How To Install Next.js on Linux Mint 22

Next.js stands as one of the most powerful React frameworks available today, offering developers the ability to build production-ready applications with server-side rendering, static site generation, and seamless deployment capabilities. Installing Next.js on Linux Mint 22 provides developers with a robust, Ubuntu-based environment that combines stability with cutting-edge development tools. This comprehensive guide walks you through every step of the installation process, from system preparation to creating your first Next.js application.
What is Next.js and Why Use It?
Next.js is a React framework developed by Vercel that extends React’s capabilities with production-ready features. The framework provides built-in support for server-side rendering (SSR), static site generation (SSG), API routes, and automatic code splitting. These features make Next.js particularly attractive for developers building modern web applications that require excellent performance and SEO optimization.
The framework offers several compelling advantages over traditional React applications. Automatic code splitting ensures that users only download the JavaScript necessary for the current page, dramatically improving load times. Built-in CSS and Sass support streamlines styling workflows, while API routes eliminate the need for separate backend services in many cases. Next.js also provides image optimization, internationalization support, and TypeScript integration out of the box.
For Linux Mint 22 users specifically, Next.js development benefits from the distribution’s stability and extensive package availability. Linux Mint 22’s Ubuntu 22.04 foundation ensures excellent compatibility with Node.js and npm packages, making it an ideal platform for JavaScript development.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Before installing Next.js on Linux Mint 22, ensure your system meets the necessary requirements. Linux Mint 22 requires a minimum of 2GB RAM, though 4GB or more is recommended for comfortable development. Your system should have at least 15GB of free storage space to accommodate Node.js, npm packages, and development projects.
Administrative privileges are essential for installing system packages and managing repositories. You’ll need basic familiarity with the command line interface, as most installation steps involve terminal commands. An active internet connection is required for downloading packages and dependencies.
The system should run Linux Mint 22 (Virginia), which is based on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS. This foundation provides long-term stability and extensive software repository support. Verify your Linux Mint version by running lsb_release -a in the terminal.
Step 1: Updating Linux Mint 22 System
System updates form the foundation of a successful Next.js installation. Outdated packages can cause compatibility issues and security vulnerabilities that may interfere with development tools. Begin by refreshing the package repository information and installing available updates.
Open your terminal application and execute the following commands:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -yThe apt update command refreshes the local package database with the latest information from repositories. The apt upgrade command installs available updates for installed packages. The -y flag automatically confirms installation prompts, streamlining the update process.
After updates complete, consider rebooting your system if kernel updates were installed. This ensures all system components operate with the latest security patches and performance improvements.
Step 2: Installing Node.js and npm
Next.js requires Node.js as its runtime environment, making Node.js installation the most critical step in the process. Linux Mint 22 offers multiple methods for installing Node.js, each with distinct advantages depending on your development needs.
Method 1: Using APT Package Manager
The APT package manager provides the simplest Node.js installation method. This approach installs Node.js directly from Ubuntu’s official repositories, ensuring stability and automatic security updates.
Execute the following command to install Node.js and npm:
sudo apt install nodejs npm -yThis command installs both the Node.js runtime and npm (Node Package Manager) simultaneously. The installation typically completes within a few minutes, depending on your internet connection speed.
Advantages of APT installation include automatic security updates, system integration, and minimal configuration requirements. However, repository versions may lag behind the latest Node.js releases, potentially limiting access to newer features.
Method 2: Using NodeSource Repository
NodeSource provides official Node.js packages with more recent versions than standard Ubuntu repositories. This method offers the latest LTS (Long Term Support) releases while maintaining package management benefits.
Add the NodeSource repository and install Node.js:
curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_lts.x | sudo -E bash -
sudo apt-get install -y nodejsThe first command downloads and executes the NodeSource setup script. This script adds the NodeSource repository to your system and imports the necessary GPG keys for package verification. The second command installs the latest LTS version of Node.js.
NodeSource advantages include access to current Node.js versions, maintained compatibility with Ubuntu systems, and regular security updates. This method is recommended for developers who need recent Node.js features while maintaining system stability.
Method 3: Using NVM (Node Version Manager)
NVM (Node Version Manager) enables multiple Node.js versions on a single system. This flexibility proves invaluable for developers working on projects with different Node.js requirements.
Install NVM using the official installation script:
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.0/install.sh | bash
source ~/.bashrcAfter NVM installation, install the latest LTS Node.js version:
nvm install --lts
nvm use --ltsNVM benefits include version switching capabilities, project-specific Node.js versions, and easy upgrades. However, NVM requires more manual management and doesn’t integrate with system package managers for automatic updates.
Step 3: Verifying Node.js and npm Installation
Verification ensures successful Node.js and npm installation before proceeding with Next.js setup. Proper verification prevents debugging issues during Next.js project creation and identifies potential installation problems early.
