How To Install Nginx Proxy Manager on Debian 12

In the realm of web traffic management, Nginx Proxy Manager stands out as a powerful tool, offering a user-friendly graphical user interface (GUI) for managing proxy hosts, SSL certificates, and web traffic. This makes it an indispensable asset for server administrators and website owners seeking to streamline their server management tasks. By leveraging Nginx Proxy Manager, users can efficiently manage multiple domains, automate SSL certificate issuance, and enhance overall server security. This article will guide you through the process of installing Nginx Proxy Manager on Debian 12, providing detailed step-by-step instructions for both Docker and manual installation methods.
Understanding Nginx Proxy Manager
Nginx Proxy Manager is built on top of Nginx, a popular web server known for its high performance and reliability. It simplifies the process of configuring Nginx by providing a web-based interface, making it easier for users to manage proxy hosts, configure SSL certificates, and set up access lists without needing extensive knowledge of Nginx configuration files. The architecture of Nginx Proxy Manager includes a Node.js backend for the admin interface, which communicates with the Nginx server to apply configurations.
Key Features of Nginx Proxy Manager
- Proxy Host Management: Easily add, edit, or remove proxy hosts for different domains.
- SSL Certificate Automation: Supports automatic issuance and renewal of SSL certificates using Let’s Encrypt.
- Access Lists: Restrict access to certain proxy hosts based on IP addresses or authentication.
- User-Friendly Interface: Simplifies complex Nginx configurations through an intuitive web interface.
Prerequisites
Before installing Nginx Proxy Manager, ensure you have the following prerequisites in place:
System Requirements
- Debian 12: Ensure your system is running the latest version of Debian.
- VPS or Dedicated Server: A virtual private server (VPS) or dedicated server is recommended for better performance and security.
- Disk Space and RAM: Allocate sufficient disk space and RAM based on your expected workload. A minimum of 2 GB RAM and 10 GB disk space is recommended.
Software Requirements
- User with Sudo Privileges: You need a user account with sudo privileges to install and configure software.
- Valid Domain Name: Ensure you have a valid domain name with DNS records pointing to your server’s IP address.
- Basic Networking Concepts: Familiarity with basic networking concepts such as ports and IP addresses is helpful.
Networking Requirements
- DNS Configuration: Ensure your domain’s DNS records are correctly configured to point to your server’s IP address.
- Required Open Ports: Open ports 80, 81, and 443 in your firewall to allow HTTP, HTTP admin interface, and HTTPS traffic.
- IP Address Considerations: Use a static IP address for your server to avoid configuration issues due to IP changes.
Method 1: Docker Installation
Docker provides a convenient way to deploy Nginx Proxy Manager by encapsulating all dependencies into containers. Here’s how to install using Docker:
Docker Environment Setup
- Install Docker Engine:
First, update your package index and install Docker Engine on Debian 12:sudo apt update sudo apt install -y ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/debian $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null sudo apt update sudo apt install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io - Install Docker Compose:
Install Docker Compose to manage multiple containers:sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.29.2/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose sudo ln -s /usr/local/bin/docker-compose /usr/bin/docker-compose - Verify Docker Installation:
Run a test container to verify Docker is working correctly:sudo docker run hello-world
Firewall Configuration
To ensure Nginx Proxy Manager works correctly, configure your firewall to allow necessary traffic:
- Install UFW:
If not already installed, set up UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) on your system:sudo apt install ufw - Open Required Ports:
