How To Install Nginx Proxy Manager on AlmaLinux 10

Managing multiple web services and domains can become overwhelming without proper tools. Nginx Proxy Manager (NPM) transforms this complexity into a streamlined, web-based solution that simplifies reverse proxy management on enterprise-grade systems.
AlmaLinux 10 provides the perfect foundation for hosting Nginx Proxy Manager. This Red Hat Enterprise Linux derivative offers enterprise stability, long-term support, and robust security features. When combined with NPM’s intuitive interface, you get a powerful platform for managing SSL certificates, load balancing, and service routing.
This comprehensive guide walks you through every step of installing and configuring Nginx Proxy Manager on AlmaLinux 10. You’ll learn to set up Docker containers, configure SSL certificates automatically, and implement security best practices. By the end, you’ll have a fully functional reverse proxy manager capable of handling multiple domains and services with professional-grade reliability.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Before diving into the installation process, ensure your AlmaLinux 10 system meets the necessary requirements. Your server should have at least 2GB of RAM and 20GB of available disk space for optimal performance. While NPM can run on smaller systems, these specifications ensure smooth operation under moderate load.
Administrative privileges are essential throughout this installation. You’ll need either root access or a user account with sudo privileges to install packages, modify system configurations, and manage Docker containers. If you’re using a cloud provider, ensure your instance has these permissions configured.
Network configuration plays a crucial role in NPM functionality. Your server requires a public IP address and properly configured DNS records pointing to your domain. The system must have ports 80, 443, and 81 available – port 80 for HTTP traffic, port 443 for HTTPS traffic, and port 81 for the NPM administrative interface.
Domain management becomes simplified with proper DNS setup. Configure A records for your primary domain and any subdomains you plan to manage through NPM. Wildcard DNS records can streamline subdomain management if you’re planning to host multiple services.
Security considerations start from day one. Ensure your AlmaLinux installation includes recent security updates and follows basic hardening practices. Disable unnecessary services, configure SSH key authentication, and implement fail2ban or similar intrusion prevention systems.
Preparing AlmaLinux 10 System
System Updates and Package Management
Start by updating your AlmaLinux 10 system to ensure all packages are current and security patches are applied. Connect to your server via SSH and execute the system update command:
sudo dnf update -yThis command downloads and installs all available updates for your system packages. The process may take several minutes depending on your internet connection and the number of pending updates.
Install essential utilities that will be required throughout the NPM installation process:
sudo dnf install -y curl wget yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2These packages provide necessary tools for downloading Docker components and managing system resources. Verify your AlmaLinux version to ensure compatibility:
cat /etc/almalinux-releaseThe output should confirm you’re running AlmaLinux 10, which provides the stable foundation needed for Docker containerization.
Configuring Firewall Rules
AlmaLinux 10 uses FirewallD as its default firewall management system. Check the current firewall status to ensure it’s active and properly configured:
sudo systemctl status firewalldIf the firewall isn’t running, start and enable it:
sudo systemctl start firewalld
sudo systemctl enable firewalldOpen the required ports for Nginx Proxy Manager operation. Port 80 handles standard HTTP traffic:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=80/tcpPort 443 manages HTTPS traffic with SSL encryption:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=443/tcpPort 81 provides access to the NPM administrative web interface:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=81/tcpApply the firewall changes and verify the configuration:
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
sudo firewall-cmd --list-portsThe output should display all three ports (80/tcp, 443/tcp, 81/tcp) as permanently opened, confirming proper firewall configuration.
Installing Docker and Docker Compose
Docker Installation Process
Docker containerization provides the foundation for running Nginx Proxy Manager efficiently. Begin by adding the official Docker repository to your AlmaLinux system:
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repoInstall Docker CE (Community Edition) along with its essential components:
sudo dnf install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-pluginThis installation includes Docker Engine, command-line interface, container runtime, and build tools necessary for container management.
Start the Docker service and configure it to launch automatically at system boot:
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable dockerAdd your current user to the docker group to enable non-root container management:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USERLog out and back in for group changes to take effect, or execute:
newgrp dockerTest your Docker installation by running a simple container:
docker run --rm hello-worldSuccessful execution confirms Docker is properly installed and functioning on your AlmaLinux 10 system.
