How To Install Odoo on Fedora 42

Odoo stands as one of the most versatile business management software solutions available today, offering a comprehensive suite of applications for everything from CRM to accounting, inventory management, and beyond. For businesses seeking a robust platform on which to deploy Odoo, Fedora 42 provides an excellent foundation with its cutting-edge features, security enhancements, and stability. This guide will walk you through the complete process of installing Odoo on Fedora 42, ensuring you have a fully functional system ready to transform your business operations.
Understanding Odoo and Fedora 42
What is Odoo?
Odoo represents a complete suite of business applications that seamlessly integrate to handle virtually all aspects of enterprise management. Originally known as OpenERP, this open-source platform has evolved into a comprehensive ecosystem of both free community and premium enterprise modules. The platform excels in providing solutions for customer relationship management, e-commerce, inventory control, manufacturing, accounting, project management, and much more.
What makes Odoo particularly appealing is its modular architecture, allowing businesses to implement only the components they need and expand functionality as requirements grow. The community edition offers robust capabilities for small to medium businesses, while the Enterprise version provides additional features and support for larger organizations.
Fedora 42 Specifics
Fedora 42 represents the latest iteration in Red Hat’s community-driven Linux distribution, known for implementing cutting-edge technologies while maintaining system stability. As a leading-edge distribution, Fedora 42 incorporates the latest kernel improvements, security features, and software updates, making it an excellent platform for business applications like Odoo.
The distribution’s focus on security, with features like enhanced SELinux policies and improved firewall management, provides a solid foundation for business-critical applications. Additionally, Fedora’s package management system (DNF) simplifies software installation and updates, streamlining the maintenance process for system administrators.
Prerequisites
System Requirements
Before beginning the installation process, ensure your system meets these minimum requirements for optimal Odoo performance on Fedora 42:
- CPU: Multi-core processor (minimum 2 cores, recommended 4+ cores)
- RAM: At least 4GB (8GB or more recommended for production environments)
- Storage: 20GB minimum free disk space (SSD storage strongly recommended for performance)
- Network: Stable internet connection for package downloads and updates
For production environments supporting multiple users, consider scaling these requirements upward, particularly RAM allocation which directly impacts Odoo’s performance under load.
Required Knowledge
This guide assumes basic familiarity with:
- Linux command line operations
- Basic understanding of database concepts
- System administration fundamentals
- Text editor usage (nano, vim, etc.)
While not mandatory, prior experience with ERP systems will help you better understand the configuration options available.
Backup Preparations
If you’re installing on an existing system with important data, create a full system backup before proceeding. For fresh installations, this step can be skipped, but establishing a backup routine should be a priority once your Odoo system becomes operational.
Software Dependencies
Odoo relies on numerous software packages and libraries to function properly, including:
- Python 3 and related development packages
- PostgreSQL database server
- Node.js for certain web features
- Various system libraries for XML processing, image manipulation, and more
We’ll install these dependencies as part of the installation process.
Step-by-Step Installation Process
Updating System Packages
Begin by ensuring your Fedora 42 system has the latest updates. This step is crucial for security and compatibility:
sudo dnf update -yThis command refreshes your system’s package lists and upgrades all installed packages to their latest versions. The `-y` flag automatically confirms any prompts, streamlining the update process.
Installing PostgreSQL
Odoo relies on PostgreSQL as its database backend. Install PostgreSQL using the following commands:
sudo dnf install postgresql-server -y
sudo postgresql-setup --initdb
sudo systemctl start postgresql.service
sudo systemctl enable postgresql.serviceThese commands install PostgreSQL, initialize the database cluster, start the PostgreSQL service, and enable it to launch automatically on system boot.
Next, create a dedicated database user for Odoo:
sudo su - postgres
createuser --createdb --username postgres --no-createrole --no-superuser --pwprompt odoo
exitWhen prompted, set a strong password for the Odoo database user and make note of it for later configuration steps.
