How To Install Nethogs on Fedora 38

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Nethogs on Fedora 38. Nethogs, short for Network Hog, is an uncomplicated yet highly effective utility crafted for monitoring network bandwidth on Linux systems. Its brilliance lies in the fact that it displays bandwidth consumption not just for the entire system but on a per-process level. This granularity makes it a preferred choice for system administrators and anyone who seeks to scrutinize network resource consumption with precision.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Nethogs on a Fedora 38.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Fedora 38.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- An active internet connection. You’ll need an internet connection to download the necessary packages and dependencies for Nethogs.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Nethogs on Fedora 38
Step 1. Before we can install the Nethogs on Fedora 38, it’s important to ensure that our system is up-to-date with the latest packages. This will ensure that we have access to the latest features and bug fixes and that we can install nethogs without any issues:
sudo dnf clean all sudo dnf update
Step 2. Installing Nethogs on Fedora 38.
There are two main methods to install nethogs on your Fedora 38 system: using the DNF package manager or building it from the source. We’ll explore both options to cater to your specific needs.
- Method 1: Using DNF Package Manager.
Now, you’re ready to install nethogs using DNF. Execute the following command:
sudo dnf install nethogs
DNF will automatically fetch the Nethogs package and its dependencies, and prompt you to confirm the installation. Press ‘Y‘ to proceed.
After the installation is complete, you can verify it by running Nethogs in your terminal:
sudo nethogs
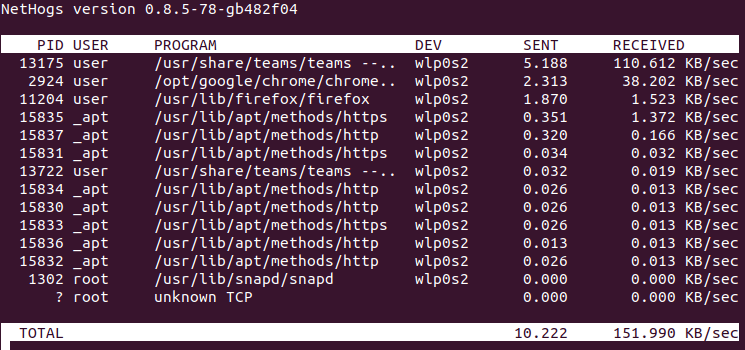
This will launch the Nethogs interface, enabling you to start monitoring your network bandwidth. You’ll see a real-time breakdown of processes consuming network resources, sorted by data sent and received.
- Method 2: Building from Source.
Begin by downloading the Nethogs source code from its GitHub repository. You can do this by issuing the following command:
git clone https://github.com/raboof/nethogs.git
Navigate to the directory where you downloaded Nethogs:
cd nethogs
Now, you’ll want to extract the source code:
make
The next steps involve compiling and installing Nethogs. Execute the following commands:
make sudo make install
These commands will compile the source code and install Nethogs on your system.
To ensure the installation was successful, you can once again verify it by running Nethogs:
sudo nethogs
Step 3. Using Nethogs.
Now that Nethogs is successfully installed on your Fedora 38 system, let’s explore how to use it to monitor your network bandwidth. To launch Nethogs, open your terminal and run the following command:
sudo nethogs
Press ‘Enter,’ and Nethogs will instantly provide you with live data on network bandwidth usage. The interface is updated in real time, showing which processes are consuming network resources.