Docker Compose Installation
Modern Docker installations include Docker Compose as a plugin, but verify its availability:
docker compose versionIf Docker Compose isn’t available, install it manually by downloading the latest stable release:
sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/latest/download/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-composeMake the Docker Compose binary executable:
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-composeCreate a symbolic link for easier access:
sudo ln -s /usr/local/bin/docker-compose /usr/bin/docker-composeVerify the installation works correctly:
docker-compose --versionThe output should display the Docker Compose version, confirming successful installation and readiness for container orchestration.
Creating Nginx Proxy Manager Setup
Directory Structure Setup
Organization is key to maintaining a clean and manageable NPM installation. Create a dedicated directory structure for your Nginx Proxy Manager deployment:
mkdir -p ~/nginx-proxy-manager/{data,letsencrypt}
cd ~/nginx-proxy-managerThis structure separates application data from SSL certificates, making backup and maintenance procedures more straightforward.
Set appropriate permissions for the data directories:
sudo chown -R $USER:$USER ~/nginx-proxy-manager
chmod -R 755 ~/nginx-proxy-managerProper permissions ensure Docker containers can read and write necessary files while maintaining system security.
Docker Compose Configuration
Create the Docker Compose configuration file that defines your NPM deployment:
nano docker-compose.ymlInsert the following comprehensive configuration:
version: '3.8'
services:
nginx-proxy-manager:
image: 'jc21/nginx-proxy-manager:latest'
container_name: nginx-proxy-manager
restart: unless-stopped
ports:
- '80:80'
- '81:81'
- '443:443'
volumes:
- ./data:/data
- ./letsencrypt:/etc/letsencrypt
environment:
DB_HOST: npm-database
DB_PORT: 3306
DB_NAME: npm
DB_USER: npm_user
DB_PASS: secure_password_here
depends_on:
- npm-database
networks:
- npm-network
npm-database:
image: 'mariadb:latest'
container_name: npm-database
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: root_password_here
MYSQL_DATABASE: npm
MYSQL_USER: npm_user
MYSQL_PASSWORD: secure_password_here
volumes:
- ./database:/var/lib/mysql
networks:
- npm-network
networks:
npm-network:
driver: bridge
volumes:
data:
database:
letsencrypt:Replace secure_password_here and root_password_here with strong, unique passwords. This configuration creates isolated containers with persistent data storage and secure database connectivity.
The volume mappings ensure your NPM configuration, SSL certificates, and database survive container restarts and updates. The dedicated network isolates NPM containers from other Docker services on your system.
Deploying and Starting Nginx Proxy Manager
Container Deployment Process
Navigate to your NPM directory and deploy the containers using Docker Compose:
cd ~/nginx-proxy-manager
docker compose up -dThe -d flag runs containers in detached mode, allowing them to continue running after you disconnect from the terminal session.
Monitor the container startup process:
docker compose logs -fWatch for successful database initialization and NPM startup messages. Initial startup may take several minutes as containers download, initialize databases, and configure services.
Verify all containers are running properly:
docker psYou should see both nginx-proxy-manager and npm-database containers with “Up” status, confirming successful deployment.
Initial System Verification
Test NPM web interface accessibility by navigating to your server’s IP address on port 81. Open a web browser and visit:
http://your-server-ip:81The NPM login screen should appear, indicating successful installation and network configuration.
Check container resource usage to ensure optimal performance:
docker statsMonitor CPU and memory usage to verify your system can handle the NPM workload effectively.
Test internal container communication by examining network connectivity:
docker network ls
docker network inspect nginx-proxy-manager_npm-networkThis inspection confirms containers can communicate securely within their isolated network environment.
Initial Configuration and Access
Web Interface Access
Access the NPM administrative interface using your server’s IP address and port 81. The default login credentials are:
- Email: admin@example.com
- Password: changeme
These temporary credentials provide initial access to the NPM dashboard. The interface loads with a clean, intuitive design showcasing main navigation options: Proxy Hosts, Redirection Hosts, Streams, 404 Hosts, Users, and Certificates.
Browser compatibility works best with modern browsers including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. Ensure JavaScript is enabled for full functionality of the administrative interface.
