How To Install Nagios on Fedora 39

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Nagios on Fedora 39. Nagios, a powerful open-source monitoring system, is a vital tool for any network administrator. It provides real-time health checks of servers, applications, and network infrastructure, enabling proactive management and issue resolution.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Nagios monitoring tool on a Fedora 39.
Prerequisites
Before diving into the installation process, let’s ensure that you have everything you need:
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Fedora 39.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- You will need access to the terminal to execute commands. Fedora 39 provides the Terminal application for this purpose. It can be found in your Applications menu.
- A network connection or internet access to download the Nagios packages.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Nagios on Fedora 39
Step 1. Before installing any new software, it’s always a good idea to update your system packages. This ensures that you have the latest versions of all software and libraries, which can help prevent compatibility issues. To update your system packages, open the terminal and run the following command:
sudo dnf clean all sudo dnf update sudo dnf install httpd php gcc glibc gd gd-devel wget tar make
Step 2. Create Nagios user and group.
Now that our system is ready, let’s proceed with the Nagios installation. Start by creating a Nagios user and group. This step enhances security by ensuring Nagios operations are performed under a specific user:
sudo useradd nagios sudo groupadd nagcmd sudo usermod -a -G nagcmd nagios
Step 3. Installing Nagios on Fedora 39.
Next, download the Nagios Core and Nagios Plugins source files. You can find the latest versions on the official Nagios website. Use the wget command to download the files:
wget https://assets.nagios.com/downloads/nagioscore/releases/nagios-4.x.tar.gz wget https://nagios-plugins.org/download/nagios-plugins-x.x.tar.gz
Extract the downloaded files and compile Nagios Core:
tar xzf nagios-4.x.tar.gz cd nagios-4.x/ ./configure --with-command-group=nagcmd make all
Install the Nagios binaries, init scripts, and sample configuration files:
sudo make install sudo make install-init sudo make install-config sudo make install-commandmode
Set the necessary permissions:
sudo usermod -a -G nagcmd apache
Finally, verify the Nagios configuration to ensure everything is set up correctly:
Step 4. Configuration.
With Nagios installed, it’s time to configure the web server to serve the Nagios web interface. Edit the Apache configuration file and add the necessary directives:
sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/nagios.conf
Add the following line:
ScriptAlias /nagios/cgi-bin "/usr/local/nagios/sbin" <Directory "/usr/local/nagios/sbin"> Options ExecCGI AllowOverride None Order allow,deny Allow from all AuthName "Nagios Access" AuthType Basic AuthUserFile /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users Require valid-user </Directory> Alias /nagios "/usr/local/nagios/share" <Directory "/usr/local/nagios/share"> Options None AllowOverride None Order allow,deny Allow from all AuthName "Nagios Access" AuthType Basic AuthUserFile /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users Require valid-user </Directory>
Save the file, then set up user authentication for the Nagios web interface. Create a nagiosadmin user and set a password:
sudo htpasswd -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users nagiosadmin
Nagios configuration files define hosts, services, and contacts. Organize these files in a way that suits your network infrastructure. Add command definitions and time periods as needed. Validate the Nagios configuration files to ensure they are correctly formatted:
/usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
Finally, start the Nagios service and enable it to start at boot:
sudo systemctl start nagios sudo systemctl enable nagios
Step 5. Accessing the Nagios Web UI.
Access the Nagios web interface by navigating to http://your_server_ip/nagios in your web browser. Complete the initial setup and start monitoring your first host and service to ensure Nagios is functioning correctly.
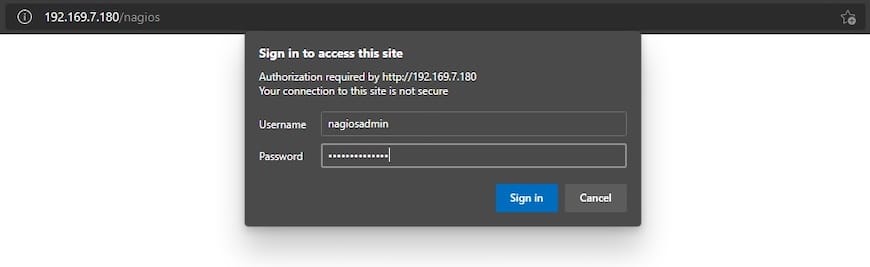
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Nagios. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Nagios open-source monitoring tool on your Fedora 39 system. For additional or useful information, we recommend you check the official Nagios website.