Allow HTTP, HTTPS, and the admin interface port (81) through UFW:sudo ufw allow http sudo ufw allow https sudo ufw allow 81/tcp - Enable UFW:
Enable the firewall and reload the rules:sudo ufw enable sudo ufw reload
Docker Compose Configuration
1. Create Project Directory:
Create a directory for your Nginx Proxy Manager project:
mkdir nginx-proxy-manager
cd nginx-proxy-manager
2. Create docker-compose.yml File:
Create a `docker-compose.yml` file with the following content:
version: '3'
services:
app:
image: 'jc21/nginx-proxy-manager:latest'
restart: unless-stopped
ports:
- "81:81"
- "80:80"
- "443:443"
environment:
DB_MYSQL_HOST: db
DB_MYSQL_PORT: 3306
DB_MYSQL_USER: npm
DB_MYSQL_PASSWORD: npm
DB_MYSQL_NAME: npm
volumes:
- ./data:/data
- ./letsencrypt:/etc/letsencrypt
depends_on:
- db
db:
image: 'mariadb:latest'
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: npm
MYSQL_DATABASE: npm
MYSQL_USER: npm
MYSQL_PASSWORD: npm
volumes:
- ./db:/var/lib/mysql
3. Launch Containers:
Start the containers using Docker Compose:
sudo docker-compose up -d
4. Verify Container Status:
Check that both containers are running:
sudo docker-compose ps
Method 2: Manual Installation
For those who prefer not to use Docker, Nginx Proxy Manager can be installed manually:
Dependencies Installation
- Install Node.js:
Install Node.js and npm (Node Package Manager) on your system:curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_lts.x | sudo -E bash - sudo apt-get install -y nodejs - Install Database Server:
Install MariaDB as the database server:sudo apt install mariadb-server - Secure MariaDB:
Run the following command to secure your MariaDB installation:sudo mysql_secure_installation - Create Database and User:
Create a database and user for Nginx Proxy Manager:sudo mysql -uroot -p CREATE DATABASE npm; CREATE USER 'npm'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'npm'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON npm.* TO 'npm'@'%'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; EXIT;
Application Setup
- Download Nginx Proxy Manager:
Clone the Nginx Proxy Manager repository:git clone https://github.com/NginxProxyManager/nginx-proxy-manager.git cd nginx-proxy-manager - Install Dependencies:
Install required Node.js packages:npm install - Configure Environment Variables:
Create a `.env` file with your database credentials:echo "DB_MYSQL_HOST=localhost DB_MYSQL_PORT=3306 DB_MYSQL_USER=npm DB_MYSQL_PASSWORD=npm DB_MYSQL_NAME=npm" > .env - Start Nginx Proxy Manager:
Start the application:npm start - Create System Service:
To ensure Nginx Proxy Manager starts automatically on boot, create asystemdservice file:sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/nginx-proxy-manager.serviceAdd the following content:
[Unit] Description=Nginx Proxy Manager After=network.target [Service] User= ExecStart=/usr/bin/npm start Restart=always [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.targetReplace `
<your_username>` with your actual username. - Enable and Start Service:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable nginx-proxy-manager sudo systemctl start nginx-proxy-manager
Initial Access and Configuration
Accessing the Web Interface
- 1Default Access URL:
Open a web browser and navigate to `http://your-server-ip:81` to access the Nginx Proxy Manager interface. - First-time Login:
Use the default credentials: `admin@example.com` with the password `changeme`. You will be prompted to change the password and set up your admin account. - Admin Account Setup:
- Change Default Password: Update your admin password for security.
- Set Up Admin Email: Configure an email address for notifications.
- Security Prompt Explanations: Understand and address any security prompts.
Creating Your First Proxy Host
Basic Proxy Host Setup
- Navigate to Proxy Hosts Section:
In the Nginx Proxy Manager interface, go to the “Proxy Hosts” section. - Add New Proxy Host:
Click on “Add Proxy Host” and fill in the required details:
– Domain Names: Enter your domain name(s).
– Scheme and Port: Choose HTTP or HTTPS and set the port accordingly.