Administrative Setup
Immediately change the default administrator credentials for security. Navigate to Users section, click on the admin user, and update:
- Email address to your preferred administrative email
- Password to a strong, unique password
- Full name and other profile information
Configure two-factor authentication if your NPM version supports it. This additional security layer protects against unauthorized access even if credentials are compromised.
Set system preferences including timezone, which affects log timestamps and certificate renewal schedules. Navigate to Settings and configure:
- Timezone matching your server location
- Default language preferences
- Interface themes if available
Enable automatic backups to protect your NPM configuration. Schedule regular backups of the /data directory to ensure you can recover quickly from system failures.
Advanced Configuration and SSL Setup
Domain Configuration
Proper DNS configuration is essential before adding domains to NPM. Ensure your domain’s A records point to your server’s public IP address. Use tools like dig or nslookup to verify DNS propagation:
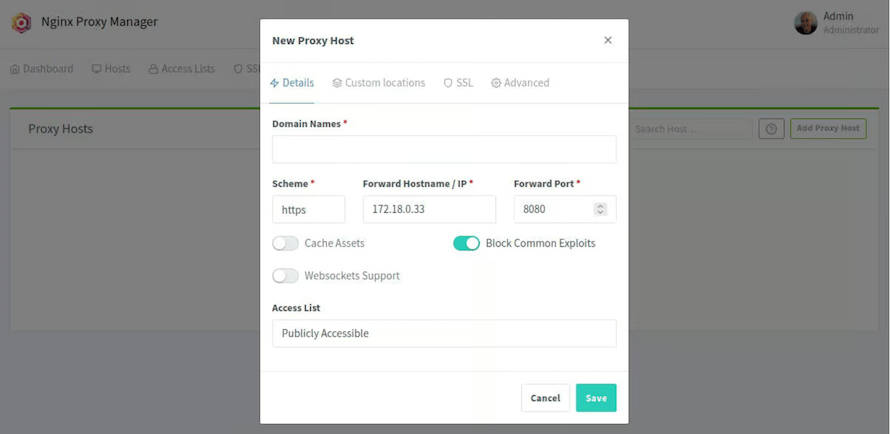
dig yourdomain.com AAdd your first proxy host through the NPM web interface. Click “Proxy Hosts” then “Add Proxy Host”. Configure:
- Domain Name: your-domain.com
- Scheme: http or https depending on your backend service
- Forward Hostname/IP: IP address of your internal service
- Forward Port: port number of your internal service
Enable websocket support if your application requires real-time communication. Many modern web applications including chat systems, live dashboards, and collaborative tools depend on websocket connectivity.
Configure access lists for enhanced security. Create IP-based restrictions to limit access to sensitive services, particularly administrative interfaces and development environments.
SSL Certificate Management
NPM’s Let’s Encrypt integration provides automatic SSL certificate generation and renewal. When adding a proxy host, navigate to the SSL tab and:
- Select “Request a new SSL Certificate”
- Choose “Use a DNS Challenge” for wildcard certificates or “Use a HTTP Challenge” for single domains
- Enable “Force SSL” to automatically redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS
- Enable “HTTP/2 Support” for improved performance
Let’s Encrypt certificates automatically renew 30 days before expiration. Monitor renewal status in the Certificates section of the NPM interface.
For wildcard certificates covering multiple subdomains, configure DNS challenge authentication. This method proves domain ownership by creating TXT records in your DNS provider, enabling certificates for unlimited subdomains.
Upload custom certificates if you prefer using existing SSL certificates from other providers. Navigate to Certificates, click “Add Certificate”, and upload your certificate files including private key, certificate, and intermediate certificates.
Configure HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) for enhanced security. HSTS prevents protocol downgrade attacks and cookie hijacking by forcing browsers to use HTTPS connections exclusively.
Security Best Practices and Optimization
Security Hardening
Implement access control lists to restrict administrative interface access. Create an access list limiting port 81 access to specific IP addresses or network ranges. Navigate to Access Lists, create a new list, and add authorized IP addresses.
Configure basic authentication for additional security layers on sensitive services. This creates username/password prompts before users reach your actual applications, providing defense in depth.
