How To Install Next.js on Debian 13

Next.js has emerged as the leading React framework for building production-ready web applications with advanced features like server-side rendering, static site generation, and API routes. Installing Next.js on Debian 13 provides developers with a stable, secure Linux environment perfect for modern web development. This comprehensive guide walks you through every step of the installation process, from system preparation to running your first Next.js application.
Whether you’re a beginner starting your web development journey or an experienced developer setting up a new development environment, this tutorial covers all the essential steps and best practices for a successful Next.js installation on Debian 13.
Understanding Next.js and Prerequisites
What is Next.js?
Next.js is a powerful React framework developed by Vercel that simplifies the development of modern web applications. This framework provides essential features out of the box, including server-side rendering (SSR), static site generation (SSG), automatic code splitting, and built-in API routes.
The framework excels at creating fast, SEO-friendly applications with minimal configuration. Developers choose Next.js for its excellent performance optimization, developer experience, and production-ready features that handle complex tasks like routing, image optimization, and deployment seamlessly.
System Requirements
Before installing Next.js on your Debian 13 system, ensure your machine meets these minimum requirements:
- 2GB RAM (4GB recommended for optimal performance)
- 10GB available disk space for Node.js, Next.js, and project files
- Active internet connection for downloading packages and dependencies
- Terminal access with sudo privileges
- Basic familiarity with command-line operations
Debian 13 provides an excellent foundation for Next.js development due to its stability, security updates, and comprehensive package management system through APT.
Preparing Your Debian 13 System
System Update and Package Management
Begin by ensuring your Debian 13 system has the latest security updates and packages. Open your terminal and execute the following commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade -yThe first command refreshes your package repository information, while the second upgrades all installed packages to their latest versions. This process ensures compatibility with the Node.js installation and prevents potential conflicts.
Next, install essential development tools that Next.js and Node.js require:
sudo apt install -y curl wget git build-essentialThese packages provide:
- curl and wget: Download tools for fetching installation scripts
- git: Version control system for managing your Next.js projects
- build-essential: Compilation tools needed for native Node.js modules
Installing Required Dependencies
Debian 13 requires several additional packages for optimal Node.js performance. Install these dependencies with:
sudo apt install -y software-properties-common apt-transport-https ca-certificates gnupg lsb-releaseConfigure your system’s firewall if you’re planning to run Next.js in a production environment. For development purposes, you may need to allow traffic on port 3000 (Next.js default):
sudo ufw allow 3000/tcpCreate a dedicated directory for your development projects:
mkdir -p ~/projects/nextjs
cd ~/projects/nextjsInstalling Node.js on Debian 13
Method 1: Installing via APT Package Manager
The simplest approach involves using Debian’s default repositories. While this method provides stability, it might not offer the latest Node.js version:
sudo apt install -y nodejs npmVerify the installation by checking the installed versions:
node --version
npm --versionThis method typically installs Node.js version 18.x or newer, which fully supports Next.js applications. However, if you require the absolute latest features, consider the alternative installation methods below.
Method 2: Installing via NodeSource Repository
For the most recent Node.js LTS version, add the official NodeSource repository:
curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_lts.x | sudo -E bash -
sudo apt install -y nodejsThis method ensures you receive the latest Long Term Support version of Node.js, which provides the best balance of stability and modern features. The NodeSource repository maintains up-to-date packages specifically optimized for Debian systems.
Verify the installation:
node --version
npm --versionMethod 3: Installing via NVM (Node Version Manager)
NVM (Node Version Manager) offers the most flexibility by allowing you to install and switch between multiple Node.js versions. This approach is particularly valuable for developers working on multiple projects with different Node.js requirements.
Install NVM using the official installation script:
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.0/install.sh | bashReload your shell configuration:
source ~/.bashrcInstall the latest Node.js LTS version:
nvm install --lts
nvm use --lts
nvm alias default nodeVerify your installation:
node --version
npm --versionNVM allows you to install specific versions when needed:
nvm install 18.17.0
nvm use 18.17.0Installing Next.js Framework
Using create-next-app (Official Method)
The recommended approach for creating Next.js applications uses the official create-next-app tool. This utility sets up a complete Next.js project with optimal configuration and modern best practices.