Installing Dependencies
Odoo requires numerous dependencies to function properly. Install them with this comprehensive command:
sudo dnf install git python3-pip python3-devel python3-setuptools python3-wheel \
libxml2-devel libxslt-devel openssl-devel libpq-devel libjpeg-devel \
zlib-devel gcc redhat-rpm-config wget nodejs npm \
libwebp-devel libtiff-devel libwmf-devel libyaml-devel python3-lxml -yThis command installs development tools, libraries for XML processing, image handling capabilities, PostgreSQL connectors, and other essential components.
Installing Wkhtmltopdf
Wkhtmltopdf is required for Odoo’s PDF report generation. Install a compatible version:
sudo dnf install https://github.com/wkhtmltopdf/packaging/releases/download/0.12.6.1-3/wkhtmltox-0.12.6.1-3.fedora37.x86_64.rpm -yWhile this package is specifically for Fedora 36, it remains compatible with Fedora 42 and provides the functionality Odoo needs for PDF generation.
Downloading and Installing Odoo
There are multiple approaches to installing Odoo. We’ll cover the most straightforward method-using a dedicated directory structure with the official GitHub repository:
sudo mkdir /opt/odoo
sudo git clone https://www.github.com/odoo/odoo --depth 1 --branch 16.0 /opt/odoo/odooThis creates a directory for Odoo and clones the latest stable version (16.0) into it. The `–depth 1` parameter ensures only the most recent commit is downloaded, saving time and disk space.
Now, install the Python dependencies required by Odoo:
sudo pip3 install -r /opt/odoo/odoo/requirements.txtCreate a dedicated system user to run Odoo for enhanced security:
sudo useradd -m -d /opt/odoo -U -r -s /bin/bash odoo
sudo chown -R odoo:odoo /opt/odooThese commands create a system user named “odoo” with a home directory at `/opt/odoo` and set the appropriate ownership permissions.
Setting Up Configuration Files
Create a directory for Odoo’s configuration and set up the configuration file:
sudo mkdir /etc/odoo
sudo nano /etc/odoo/odoo.confAdd the following content to the configuration file:
[options]
; This is the password that allows database operations:
admin_passwd = my_secure_admin_password
db_host = False
db_port = False
db_user = odoo
db_password = your_postgresql_password
addons_path = /opt/odoo/odoo/addons
logfile = /var/log/odoo/odoo-server.logReplace `my_secure_admin_password` with a strong password for database administration and `your_postgresql_password` with the password you set for the PostgreSQL odoo user.
Create a directory for logs and set appropriate permissions:
sudo mkdir /var/log/odoo
sudo chown odoo:odoo /var/log/odooCreating Systemd Service
To ensure Odoo starts automatically with your system, create a systemd service file:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/odoo.serviceAdd the following content:
[Unit]
Description=Odoo
Requires=postgresql.service
After=network.target postgresql.service
[Service]
Type=simple
SyslogIdentifier=odoo
PermissionsStartOnly=true
User=odoo
Group=odoo
ExecStart=/opt/odoo/odoo/odoo-bin -c /etc/odoo/odoo.conf
StandardOutput=journal+console
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetThis configuration ensures Odoo starts after the network and PostgreSQL services are available.
Enable and start the Odoo service:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable odoo
sudo systemctl start odooCheck the status to ensure it’s running correctly:
sudo systemctl status odooIf you encounter the error “No module named ‘odoo'” on Fedora, you might need to create symbolic links to correct Python module paths as described in search result :
cd /usr/lib/python3.11/site-packages
sudo ln -s ../../python3.10/site-packages/odoo
sudo ln -s ../../python3.10/site-packages/odoo-*.egg-infoThen modify your `/etc/odoo/odoo.conf` to point to the correct addons path:
addons_path = /usr/lib/python3.11/site-packages/odoo/addonsConfiguring Firewall
Allow access to Odoo’s default port through the firewall:
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8069/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadThis configuration permits external access to Odoo’s web interface.