Check your Node.js installation by running:
node -vThis command should output a version number similar to v18.17.0 or newer. Next.js requires Node.js version 16.8 or later for optimal compatibility and feature support.
Verify npm installation with:
npm -vThe output should display an npm version number like 9.6.7 or newer. Npm typically installs automatically with Node.js, but separate verification ensures both components function correctly.
If either command fails or returns unexpected output, revisit the installation steps for your chosen method. Common issues include PATH configuration problems or incomplete installations that require reinstallation or manual PATH updates.
Step 4: Installing Development Tools and Dependencies
Development tools and build dependencies ensure smooth compilation of native npm packages and Next.js applications. Linux systems require specific build tools for compiling binary packages that many Node.js projects depend on.
Install essential build tools using:
sudo apt install curl build-essential -yThe build-essential package includes GCC compiler, make, and other essential tools for compiling software from source. These tools are crucial for installing npm packages that contain native code or require compilation during installation.
Additional recommended development tools include Git for version control and a modern text editor. Install Git if not already available:
sudo apt install git -yConfigure Git with your developer information:
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git config --global user.email "your.email@example.com"These development tools create a complete environment for Next.js development, ensuring compatibility with the broader JavaScript ecosystem and enabling advanced development workflows.
Step 5: Creating Your First Next.js Application
Creating a Next.js application demonstrates successful installation and provides a foundation for development. The create-next-app tool streamlines project setup with modern defaults and configuration options.
Generate a new Next.js project using:
npx create-next-app@latest my-nextjs-appThis command downloads and executes the latest version of create-next-app. The tool presents several configuration prompts that customize your project setup:
- TypeScript: Adds static type checking for enhanced development experience
- ESLint: Provides code linting for maintaining code quality standards
- Tailwind CSS: Includes utility-first CSS framework for rapid styling
- App Router: Enables the new app directory structure (recommended)
- Import alias: Configures path aliasing for cleaner import statements
Recommended responses for beginners include enabling TypeScript, ESLint, and the App Router while potentially deferring Tailwind CSS until familiarity with Next.js basics develops. These selections provide excellent developer experience without overwhelming complexity.
The creation process downloads necessary dependencies and generates a complete project structure. Project generation typically requires 2-5 minutes depending on internet speed and system performance.
Step 6: Understanding the Next.js Project Structure
Next.js project structure follows conventions that optimize development workflow and application performance. Understanding this structure helps developers navigate projects efficiently and implement features correctly.
Navigate to your project directory:
cd my-nextjs-appExamine the generated structure:
app/directory: Contains application pages, layouts, and route handlers (App Router)public/directory: Stores static assets like images, fonts, and iconspackage.json: Defines project dependencies, scripts, and metadatanext.config.js: Configuration file for Next.js-specific settingstailwind.config.js: Tailwind CSS configuration (if enabled).next/directory: Build output and cached files (created during development)
The app/ directory structure represents Next.js 13+ App Router conventions. Files like layout.js define shared UI components, while page.js files create routable pages. This structure enables powerful features like nested layouts, loading states, and server components.
Configuration files control various aspects of the development environment. package.json manages dependencies and defines build scripts. next.config.js allows customization of webpack configuration, environment variables, and deployment settings.
Understanding this structure accelerates development by clarifying where different types of code belong and how Next.js processes different file types during build and runtime operations.
Step 7: Running Your Next.js Application
Starting the development server activates Next.js’s development features including hot reloading, error reporting, and automatic compilation. The development server provides an interactive environment for building and testing applications.
Start the development server with:
npm run devThis command executes the development script defined in package.json. Next.js typically starts the server on port 3000, displaying startup information including the local access URL.
Expected startup output includes compilation messages, port information, and ready status indicators. The console displays “ready – started server on 0.0.0.0:3000” or similar messaging indicating successful startup.
Access your application by opening a web browser and navigating to http://localhost:3000. The default Next.js welcome page appears, featuring documentation links, deployment options, and example components that demonstrate framework capabilities.
