How To Install Nginx on Fedora 40

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Nginx on Fedora 40. Nginx pronounced as “engine-x,” is a powerful and versatile open-source web server that has gained significant popularity among developers and system administrators. Known for its high performance, stability, and low resource consumption, Nginx is an excellent choice for serving web content, acting as a reverse proxy, and handling load balancing.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Nginx web server on a Fedora 40.
Prerequisites
Before we dive into the installation process, ensure that you have the following prerequisites in place:
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Fedora 40.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- You will need access to the terminal to execute commands. Fedora provides the Terminal application for this purpose. It can be found in your Applications menu.
- A stable internet connection to download the necessary packages.
- A non-root sudo user or access to the root user. We recommend acting as a non-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Nginx on Fedora 40
Step 1. Update the System.
To ensure a smooth and secure installation, it is crucial to update your Fedora 40 system before proceeding with the Nginx installation. Updating the system ensures that you have the latest security patches, bug fixes, and compatible dependencies. Open your terminal and run the following command:
sudo dnf clean all sudo dnf update
This command will fetch the latest package information from the Fedora repositories and upgrade any outdated packages to their latest versions. The process may take a few minutes, depending on the number of updates available.
Step 2. Installing Nginx on Fedora 40.
Nginx is readily available in Fedora’s default repositories, making the installation process straightforward. To install Nginx, use the following command:
sudo dnf install nginx
The dnf package manager will resolve any dependencies and download the necessary packages for Nginx. Confirm the installation by typing “y” when prompted.
Once the installation is complete, you can verify the installed version of Nginx by running:
nginx -v
This command will display the Nginx version number, confirming that the installation was successful.
Step 3. Manage the Nginx Service.
With Nginx installed, you can now manage the Nginx service using the systemctl utility. The systemctl command allows you to start, stop, restart, and check the status of the Nginx service.
To start the Nginx service, run:
sudo systemctl start nginx
To stop the Nginx service, use:
sudo systemctl stop nginx
If you need to restart the Nginx service, execute:
sudo systemctl restart nginx
To enable Nginx to start automatically at system boot, run:
sudo systemctl enable nginx
This command will create the necessary symlinks to ensure that Nginx starts during the system boot process.
Step 4. Configure Firewall.
By default, Fedora uses the firewalld utility to manage firewall rules. To allow incoming traffic to Nginx, you need to configure the firewall to open the necessary ports.
To open port 80 for HTTP traffic, run:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
To open port 443 for HTTPS traffic, use:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https
After adding the firewall rules, reload the firewall configuration:
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
These commands will ensure that incoming HTTP and HTTPS traffic can reach your Nginx server.
Step 5. Test Nginx.
With Nginx installed and the firewall configured, it’s time to test if Nginx is running correctly. Open a web browser and enter your server’s IP address or domain name in the address bar.
If everything is set up properly, you should see the default Nginx landing page, which displays a message similar to “Welcome to Nginx!”.
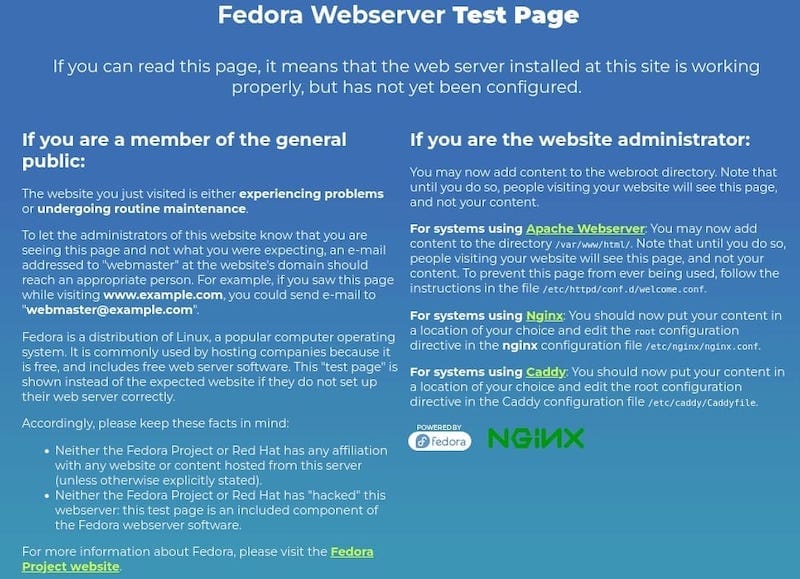
If the page doesn’t load, double-check your firewall settings and ensure that Nginx is running by checking its status with sudo systemctl status nginx. You can also examine the Nginx error logs in /var/log/nginx/error.log for any potential issues.
Step 6. Configure Server Blocks.
Nginx uses the concept of server blocks, also known as virtual hosts, to host multiple websites on a single server. Each server block represents a separate website configuration.
To set up a new website, create a directory for it:
sudo mkdir -p /var/www/example.com/html
Next, grant ownership of the website directory to your non-root user:
sudo chown -R $USER:$USER /var/www/example.com/html
Create a sample index.html file in the website directory:
echo "<html><body><h1>Welcome to Example.com!</h1></body></html>" > /var/www/example.com/html/index.html
Now, create a new server block configuration file for your website:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/example.com.conf
Add the following configuration to the file:
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com www.example.com;
root /var/www/example.com/html;
index index.html;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
}
Save the file and exit the editor, then test the Nginx configuration for any syntax errors:
sudo nginx -t
If the configuration is valid, reload Nginx to apply the changes:
sudo systemctl reload nginx
Your new website should now be accessible at http://example.com.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Nginx. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Nginx web server on your Fedora 40 system. For additional or useful information, we recommend you check the official Nginx website.