
Click Install and enter your administrator password when prompted. The system automatically resolves dependencies and completes the installation.
Command Line Installation
Open a terminal and navigate to your Downloads directory:
cd ~/DownloadsInstall the DEB package using the following command:
sudo apt install ./LocalSend-*.debReplace the asterisk with the actual version number from your downloaded file. The system installs LocalSend and all required dependencies.
Dependency Resolution
If dependency errors occur, resolve them using:
sudo apt install -fThis command installs missing dependencies and completes the LocalSend installation process.
Method 4: Installing LocalSend via AppImage
Downloading and Preparing AppImage
Visit the LocalSend GitHub releases page and download the latest AppImage file. Save it to your preferred location, such as a dedicated Applications folder.
Making AppImage Executable
Using File Manager
Right-click the AppImage file and select Properties. Navigate to the Permissions tab and enable Allow executing file as program.
Using Terminal
Navigate to the AppImage location and execute:
chmod +x LocalSend-*.AppImageRunning LocalSend AppImage
Double-click the AppImage file to launch LocalSend immediately. No installation is required, and the application runs in a contained environment.
Alternatively, launch from the terminal:
./LocalSend-*.AppImageCreating Desktop Integration
For better system integration, consider using AppImageLauncher:
sudo apt install appimagelauncherAppImageLauncher automatically creates desktop entries and menu shortcuts for your AppImage applications.
Initial Configuration and Setup
First Launch Configuration
Upon launching LocalSend for the first time, configure essential settings to optimize your experience. The application automatically generates a device name based on your system hostname.
Customize your device name to something memorable and descriptive. This name appears to other devices on your network during file sharing operations.
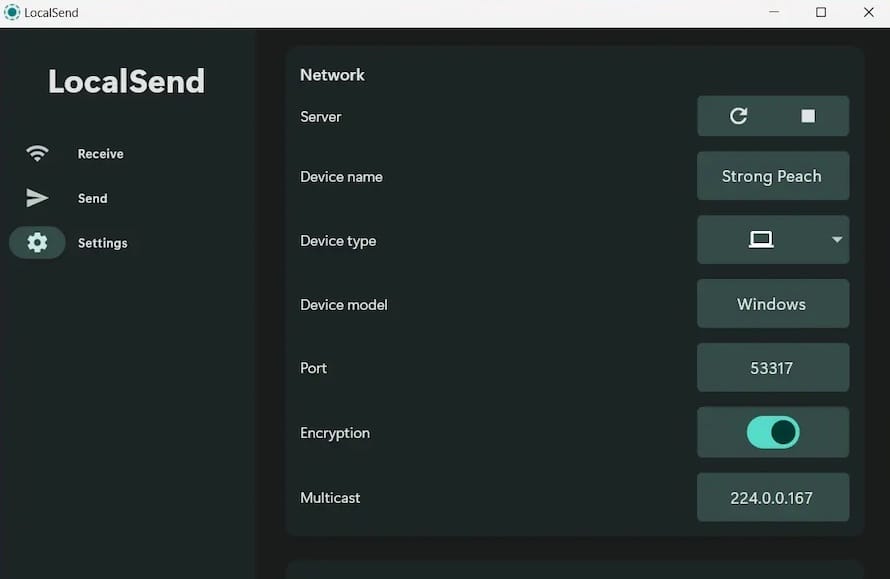
Essential Settings Configuration
Device Settings Optimization
Access the settings menu to configure device-specific options:
- Device Name: Choose a unique, descriptive name for network identification
- Device Alias: Set an alternative name for specific network environments
- Port Configuration: Maintain the default port 53317 unless conflicts arise
Network Interface Selection
LocalSend automatically detects available network interfaces. Select the appropriate interface for your network environment, typically your Wi-Fi or Ethernet connection.
Download Location Setup
Configure your default download location to organize received files efficiently. Choose a location with sufficient storage space for anticipated file transfers.
User Interface Familiarization
The LocalSend interface consists of four primary sections:
- Send Tab enables file and message transmission to discovered devices. Drag and drop files directly onto the interface or use the file selection dialog.
- Receive Tab displays incoming transfer requests and allows management of received files. Configure auto-accept settings based on your security preferences.
- Settings Tab provides access to all configuration options, including network settings, security preferences, and appearance customization.
- History Tab maintains a record of all file transfers, enabling easy access to recently shared files and transfer statistics.
Firewall Configuration and Network Setup
Understanding LocalSend Network Requirements
LocalSend requires specific network configurations to function properly. The application uses port 53317 for both incoming and outgoing communications over TCP and UDP protocols.
Configuring Linux Mint Firewall
Using UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall)
Linux Mint 22 includes UFW for firewall management. Configure LocalSend access using these commands:
sudo ufw allow 53317/tcp
sudo ufw allow 53317/udp
sudo ufw reloadUsing GUI Firewall Tools
Access the firewall configuration through System Settings > Firewall Configuration. Create a new rule allowing port 53317 for both TCP and UDP protocols.