Regular security updates maintain protection against vulnerabilities. Update NPM containers monthly or when security patches are released:
cd ~/nginx-proxy-manager
docker compose pull
docker compose up -dMonitor system logs for suspicious activity. NPM logs access attempts, certificate requests, and configuration changes. Review logs regularly for signs of unauthorized access or attack attempts.
Implement fail2ban to automatically block IP addresses showing malicious behavior. Configure fail2ban to monitor NPM logs and temporarily ban IPs attempting brute force attacks or exploiting vulnerabilities.
Performance Optimization
Configure caching headers to improve website loading speeds. Navigate to Advanced settings for each proxy host and add custom nginx configuration:
proxy_cache_valid 200 302 10m;
proxy_cache_valid 404 1m;
proxy_cache_use_stale error timeout updating http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504;Set up load balancing for high-availability applications. Create multiple proxy hosts pointing to different backend servers, distributing traffic across multiple instances of your application.
Monitor system resources regularly using tools like htop, iotop, and docker stats. Ensure adequate CPU, memory, and disk space for optimal NPM performance.
Optimize MariaDB performance by adjusting configuration parameters. Create a custom MariaDB configuration file mounted into the database container:
mkdir -p ~/nginx-proxy-manager/mysql-config
nano ~/nginx-proxy-manager/mysql-config/my.cnfAdd performance optimizations:
[mysqld]
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 256M
innodb_log_file_size = 64M
max_connections = 100
query_cache_size = 32MTroubleshooting Common Issues
Container startup failures often result from port conflicts or permission issues. Check if ports 80, 443, or 81 are already in use:
sudo netstat -tlnp | grep :80
sudo netstat -tlnp | grep :443
sudo netstat -tlnp | grep :81Stop conflicting services or modify NPM port mappings in the Docker Compose file if necessary.
Database connectivity problems typically stem from incorrect environment variables or networking issues. Verify database container logs:
docker compose logs npm-databaseCheck for database initialization errors, connection refused messages, or authentication failures.
SSL certificate generation failures often occur due to DNS propagation delays or firewall restrictions. Ensure:
- DNS records point to your server IP
- Ports 80 and 443 are accessible from the internet
- No other services are blocking Let’s Encrypt validation
Performance issues may indicate resource constraints or configuration problems. Monitor container resources:
docker stats --no-streamIncrease server resources or optimize container configurations if CPU or memory usage consistently exceeds 80%.
Log analysis provides insights into NPM behavior and problems. Access NPM logs:
docker compose logs nginx-proxy-manager | tail -100Look for error messages, timeout warnings, or unusual access patterns that might indicate configuration issues or security concerns.
Maintenance and Updates
Regular maintenance ensures NPM continues operating efficiently and securely. Schedule monthly update procedures to apply security patches and feature updates:
cd ~/nginx-proxy-manager
docker compose pull
docker compose down
docker compose up -dThis process downloads updated container images, stops existing containers, and starts new ones with latest updates.
Database maintenance includes periodic optimization and cleanup. Connect to the MariaDB container and run optimization commands:
docker exec -it npm-database mysql -u npm_user -p npmExecute database optimization:
OPTIMIZE TABLE proxy_host;
OPTIMIZE TABLE certificate;
OPTIMIZE TABLE user;Certificate renewal monitoring prevents expired SSL certificates from causing service interruptions. NPM automatically renews Let’s Encrypt certificates, but monitor the process in the Certificates section of the web interface.
Backup strategies protect against data loss and enable quick recovery from failures. Create automated backup scripts:
#!/bin/bash
BACKUP_DIR="/backup/npm-$(date +%Y%m%d)"
mkdir -p $BACKUP_DIR
cp -r ~/nginx-proxy-manager/data $BACKUP_DIR/
cp -r ~/nginx-proxy-manager/letsencrypt $BACKUP_DIR/
docker exec npm-database mysqldump -u npm_user -p npm > $BACKUP_DIR/database.sqlSchedule this script to run daily using cron, ensuring you maintain recent backups of all NPM components.
Security audits identify potential vulnerabilities and configuration weaknesses. Review user accounts, access lists, and proxy configurations quarterly. Remove unused accounts, update passwords, and verify access restrictions remain appropriate.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Nginx Proxy Manager. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Nginx Proxy Manager on AlmaLinux OS 10 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Nginx website.