Create your first Next.js application:
npx create-next-app@latest my-nextjs-appDuring the setup process, you’ll encounter several configuration prompts:
- TypeScript support: Choose “Yes” for type safety (recommended)
- ESLint integration: Select “Yes” for code quality enforcement
- Tailwind CSS: Choose based on your styling preferences
- App Router: Select “Yes” for the modern Next.js routing system
- Source directory: Choose “No” for simpler project structure initially
- Import alias: Accept the default “@/*” configuration
Navigate to your new project directory:
cd my-nextjs-appProject Structure Overview
Understanding the generated project structure helps you navigate and modify your Next.js application effectively:
my-nextjs-app/
├── app/ # App Router directory (Next.js 13+)
│ ├── globals.css # Global CSS styles
│ ├── layout.tsx # Root layout component
│ └── page.tsx # Home page component
├── public/ # Static assets (images, icons)
├── next.config.js # Next.js configuration
├── package.json # Project dependencies and scripts
├── tailwind.config.ts # Tailwind CSS configuration
└── tsconfig.json # TypeScript configurationKey files serve specific purposes:
- package.json: Contains project metadata, dependencies, and npm scripts
- next.config.js: Customizes Next.js behavior and build settings
- app/layout.tsx: Defines the root layout for all pages
- app/page.tsx: Your application’s home page component
Installing Dependencies
Ensure all project dependencies are properly installed:
npm installThis command downloads and installs all packages listed in your package.json file, including Next.js, React, and any additional dependencies. The installation process creates a node_modules directory containing all required libraries and a package-lock.json file that locks dependency versions for consistent installations.
Configuring and Running Your Next.js Application
Development Server Setup
Launch your Next.js application in development mode to begin coding:
npm run devThis command starts the development server with several powerful features:
- Hot reloading: Automatically updates your browser when you save changes
- Error overlay: Displays helpful error messages directly in the browser
- Fast refresh: Preserves component state during code updates
- Built-in optimization: Automatically optimizes images and code
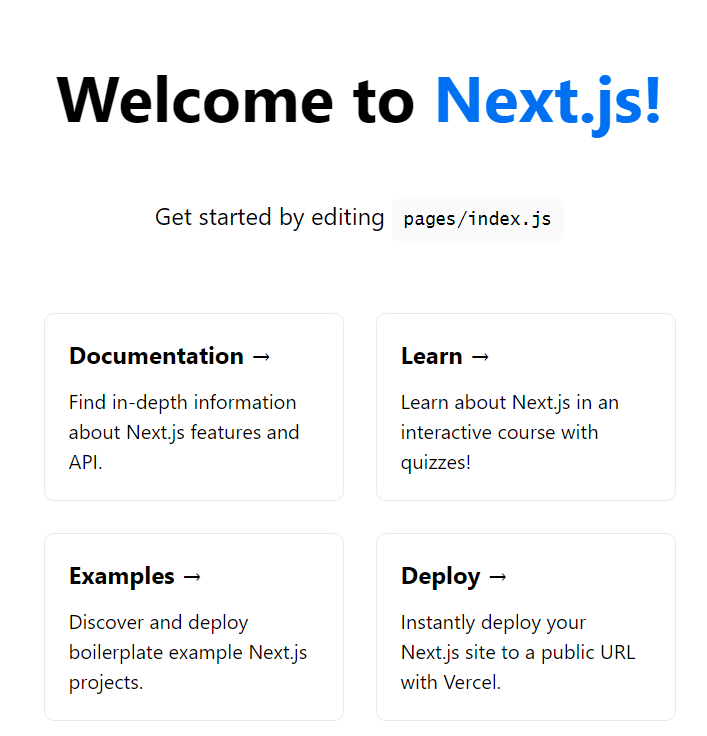
Your application will be available at http://localhost:3000. The terminal output provides helpful information about compilation status and any errors or warnings.
Open your web browser and navigate to the local development server to see your “Hello World” Next.js application running successfully.
Production Build Process
When you’re ready to deploy your application, create an optimized production build:
npm run buildThis process performs several important optimizations:
- Code minification: Reduces file sizes for faster loading
- Tree shaking: Removes unused code from your bundle
- Static generation: Pre-renders pages when possible
- Asset optimization: Compresses images and other static files
The build process generates a .next directory containing all optimized files ready for production deployment.
Running in Production Mode
After building your application, start it in production mode:
npm startProduction mode provides enhanced performance and security compared to development mode. The server uses optimized code and enables features like compression and caching for better user experience.
Monitor your application’s performance and memory usage while running in production mode to ensure optimal resource utilization.
Advanced Configuration and Optimization
Environment Configuration
Create environment-specific configuration files to manage different deployment scenarios. Start with a .env.local file for development:
touch .env.localAdd environment variables for database connections, API keys, and other configuration:
NEXT_PUBLIC_API_URL=http://localhost:3000/api
DATABASE_URL=postgresql://user:password@localhost:5432/mydb
SECRET_KEY=your-secret-key-hereNext.js automatically loads environment variables with the NEXT_PUBLIC_ prefix on the client side, while other variables remain server-side only for security.