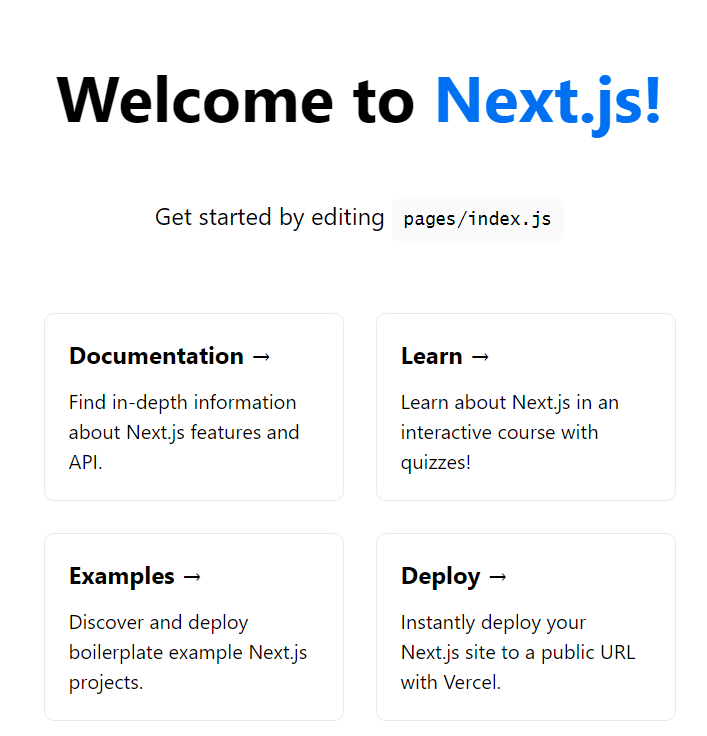
Development server features include automatic code reloading when files change, error overlay for debugging, and real-time compilation feedback. These features significantly enhance the development experience by providing immediate feedback on code changes.
Step 8: Customizing Your Next.js Application
Application customization demonstrates Next.js functionality while creating a foundation for further development. Basic modifications help developers understand component structure, routing, and styling approaches within the Next.js ecosystem.
Edit the main page by opening app/page.js in your preferred text editor:
export default function Home() {
return (
<main className="flex min-h-screen flex-col items-center justify-between p-24">
<div className="z-10 max-w-5xl w-full items-center justify-between font-mono text-sm">
<h1 className="text-4xl font-bold text-center">
Welcome to My Next.js App on Linux Mint 22!
</h1>
<p className="mt-4 text-center">
This application is running successfully on Linux Mint 22.
</p>
</div>
</main>
)
}Creating additional pages involves adding new page.js files within the app/ directory structure. For example, create app/about/page.js for an about page:
export default function About() {
return (
<div className="container mx-auto p-4">
<h1 className="text-2xl font-bold">About This Application</h1>
<p>Built with Next.js on Linux Mint 22</p>
</div>
)
}Save your changes and observe automatic hot reloading in the browser. Next.js detects file modifications and updates the application without manual refresh, streamlining the development process.
Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
Installation troubleshooting addresses frequent problems that developers encounter during Next.js setup on Linux Mint 22. Systematic problem-solving approaches resolve most issues quickly and prevent future complications.
Permission-related errors often occur during npm package installation. If you encounter permission denied errors, avoid using sudo with npm. Instead, configure npm’s default directory:
mkdir ~/.npm-global
npm config set prefix '~/.npm-global'
echo 'export PATH=~/.npm-global/bin:$PATH' >> ~/.profile
source ~/.profileNode.js version conflicts may arise when multiple installation methods coexist. Check active Node.js versions:
which node
which npmEnsure both commands point to the same installation location. Mixed installations can cause unexpected behavior and package compatibility issues.
Network connectivity problems during package installation often manifest as timeout errors or failed downloads. Configure npm to use alternative registries or increase timeout values:
npm config set registry https://registry.npmjs.org/
npm config set timeout 60000Port conflicts prevent development server startup when port 3000 is already in use. Specify alternative ports:
npm run dev -- --port 3001Build tool compilation errors typically indicate missing development dependencies. Reinstall build-essential and related packages:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install build-essential python3-dev -yThese troubleshooting steps resolve the majority of installation and setup issues, enabling smooth Next.js development on Linux Mint 22.
Best Practices and Security Considerations
Security best practices protect your development environment and applications from potential vulnerabilities while maintaining efficient development workflows. Implementing security measures from the beginning prevents issues during development and deployment phases.
Keep dependencies updated by regularly checking for package updates and security patches:
npm audit
npm audit fixThe npm audit command identifies known vulnerabilities in project dependencies. The npm audit fix command automatically updates packages to secure versions when possible.
Use proper file permissions for project directories and files. Avoid running development servers or npm commands with sudo privileges, as this can create security vulnerabilities and ownership conflicts:
chown -R $USER:$USER ~/.npm
chmod 755 ~/.npmEnvironment variable management secures sensitive configuration data like API keys and database credentials. Create .env.local files for local development secrets and ensure these files are excluded from version control:
echo "NEXT_PUBLIC_API_URL=http://localhost:3000/api" >> .env.local
echo ".env.local" >> .gitignoreFirewall configuration may be necessary when running development servers accessible from external networks. Configure UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) to control network access:
sudo ufw enable
sudo ufw allow 3000/tcpThese security practices establish a foundation for secure Next.js development while maintaining the flexibility needed for efficient application building.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Next.js. Thanks for using this tutorial to install the latest version of the Next.js react framework on Linux Mint 22. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Next.js website.