Post-Installation Configuration
Accessing the Web Interface
Open a web browser and navigate to:
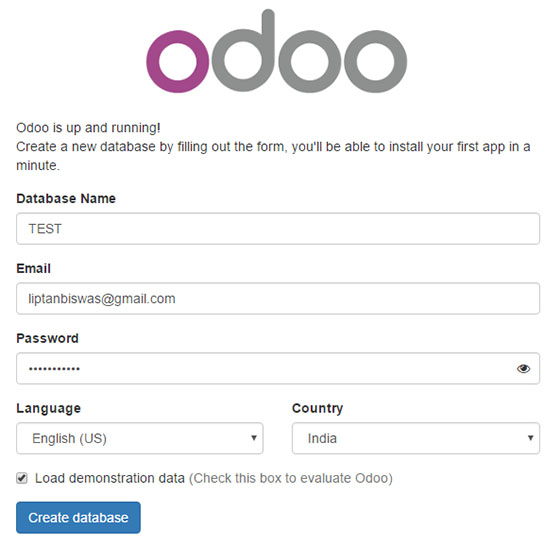
http://your_server_ip:8069Replace `your_server_ip` with your server’s actual IP address or hostname. You should see the Odoo database creation screen.
Create your first database by providing:
- A database name (e.g., “company_database”)
- An email address for the administrator account
- A password for the administrator account
- Language preference
Click “Create database” and wait for the process to complete. Once finished, you’ll be redirected to the Odoo dashboard.
Security Setup
Implement these security best practices for your Odoo installation:
- Change the default master password in `
/etc/odoo/odoo.conf` - Configure your firewall to restrict access to the PostgreSQL port (5432)
- Consider setting up HTTPS with a reverse proxy for encrypted connections
- Implement regular database backups
Basic Odoo Configuration
After accessing Odoo for the first time, complete these initial configuration steps:
- Set up company information (Settings → Users & Companies → Companies)
- Configure user accounts and access rights (Settings → Users & Companies → Users)
- Install required modules (Apps menu)
- Set up localization for your region (Settings → General Settings)
- Configure accounting parameters if using that module
Performance Optimization
PostgreSQL Tuning
Optimize PostgreSQL performance by editing `/var/lib/pgsql/data/postgresql.conf`:
# Memory configuration
shared_buffers = 1GB # 25% of available RAM, up to 8GB
work_mem = 128MB # Adjust based on complex query needs
maintenance_work_mem = 256MB # For maintenance operations
# Checkpoint configuration
checkpoint_timeout = 1h
checkpoint_completion_target = 0.9
# Planner configuration
effective_cache_size = 3GB # 75% of available RAMRestart PostgreSQL after making changes:
sudo systemctl restart postgresqlOdoo Performance Parameters
Enhance Odoo’s performance by adding these parameters to `/etc/odoo/odoo.conf`:
workers = 4 # Set to (2 x number_of_cpu_cores) + 1
max_cron_threads = 2 # Number of workers dedicated to cron jobs
limit_memory_hard = 2684354560 # 2.5GB in bytes
limit_memory_soft = 2147483648 # 2GB in bytes
limit_time_cpu = 600 # Maximum allowed CPU time per request (seconds)
limit_time_real = 1200 # Maximum real time per request (seconds)Restart Odoo to apply these changes:
sudo systemctl restart odooTroubleshooting Common Issues
Installation Problems
- Dependency Issues:
If you encounter missing dependencies, try installing them individually:sudo dnf install package-name -y - Permission Errors:
Check file and directory ownership:sudo chown -R odoo:odoo /opt/odoo /var/log/odoo - Python Module Path Issues:
If Fedora 42 can’t find Odoo modules, create symbolic links between Python versions as described in the installation section.