Process Management with PM2
For production deployments, install PM2 process manager to handle application lifecycle:
npm install -g pm2Create a PM2 ecosystem file (ecosystem.config.js):
module.exports = {
apps: [{
name: 'my-nextjs-app',
script: 'npm',
args: 'start',
cwd: '/path/to/your/app',
env: {
NODE_ENV: 'production',
PORT: 3000
}
}]
};Start your application with PM2:
pm2 start ecosystem.config.js
pm2 save
pm2 startupReverse Proxy Setup with Nginx
Configure Nginx as a reverse proxy to handle SSL termination and load balancing:
sudo apt install nginxCreate an Nginx configuration file (/etc/nginx/sites-available/nextjs-app):
server {
listen 80;
server_name your-domain.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade';
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
}
}Enable the configuration and restart Nginx:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/nextjs-app /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl restart nginxSecurity Best Practices
System Security
Implement comprehensive security measures to protect your Next.js installation and applications:
Configure a firewall using UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall):
sudo ufw enable
sudo ufw allow ssh
sudo ufw allow 80/tcp
sudo ufw allow 443/tcp
sudo ufw allow 3000/tcpCreate a dedicated user for running Next.js applications:
sudo useradd -m -s /bin/bash nextjs-user
sudo usermod -aG sudo nextjs-userSet appropriate file permissions for your project directories:
sudo chown -R nextjs-user:nextjs-user ~/projects/nextjs
chmod -R 755 ~/projects/nextjsRegularly update your system and Node.js packages to address security vulnerabilities:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
npm audit fixApplication Security
Implement application-level security measures to protect against common web vulnerabilities:
Install and configure security-focused packages:
npm install helmet next-secure-headersConfigure Content Security Policy in your next.config.js:
const secureHeaders = [
{
key: 'X-DNS-Prefetch-Control',
value: 'on'
},
{
key: 'X-XSS-Protection',
value: '1; mode=block'
},
{
key: 'X-Frame-Options',
value: 'SAMEORIGIN'
}
];
module.exports = {
async headers() {
return [
{
source: '/(.*)',
headers: secureHeaders,
},
];
},
};Regularly audit your dependencies for known vulnerabilities:
npm audit
npm updateTroubleshooting Common Issues
Installation Problems
Node.js version compatibility represents the most common installation issue. Next.js requires Node.js version 16.14 or higher. If you encounter version-related errors:
node --version # Check current version
nvm install --lts # Install latest LTS if using NVMPermission errors often occur when installing packages globally. Use NVM or adjust npm permissions:
mkdir ~/.npm-global
npm config set prefix '~/.npm-global'
export PATH=~/.npm-global/bin:$PATHNetwork connectivity issues can interrupt package downloads. Configure npm to use a different registry if needed:
npm config set registry https://registry.npmjs.org/
npm config set strict-ssl false # Only if behind corporate firewallDependency conflicts may arise when mixing different installation methods. Clean your npm cache and reinstall:
npm cache clean --force
rm -rf node_modules package-lock.json
npm installRuntime Issues
Port binding problems occur when port 3000 is already in use. Check running processes:
sudo lsof -i :3000
# Kill the process using the port
sudo kill -9 <PID>Alternatively, specify a different port:
npm run dev -- -p 3001Memory issues may arise with large projects. Increase Node.js memory limit:
export NODE_OPTIONS="--max-old-space-size=4096"
npm run devBuild failures often result from TypeScript errors or missing dependencies:
npm run build --verbose # Get detailed error information
npm install --save-dev @types/node @types/reactHot reloading issues can be resolved by checking file system limits:
echo fs.inotify.max_user_watches=524288 | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf
sudo sysctl -pPerformance Optimization Tips
Development Performance
Optimize your development environment for faster iteration cycles:
Enable experimental features in next.config.js for improved build speed:
module.exports = {
experimental: {
turbo: true, // Enable Turbopack
swcMinify: true // Use SWC for minification
}
};Configure TypeScript for better performance by adding to tsconfig.json:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"incremental": true,
"tsBuildInfoFile": ".next/.tsbuildinfo"
}
}Use efficient import patterns to reduce bundle size:
// Good: Import only what you need
import { useState } from 'react';
// Avoid: Importing entire libraries
import * as React from 'react';Production Performance
Implement production optimizations for better user experience:
Enable gzip compression in your Nginx configuration:
gzip on;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_min_length 1000;
gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json application/javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript;Configure static asset caching with appropriate headers:
module.exports = {
async headers() {
return [
{
source: '/_next/static/(.*)',
headers: [
{
key: 'Cache-Control',
value: 'public, max-age=31536000, immutable',
},
],
},
];
},
};Implement image optimization using Next.js built-in features:
import Image from 'next/image';
export default function MyComponent() {
return (
<Image
src="/my-image.jpg"
alt="Description"
width={500}
height={300}
priority={true} // For above-the-fold images
/>
);
}Congratulations! You have successfully installed Next.js. Thanks for using this tutorial to install the latest version of the Next.js react framework on Debian 13 “Trixie”. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Next.js website.