– Forward Hostname/IP: Enter the target server’s IP address or hostname.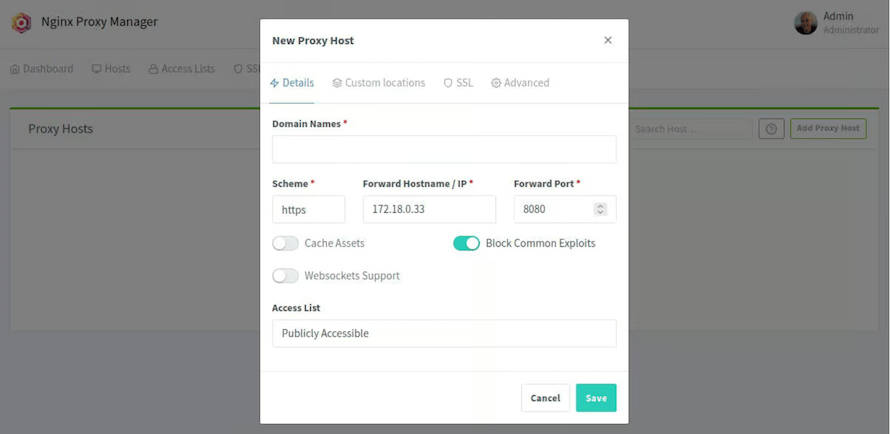
- SSL Certificate Management:
– Let’s Encrypt Integration: Enable automatic SSL certificate issuance using Let’s Encrypt.
– Certificate Issuance Process: Nginx Proxy Manager will handle certificate issuance and renewal.
– Manual Certificate Upload: Optionally, you can upload a custom SSL certificate.
Advanced Proxy Settings
- Custom Locations: Configure custom locations for specific paths.
- WebSocket Support: Enable WebSocket support if needed.
- Cache Control Options: Configure caching settings for better performance.
- Header Modifications: Add or modify HTTP headers as required.
Security Best Practices
Access Control Lists
- Creating Access Lists:
Set up access lists to restrict access to certain proxy hosts based on IP addresses. - IP Restriction Implementation:
Configure IP restrictions to limit access to authorized users. - Authentication Requirements:
Implement authentication for sensitive proxy hosts.
Admin Interface Security
- Restrict Admin Interface Access:
Limit access to the admin interface by IP address or VPN. - Two-Factor Authentication:
Enable two-factor authentication for enhanced security. - Session Management:
Configure session timeouts and secure cookie settings. - Secure Connection Requirements:
Ensure all connections to the admin interface are encrypted.
System-level Security
- Regular Updates:
Keep your system and software up-to-date with the latest security patches. - Backup Strategies:
Implement regular backups of your configuration and database. - Monitoring and Logging:
Set up monitoring tools to track system activity and logs. - Intrusion Detection:
Use intrusion detection systems to identify potential security threats.
Performance Optimization
Caching Strategies
- Browser Caching:
Configure browser caching to reduce the load on your server. - Proxy Caching:
Enable caching at the proxy level to improve response times. - Cache Invalidation Methods:
Set up cache invalidation to ensure freshness of content.
Resource Management
- Docker Resource Allocation:
Adjust resource limits for Docker containers to optimize performance. - Connection Limits:
Configure connection limits to prevent overload. - Worker Processes Optimization:
Optimize the number of worker processes for better performance. - Memory Management:
Monitor and manage memory usage to prevent bottlenecks.
Advanced Configuration
Custom Nginx Configurations
- Adding Custom Nginx Snippets:
Insert custom Nginx configuration snippets for advanced settings. - Advanced Location Blocks:
Configure complex location blocks for specific URL paths. - Redirect Rules:
Set up redirect rules for URL rewriting or forwarding. - Error Page Customization:
Customize error pages for better user experience.
Stream Proxying
- TCP/UDP Proxy Setup:
Configure Nginx Proxy Manager to proxy non-HTTP services like TCP or UDP. - Non-HTTP Service Proxying:
Use stream proxying for services that don’t use HTTP. - Stream Configuration Options:
Explore advanced stream configuration options for custom scenarios.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Nginx Proxy Manager. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Nginx Proxy Manager on Debian 12 “Bookworm” system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Nginx website.