Set the rule to apply to your local network subnet (typically 192.168.0.0/24 or 10.0.0.0/8) for enhanced security.
Router Configuration Considerations
Ensure your router supports multicast traffic, which LocalSend uses for device discovery. Disable AP isolation if enabled, as this feature prevents device-to-device communication.
Verify that all devices connect to the same network segment. Guest networks often isolate devices, preventing LocalSend functionality.
Network Troubleshooting Tips
Test device connectivity using ping commands between devices. Ensure all devices can communicate before troubleshooting LocalSend-specific issues.
Monitor network traffic using tools like tcpdump or Wireshark to identify connectivity problems:
sudo tcpdump -i wlan0 port 53317Advanced Usage and Features
Maximizing LocalSend Capabilities
LocalSend offers advanced features that enhance productivity and streamline file sharing workflows. Understanding these capabilities helps you leverage the application’s full potential.
Batch File Operations
Select multiple files simultaneously for efficient batch transfers. Use Ctrl+click to select individual files or Shift+click to select ranges.
Directory Sharing
Share entire directories by dragging folders directly onto the LocalSend interface. The application preserves directory structure during transfers.
Text Message Transmission
Send text messages and notes between devices using the message feature. This capability proves useful for sharing URLs, notes, or quick information.
Automation and Integration
Command Line Integration
LocalSend supports command-line arguments for automation and scripting purposes. Create scripts to automate routine file sharing tasks.
Startup Configuration
Configure LocalSend to start automatically with your system:
sudo systemctl enable localsendHidden Mode Operation
Run LocalSend in the background without displaying the main interface:
localsend --hiddenCross-Platform Optimization
Configure LocalSend for optimal performance across different device types. Adjust transfer settings based on target device capabilities and network conditions.
Test transfers between different platforms to ensure compatibility and identify any platform-specific issues.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Device Discovery Problems
Issue: LocalSend cannot discover other devices on the network.
Solutions:
- Verify all devices connect to the same network segment
- Check firewall configurations on all devices
- Ensure multicast support is enabled on your router
- Restart LocalSend on all devices to refresh discovery
Transfer Failures and Interruptions
Issue: File transfers fail or stop unexpectedly.
Solutions:
- Verify sufficient storage space on receiving devices
- Check network stability and connection quality
- Disable power management settings that might interrupt transfers
- Ensure antivirus software isn’t blocking LocalSend operations
Performance Optimization
Issue: Slow transfer speeds or high resource usage.
Solutions:
- Close unnecessary applications during large transfers
- Use wired connections for maximum transfer speeds
- Adjust transfer buffer sizes in LocalSend settings
- Monitor system resources during transfers
Linux Mint Specific Issues
Issue: LocalSend doesn’t appear in the application menu after installation.
Solutions:
- Refresh the application database:
sudo updatedb - Log out and log back in to refresh the desktop environment
- Manually create a desktop entry if necessary
- Check installation logs for error messages
Permission and Access Issues
Issue: LocalSend cannot access certain files or directories.
Solutions:
- Verify file permissions using
ls -la - Ensure your user account has read access to source files
- Check Snap or Flatpak permissions for sandboxed installations
- Use
sudofor system-level file access when appropriate
Security Considerations and Best Practices
Understanding LocalSend Security Architecture
LocalSend implements robust security measures to protect your data during transfers. The application uses HTTPS encryption with automatically generated TLS/SSL certificates for all communications.
All transfers occur exclusively within your local network, eliminating exposure to external threats and maintaining complete privacy. No data passes through external servers or cloud services.
Implementing Security Best Practices
Network Segmentation
Consider creating a dedicated network segment for file sharing activities. This approach isolates LocalSend traffic from critical business or personal data.
Regular Security Updates
Maintain current LocalSend versions to benefit from security patches and feature improvements. Enable automatic updates when using Snap or Flatpak installations.
File Scanning Protocols
Implement antivirus scanning for received files, especially in enterprise environments. Configure your antivirus software to scan LocalSend download directories automatically.
Privacy Protection Measures
LocalSend respects user privacy by avoiding data collection and telemetry. The application operates entirely offline, ensuring your file sharing activities remain private.
Review and customize Quick Save settings to maintain control over automatically accepted transfers. Disable this feature in environments where security takes precedence over convenience.
Enterprise Security Considerations
Organizations should implement additional security measures, including:
- Network monitoring and logging of file transfer activities
- User training on safe file sharing practices
- Regular security audits of LocalSend configurations
- Integration with existing security infrastructure
Congratulations! You have successfully installed LocalSend. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing LocalSend on Linux Mint 22 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official LocalSend website.