Runtime Errors
- Log Analysis:
Check Odoo logs for detailed error messages:sudo tail -f /var/log/odoo/odoo-server.log - Service Fails to Start:
Verify configuration file syntax:sudo -u odoo /opt/odoo/odoo/odoo-bin -c /etc/odoo/odoo.conf - Database Connection Issues:
Confirm PostgreSQL service is running:sudo systemctl status postgresqlVerify database user credentials in
odoo.conf
Performance Issues
- Identify Bottlenecks:
Monitor system resource usage:topCheck for slow database queries in PostgreSQL logs
- Memory Optimization:
If Odoo consumes excessive memory, adjustlimit_memory_hardandlimit_memory_softvalues in the configuration file
Advanced Configuration
Reverse Proxy Setup
Configure Nginx as a reverse proxy for Odoo:
sudo dnf install nginx -y
sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/odoo.confAdd this configuration:
upstream odoo {
server 127.0.0.1:8069;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name odoo.yourdomain.com;
access_log /var/log/nginx/odoo.access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/odoo.error.log;
location / {
proxy_pass http://odoo;
proxy_next_upstream error timeout invalid_header http_500 http_502 http_503;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
}Enable and start Nginx:
sudo systemctl enable nginx
sudo systemctl start nginxDatabase Backup and Restore
Create a backup script `/opt/odoo/backup.sh`:
#!/bin/bash
BACKUP_DIR="/opt/odoo/backups"
ODOO_DATABASE="your_database_name"
DATE=$(date +%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S)
mkdir -p $BACKUP_DIR
cd /opt/odoo/odoo
# Stop Odoo service
sudo systemctl stop odoo
# Backup the database
sudo -u odoo python3 /opt/odoo/odoo/odoo-bin -c /etc/odoo/odoo.conf -d $ODOO_DATABASE --backup --backup-format=zip --backup-file="$BACKUP_DIR/$ODOO_DATABASE-$DATE"
# Start Odoo service
sudo systemctl start odoo
# Keep only the last 7 days of backups
find $BACKUP_DIR -type f -name "*.zip" -mtime +7 -deleteMake it executable:
sudo chmod +x /opt/odoo/backup.shSet up a cron job to run nightly backups:
sudo crontab -eAdd this line:
0 2 * * * /opt/odoo/backup.sh >/dev/null 2>&1Multi-database Setup
To manage multiple databases, add these settings to `/etc/odoo/odoo.conf`:
dbfilter = ^%d$
list_db = FalseThis configuration improves security by hiding the database selector and using subdomain-based filtering.
Upgrading and Maintenance
Keeping Odoo Updated
To update Odoo to the latest version in its branch:
sudo systemctl stop odoo
cd /opt/odoo/odoo
sudo git pull
sudo pip3 install --upgrade -r requirements.txt
sudo systemctl start odooFor major version upgrades, follow Odoo’s official migration guides as database schema changes may be required.
System Maintenance
Implement these maintenance practices:
- Regular Updates:
sudo dnf update -y - Log Rotation:
Create `/etc/logrotate.d/odoo`:/var/log/odoo/*.log { weekly missingok rotate 10 compress delaycompress notifempty create 0640 odoo odoo } - Database Vacuum:
Schedule regular database maintenance:sudo -u postgres psql -c "VACUUM FULL ANALYZE;"
Alternative Installation Methods
Docker Installation
For a containerized approach, use Docker:
sudo dnf install docker docker-compose -y
sudo systemctl enable docker
sudo systemctl start docker
mkdir ~/odoo-docker && cd ~/odoo-dockerCreate `docker-compose.yml`:
version: '3'
services:
web:
image: odoo:16.0
depends_on:
- db
ports:
- "8069:8069"
volumes:
- odoo-web-data:/var/lib/odoo
- ./config:/etc/odoo
- ./addons:/mnt/extra-addons
environment:
- HOST=db
- USER=odoo
- PASSWORD=odoo
db:
image: postgres:15
environment:
- POSTGRES_DB=postgres
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=odoo
- POSTGRES_USER=odoo
volumes:
- odoo-db-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
volumes:
odoo-web-data:
odoo-db-data:Launch the containers:
sudo docker-compose up -dPython Virtual Environment
For a cleaner, isolated installation:
sudo dnf install python3-virtualenv -y
sudo mkdir -p /opt/odoo-venv
sudo chown $(whoami): /opt/odoo-venv
cd /opt/odoo-venv
virtualenv -p python3 venv
source venv/bin/activate
git clone https://www.github.com/odoo/odoo --depth 1 --branch 16.0 odoo
cd odoo
pip install -r requirements.txtCreate a custom service file for this installation method.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Odoo. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Odoo open-source ERP and CRM on Fedora 42 Linux system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Odoo website.