How To Install Nginx on Fedora 37

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Nginx on Fedora 37. For those of you who didn’t know, Nginx, pronounced “Engine-X,” is a popular open-source web server that is used to serve a wide range of websites and applications. It is known for its high performance, low resource usage, and ease of use. One of the key advantages of Nginx is its event-driven architecture, which allows it to handle many concurrent connections with small memory. This makes it well-suited for high-traffic websites and applications. Nginx also supports various protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, and FastCGI, making it a flexible solution for a variety of use cases.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Nginx web server on a Fedora 37.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Fedora 37.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- An active internet connection. You’ll need an internet connection to download the necessary packages and dependencies for Nginx.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Nginx on Fedora 37
Step 1. Before proceeding, update your Fedora operating system to make sure all existing packages are up to date. Use this command to update the server packages:
sudo dnf upgrade sudo dnf update
Step 2. Installing Nginx on Fedora 37.
By default, the Nginx package comes in the default Fedora 37 repository. Now run the following command below to install Nginx to your Fedora system:
sudo dnf install nginx
After the installation is complete, start the Nginx service and enable it to start automatically on boot by running the following commands:
sudo systemctl start nginx sudo systemctl enable nginx
Step 3. Configuring Nginx.
The default Nginx configuration file is located at /etc/nginx/nginx.conf. You can edit this file to configure Nginx to meet your needs. For example, you can change the default listen port, configure virtual hosts, and set up SSL certificates.
It is important to be careful when making changes to the Nginx configuration file, as a misconfiguration can result in a broken web server. Always make sure to back up the configuration file before making any changes.
Step 4. Configure FirewallD Rules.
We need to enable the firewall in order to filter traffic into our server. Now we add HTTP and HTTPS ports in the firewall using the following command:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Step 5. Verifying the Installation.
To verify the installation of Nginx, you can access the default welcome page by opening a web browser and navigating to http://localhost or http://your-IP-address. You will get the following screen:
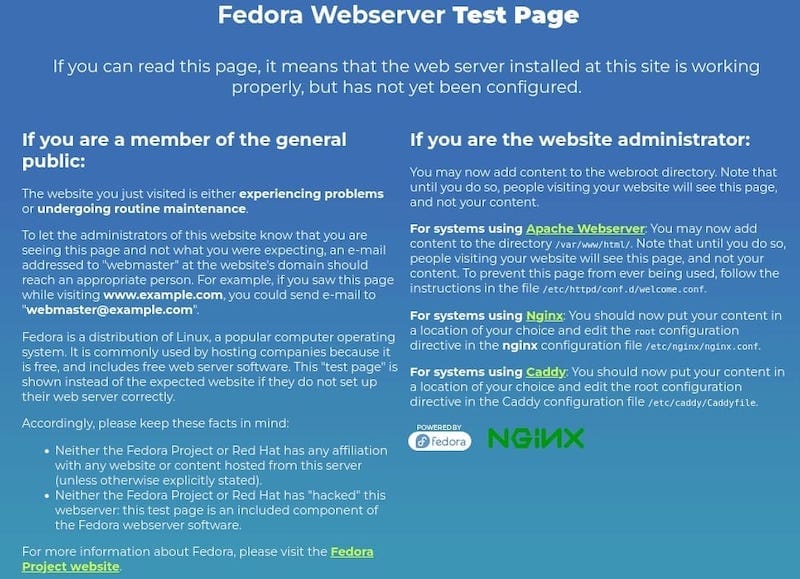
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Nginx. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Nginx web server on your Fedora 37 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Nginx website.