How To Install Monitorix on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS

In the world of system administration, keeping a close eye on your server’s performance is crucial. Monitorix is a powerful, lightweight, and open-source system monitoring tool that can help you achieve this goal. This article will guide you through the process of installing Monitorix on Ubuntu 24.04, providing you with a comprehensive solution for monitoring your system’s vital statistics.
What is Monitorix?
Monitorix is a free, open-source, and lightweight system monitoring tool designed to monitor system and network resources. It’s particularly well-suited for Linux and UNIX systems, making it an excellent choice for Ubuntu users. Monitorix collects system data and presents it through a web interface, allowing you to visualize various aspects of your system’s performance over time.
Key features of Monitorix include:
- Real-time monitoring of system resources
- Customizable graphs for various metrics
- Low resource consumption
- Easy installation and configuration
- Support for multiple operating systems
Compared to other monitoring tools like Nagios or Zabbix, Monitorix stands out for its simplicity and low overhead, making it ideal for personal servers or small to medium-sized deployments.
Prerequisites
Before we begin the installation process, ensure that your system meets the following requirements:
- Ubuntu 24.04 LTS installed and updated
- Root or sudo access to the system
- A stable internet connection
- Basic familiarity with the command line interface
Additionally, you’ll need to have the following tools installed:
- curl
- apt-transport-https
- ca-certificates
Preparing Your Ubuntu 24.04 System
To ensure a smooth installation process, let’s start by updating your system and installing the necessary dependencies:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade -y
sudo apt install curl apt-transport-https ca-certificates -yIf you have a firewall enabled, you’ll need to allow incoming connections on port 8080, which is the default port used by Monitorix’s web interface. For UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall), use the following command:
sudo ufw allow 8080/tcpRemember to reload the firewall after making changes:
sudo ufw reloadInstalling Monitorix on Ubuntu 24.04
Now that our system is prepared, let’s proceed with the installation of Monitorix:
1. Add the Monitorix Repository
First, we need to add the Monitorix repository to our system. Create a new file named monitorix.list in the /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ directory:
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list.d/monitorix.listAdd the following line to the file:
deb [arch=amd64] https://apt.izzysoft.de/ubuntu generic universeSave and close the file (Ctrl+X, then Y, then Enter).
2. Import the GPG Key
To ensure the authenticity of the packages, import the repository’s GPG key:
curl -fsSL https://apt.izzysoft.de/izzysoft.asc | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/izzysoft-archive-keyring.gpg3. Update Package Lists
Update your package lists to include the new repository:
sudo apt update4. Install Monitorix
Now, install Monitorix using the following command:
sudo apt install monitorix -y5. Verify Installation
To verify that Monitorix has been installed correctly, check its status:
sudo systemctl status monitorixYou should see output indicating that the service is active and running.
Configuring Monitorix
After installation, you may want to customize Monitorix to suit your needs. The main configuration file is located at /etc/monitorix/monitorix.conf. Let’s take a look at some essential configuration options:
sudo nano /etc/monitorix/monitorix.confHere are some key settings you might want to adjust:
title: Set a custom title for your Monitorix instancehostname: Specify the hostname of your servertheme: Choose between ‘white’ and ‘black’ themesrefresh_rate: Set the refresh rate for graphs (in seconds)enable_zoom: Enable or disable graph zooming
You can also enable or disable specific monitoring modules by commenting or uncommenting the relevant sections in the configuration file.
After making changes, save the file and restart Monitorix:
sudo systemctl restart monitorixStarting and Enabling Monitorix Service
Monitorix should start automatically after installation. However, if it doesn’t, you can start it manually:
sudo systemctl start monitorixTo ensure that Monitorix starts automatically on system boot, enable the service:
sudo systemctl enable monitorixYou can check the status of the Monitorix service at any time using:
sudo systemctl status monitorixAccessing Monitorix Web Interface
Monitorix provides a web interface to view your system’s statistics. By default, it’s accessible at:
http://your_server_ip:8080/monitorixReplace your_server_ip with your server’s actual IP address or domain name.
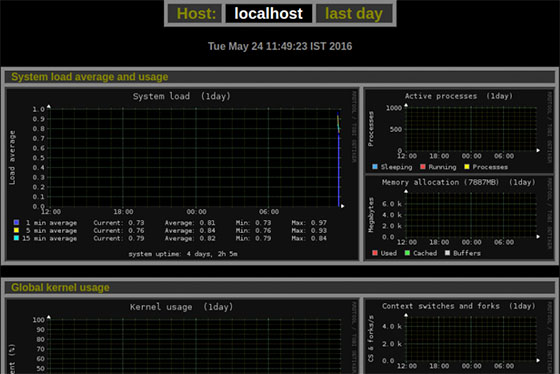
If you’re using Apache or Nginx as your web server, you might want to set up a reverse proxy for easier access. Here’s a basic Nginx configuration:
server {
listen 80;
server_name monitorix.yourdomain.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
}For added security, consider setting up authentication for the Monitorix web interface. You can do this by editing the Apache configuration file for Monitorix:
sudo nano /etc/apache2/conf-available/monitorix.confAdd the following lines within the <Directory> block:
AuthType Basic
AuthName "Monitorix Access"
AuthUserFile /etc/monitorix/.htpasswd
Require valid-userThen, create a password file:
sudo htpasswd -c /etc/monitorix/.htpasswd your_usernameRemember to restart Apache after making these changes:
sudo systemctl restart apache2Exploring Monitorix Features
Once you’ve accessed the Monitorix web interface, you’ll be presented with a wealth of information about your system. Here’s a brief overview of some key features:
- System Load: View CPU usage, memory consumption, and system load averages.
- Network Traffic: Monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic on all interfaces.
- Disk Usage: Track disk I/O operations and available space on all mounted filesystems.
- System Services: Monitor the status of key system services like Apache, MySQL, and SSH.
- System Temperature: Keep an eye on your system’s temperature (if sensors are available).
To customize your dashboard, you can rearrange graphs by dragging and dropping them. You can also zoom in on specific time periods for more detailed analysis.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While Monitorix is generally reliable, you might encounter some issues. Here are solutions to common problems:
Service Not Starting
If the Monitorix service fails to start, check the system logs:
sudo journalctl -u monitorixLook for any error messages that might indicate the cause of the problem.
Web Interface Not Accessible
If you can’t access the web interface, ensure that:
- The Monitorix service is running
- Your firewall allows connections on port 8080
- The web server (if using one) is correctly configured
Graphs Not Updating
If graphs aren’t updating, check that:
- The Monitorix service is running
- The system time is correct
- There’s sufficient disk space for storing RRD files
Updating Monitorix
To keep Monitorix up-to-date, regularly check for updates:
sudo apt updateIf updates are available, apply them safely:
sudo apt upgrade monitorixAfter updating, restart the Monitorix service:
sudo systemctl restart monitorixCongratulations! You have successfully installed Monitorix. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Monitorix system monitoring tool on your Ubuntu 24.04 LTS system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Monitorix website.